- Privacy Policy

Home » Review Article vs Research Article

Review Article vs Research Article
Table of Contents

Review articles and Research Articles are two different types of scholarly publications that serve distinct purposes in the academic literature.
Research Articles
A Research Article is a primary source that presents original research findings based on a specific research question or hypothesis. These articles typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. Research articles often include detailed descriptions of the research design, data collection and analysis procedures, and the results of statistical tests. These articles are typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet rigorous scientific standards before publication.
Review Articles
A Review Article is a secondary source that summarizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic or research question. These articles provide an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic, including a critical analysis of the strengths and limitations of previous research. Review articles often include a meta-analysis of the existing literature, which involves combining and analyzing data from multiple studies to draw more general conclusions about the research question or topic. Review articles are also typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they are comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date.
Difference Between Review Article and Research Article
Here are some key differences between review articles and research articles:
| Aspect | Research Article | Review Article |
|---|---|---|
| Present original research findings based on a research question or hypothesis | Summarize and analyze existing research on a particular topic or research question | |
| Standard sections including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion | Depends on the journal and topic, but typically includes an introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion | |
| Describe the research design, data collection and analysis procedures, and results of statistical tests | Describe the methodology used to identify and analyze the literature | |
| Statistical analysis of data | Meta-analysis or systematic review of existing literature | |
| Presents original data collected through research | Does not present original data, but rather synthesizes and analyzes existing data | |
| Based on the results of the research conducted | Based on the analysis of existing literature | |
| Peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet rigorous scientific standards before publication | Peer-reviewed to ensure that they are comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date |
In summary, research articles and review articles serve different purposes in the academic literature. Research articles present original research findings based on a specific research question or hypothesis, while review articles summarize and analyze existing research on a particular topic or research question. Both types of articles are typically peer-reviewed to ensure that they meet high standards of scientific rigor and accuracy.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Exploratory Vs Explanatory Research

Reliability Vs Validity

Inductive Vs Deductive Research

Correlational Research Vs Experimental Research

Primary Vs Secondary Research

Qualitative Vs Quantitative Research
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews
How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,120,351 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Study resources
- Calendar - Graduate
- Calendar - Undergraduate
- Class schedules
- Class cancellations
- Course registration
- Important academic dates
- More academic resources
- Campus services
- IT services
- Job opportunities
- Safety & prevention
- Mental health support
- Student Service Centre (Birks)
- All campus services
- Calendar of events
- Latest news
- Media Relations
- Faculties, Schools & Colleges
- Arts and Science
- Gina Cody School of Engineering and Computer Science
- John Molson School of Business
- School of Graduate Studies
- All Schools, Colleges & Departments.
- Directories
- My Library account Renew books and more
- Book a study room or scanner Reserve a space for your group online
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo) Request books from external libraries
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks) Manage your citations and create bibliographies
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver Request a PDF of an article/chapter we have in our physical collection
- Contactless Book Pickup Request books, DVDs and more from our physical collection while the Library is closed
- WebPrint Upload documents to print on campus
- Course reserves Online course readings
- Spectrum Deposit a thesis or article
- Sofia Discovery tool
- Databases by subject
- Course Reserves
- E-journals via Browzine
- E-journals via Sofia
- Article/chapter scan
- Intercampus delivery of bound periodicals/microforms
- Interlibrary loans
- Spectrum Research Repository
- Special Collections
- Additional resources & services
- Subject & course guides
- Borrowing & renewing
- Open Educational Resources Guide
- Instructional Services
- General guides for users
- Ask a librarian
- Research Skills Tutorial
- Quick Things for Digital Knowledge
- Critical Toolkit for Navigating Information
- Bibliometrics & research impact guide
- Concordia University Press
- Copyright guide
- Copyright guide for thesis preparation
- Digital scholarship
- Digital preservation
- Open Access
- ORCiD at Concordia
- Research data management guide
- Scholarship of Teaching & Learning
- Systematic Reviews
- Borrow (laptops, tablets, equipment)
- Connect (netname, Wi-Fi, guest accounts)
- Desktop computers, software & availability maps
- Group study, presentation practice & classrooms
- Printers, copiers & scanners
- Technology Sandbox
- Visualization Studio
- Webster Library
- Vanier Library
- Grey Nuns Reading Room
- Study spaces
- Floor plans
- Book a group study room/scanner
- Room booking for academic events
- Exhibitions
- Librarians & staff
- Work with us
- Memberships & collaborations
- Indigenous Student Librarian program
- Wikipedian in residence
- Researcher in residence
- Feedback & improvement
- Annual reports & fast facts
- Strategic Plan 2016/21
- Library Services Fund
- Giving to the Library
- Policies & Code of Conduct
- My Library account
- Book a study room or scanner
- Interlibrary loans (Colombo)
- Zotero (formerly RefWorks)
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver
- Contactless Book Pickup
- Course reserves
Review vs. Research Articles
How can you tell if you are looking at a research paper, review paper or a systematic review examples and article characteristics are provided below to help you figure it out., research papers.
A research article describes a study that was performed by the article’s author(s). It explains the methodology of the study, such as how data was collected and analyzed, and clarifies what the results mean. Each step of the study is reported in detail so that other researchers can repeat the experiment.
To determine if a paper is a research article, examine its wording. Research articles describe actions taken by the researcher(s) during the experimental process. Look for statements like “we tested,” “I measured,” or “we investigated.” Research articles also describe the outcomes of studies. Check for phrases like “the study found” or “the results indicate.” Next, look closely at the formatting of the article. Research papers are divided into sections that occur in a particular order: abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and references.
Let's take a closer look at this research paper by Bacon et al. published in the International Journal of Hypertension :

Review Papers
Review articles do not describe original research conducted by the author(s). Instead, they give an overview of a specific subject by examining previously published studies on the topic. The author searches for and selects studies on the subject and then tries to make sense of their findings. In particular, review articles look at whether the outcomes of the chosen studies are similar, and if they are not, attempt to explain the conflicting results. By interpreting the findings of previous studies, review articles are able to present the current knowledge and understanding of a specific topic.
Since review articles summarize the research on a particular topic, students should read them for background information before consulting detailed, technical research articles. Furthermore, review articles are a useful starting point for a research project because their reference lists can be used to find additional articles on the subject.
Let's take a closer look at this review paper by Bacon et al. published in Sports Medicine :

Systematic Review Papers
A systematic review is a type of review article that tries to limit the occurrence of bias. Traditional, non-systematic reviews can be biased because they do not include all of the available papers on the review’s topic; only certain studies are discussed by the author. No formal process is used to decide which articles to include in the review. Consequently, unpublished articles, older papers, works in foreign languages, manuscripts published in small journals, and studies that conflict with the author’s beliefs can be overlooked or excluded. Since traditional reviews do not have to explain the techniques used to select the studies, it can be difficult to determine if the author’s bias affected the review’s findings.
Systematic reviews were developed to address the problem of bias. Unlike traditional reviews, which cover a broad topic, systematic reviews focus on a single question, such as if a particular intervention successfully treats a medical condition. Systematic reviews then track down all of the available studies that address the question, choose some to include in the review, and critique them using predetermined criteria. The studies are found, selected, and evaluated using a formal, scientific methodology in order to minimize the effect of the author’s bias. The methodology is clearly explained in the systematic review so that readers can form opinions about the quality of the review.
Let's take a closer look this systematic review paper by Vigano et al. published in Lancet Oncology :
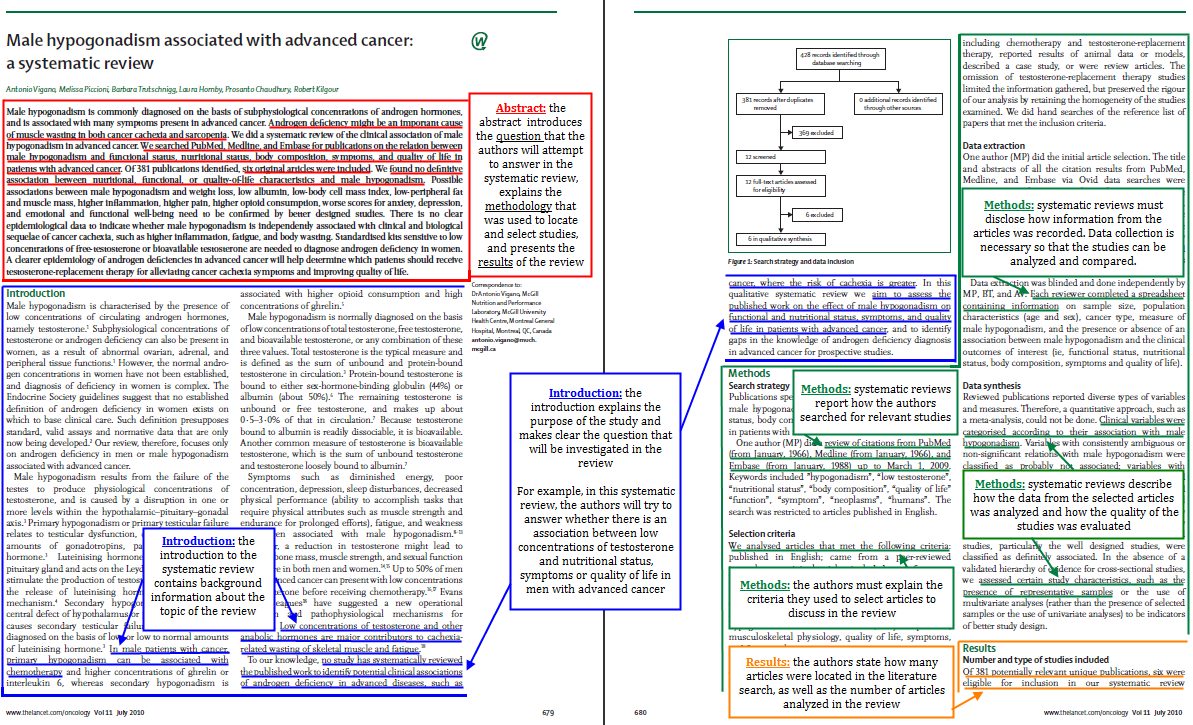
Finding Review and Research Papers in PubMed
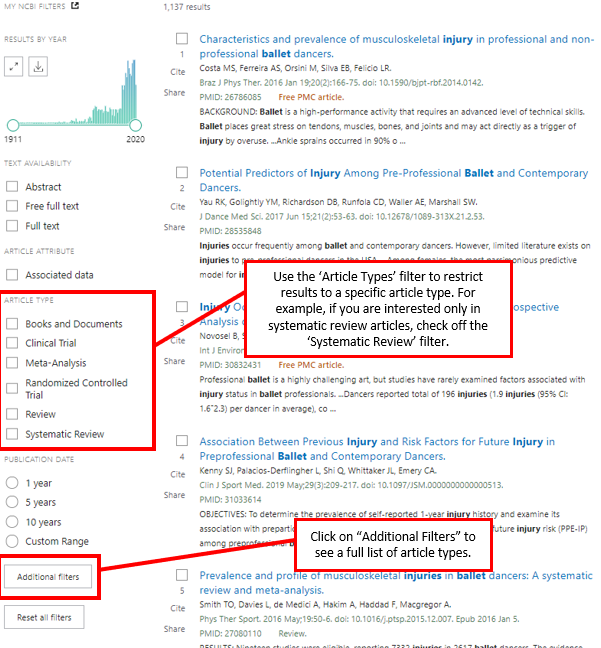
Many databases have special features that allow the searcher to restrict results to articles that match specific criteria. In other words, only articles of a certain type will be displayed in the search results. These “limiters” can be useful when searching for research or review articles. PubMed has a limiter for article type, which is located on the left sidebar of the search results page. This limiter can filter the search results to show only review articles.
© Concordia University
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Review articles: purpose, process, and structure
- Published: 02 October 2017
- Volume 46 , pages 1–5, ( 2018 )
Cite this article

- Robert W. Palmatier 1 ,
- Mark B. Houston 2 &
- John Hulland 3
236k Accesses
64 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Many research disciplines feature high-impact journals that are dedicated outlets for review papers (or review–conceptual combinations) (e.g., Academy of Management Review , Psychology Bulletin , Medicinal Research Reviews ). The rationale for such outlets is the premise that research integration and synthesis provides an important, and possibly even a required, step in the scientific process. Review papers tend to include both quantitative (i.e., meta-analytic, systematic reviews) and narrative or more qualitative components; together, they provide platforms for new conceptual frameworks, reveal inconsistencies in the extant body of research, synthesize diverse results, and generally give other scholars a “state-of-the-art” snapshot of a domain, often written by topic experts (Bem 1995 ). Many premier marketing journals publish meta-analytic review papers too, though authors often must overcome reviewers’ concerns that their contributions are limited due to the absence of “new data.” Furthermore, relatively few non-meta-analysis review papers appear in marketing journals, probably due to researchers’ perceptions that such papers have limited publication opportunities or their beliefs that the field lacks a research tradition or “respect” for such papers. In many cases, an editor must provide strong support to help such review papers navigate the review process. Yet, once published, such papers tend to be widely cited, suggesting that members of the field find them useful (see Bettencourt and Houston 2001 ).
In this editorial, we seek to address three topics relevant to review papers. First, we outline a case for their importance to the scientific process, by describing the purpose of review papers . Second, we detail the review paper editorial initiative conducted over the past two years by the Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science ( JAMS ), focused on increasing the prevalence of review papers. Third, we describe a process and structure for systematic ( i.e. , non-meta-analytic) review papers , referring to Grewal et al. ( 2018 ) insights into parallel meta-analytic (effects estimation) review papers. (For some strong recent examples of marketing-related meta-analyses, see Knoll and Matthes 2017 ; Verma et al. 2016 ).
Purpose of review papers
In their most general form, review papers “are critical evaluations of material that has already been published,” some that include quantitative effects estimation (i.e., meta-analyses) and some that do not (i.e., systematic reviews) (Bem 1995 , p. 172). They carefully identify and synthesize relevant literature to evaluate a specific research question, substantive domain, theoretical approach, or methodology and thereby provide readers with a state-of-the-art understanding of the research topic. Many of these benefits are highlighted in Hanssens’ ( 2018 ) paper titled “The Value of Empirical Generalizations in Marketing,” published in this same issue of JAMS.
The purpose of and contributions associated with review papers can vary depending on their specific type and research question, but in general, they aim to
Resolve definitional ambiguities and outline the scope of the topic.
Provide an integrated, synthesized overview of the current state of knowledge.
Identify inconsistencies in prior results and potential explanations (e.g., moderators, mediators, measures, approaches).
Evaluate existing methodological approaches and unique insights.
Develop conceptual frameworks to reconcile and extend past research.
Describe research insights, existing gaps, and future research directions.
Not every review paper can offer all of these benefits, but this list represents their key contributions. To provide a sufficient contribution, a review paper needs to achieve three key standards. First, the research domain needs to be well suited for a review paper, such that a sufficient body of past research exists to make the integration and synthesis valuable—especially if extant research reveals theoretical inconsistences or heterogeneity in its effects. Second, the review paper must be well executed, with an appropriate literature collection and analysis techniques, sufficient breadth and depth of literature coverage, and a compelling writing style. Third, the manuscript must offer significant new insights based on its systematic comparison of multiple studies, rather than simply a “book report” that describes past research. This third, most critical standard is often the most difficult, especially for authors who have not “lived” with the research domain for many years, because achieving it requires drawing some non-obvious connections and insights from multiple studies and their many different aspects (e.g., context, method, measures). Typically, after the “review” portion of the paper has been completed, the authors must spend many more months identifying the connections to uncover incremental insights, each of which takes time to detail and explicate.
The increasing methodological rigor and technical sophistication of many marketing studies also means that they often focus on smaller problems with fewer constructs. By synthesizing these piecemeal findings, reconciling conflicting evidence, and drawing a “big picture,” meta-analyses and systematic review papers become indispensable to our comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon, among both academic and practitioner communities. Thus, good review papers provide a solid platform for future research, in the reviewed domain but also in other areas, in that researchers can use a good review paper to learn about and extend key insights to new areas.
This domain extension, outside of the core area being reviewed, is one of the key benefits of review papers that often gets overlooked. Yet it also is becoming ever more important with the expanding breadth of marketing (e.g., econometric modeling, finance, strategic management, applied psychology, sociology) and the increasing velocity in the accumulation of marketing knowledge (e.g., digital marketing, social media, big data). Against this backdrop, systematic review papers and meta-analyses help academics and interested managers keep track of research findings that fall outside their main area of specialization.
JAMS’ review paper editorial initiative
With a strong belief in the importance of review papers, the editorial team of JAMS has purposely sought out leading scholars to provide substantive review papers, both meta-analysis and systematic, for publication in JAMS . Many of the scholars approached have voiced concerns about the risk of such endeavors, due to the lack of alternative outlets for these types of papers. Therefore, we have instituted a unique process, in which the authors develop a detailed outline of their paper, key tables and figures, and a description of their literature review process. On the basis of this outline, we grant assurances that the contribution hurdle will not be an issue for publication in JAMS , as long as the authors execute the proposed outline as written. Each paper still goes through the normal review process and must meet all publication quality standards, of course. In many cases, an Area Editor takes an active role to help ensure that each paper provides sufficient insights, as required for a high-quality review paper. This process gives the author team confidence to invest effort in the process. An analysis of the marketing journals in the Financial Times (FT 50) journal list for the past five years (2012–2016) shows that JAMS has become the most common outlet for these papers, publishing 31% of all review papers that appeared in the top six marketing journals.
As a next step in positioning JAMS as a receptive marketing outlet for review papers, we are conducting a Thought Leaders Conference on Generalizations in Marketing: Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses , with a corresponding special issue (see www.springer.com/jams ). We will continue our process of seeking out review papers as an editorial strategy in areas that could be advanced by the integration and synthesis of extant research. We expect that, ultimately, such efforts will become unnecessary, as authors initiate review papers on topics of their own choosing to submit them to JAMS . In the past two years, JAMS already has increased the number of papers it publishes annually, from just over 40 to around 60 papers per year; this growth has provided “space” for 8–10 review papers per year, reflecting our editorial target.
Consistent with JAMS ’ overall focus on managerially relevant and strategy-focused topics, all review papers should reflect this emphasis. For example, the domains, theories, and methods reviewed need to have some application to past or emerging managerial research. A good rule of thumb is that the substantive domain, theory, or method should attract the attention of readers of JAMS .
The efforts of multiple editors and Area Editors in turn have generated a body of review papers that can serve as useful examples of the different types and approaches that JAMS has published.
Domain-based review papers
Domain-based review papers review, synthetize, and extend a body of literature in the same substantive domain. For example, in “The Role of Privacy in Marketing” (Martin and Murphy 2017 ), the authors identify and define various privacy-related constructs that have appeared in recent literature. Then they examine the different theoretical perspectives brought to bear on privacy topics related to consumers and organizations, including ethical and legal perspectives. These foundations lead in to their systematic review of privacy-related articles over a clearly defined date range, from which they extract key insights from each study. This exercise of synthesizing diverse perspectives allows these authors to describe state-of-the-art knowledge regarding privacy in marketing and identify useful paths for research. Similarly, a new paper by Cleeren et al. ( 2017 ), “Marketing Research on Product-Harm Crises: A Review, Managerial Implications, and an Agenda for Future Research,” provides a rich systematic review, synthesizes extant research, and points the way forward for scholars who are interested in issues related to defective or dangerous market offerings.
Theory-based review papers
Theory-based review papers review, synthetize, and extend a body of literature that uses the same underlying theory. For example, Rindfleisch and Heide’s ( 1997 ) classic review of research in marketing using transaction cost economics has been cited more than 2200 times, with a significant impact on applications of the theory to the discipline in the past 20 years. A recent paper in JAMS with similar intent, which could serve as a helpful model, focuses on “Resource-Based Theory in Marketing” (Kozlenkova et al. 2014 ). The article dives deeply into a description of the theory and its underlying assumptions, then organizes a systematic review of relevant literature according to various perspectives through which the theory has been applied in marketing. The authors conclude by identifying topical domains in marketing that might benefit from additional applications of the theory (e.g., marketing exchange), as well as related theories that could be integrated meaningfully with insights from the resource-based theory.
Method-based review papers
Method-based review papers review, synthetize, and extend a body of literature that uses the same underlying method. For example, in “Event Study Methodology in the Marketing Literature: An Overview” (Sorescu et al. 2017 ), the authors identify published studies in marketing that use an event study methodology. After a brief review of the theoretical foundations of event studies, they describe in detail the key design considerations associated with this method. The article then provides a roadmap for conducting event studies and compares this approach with a stock market returns analysis. The authors finish with a summary of the strengths and weaknesses of the event study method, which in turn suggests three main areas for further research. Similarly, “Discriminant Validity Testing in Marketing: An Analysis, Causes for Concern, and Proposed Remedies” (Voorhies et al. 2016 ) systematically reviews existing approaches for assessing discriminant validity in marketing contexts, then uses Monte Carlo simulation to determine which tests are most effective.
Our long-term editorial strategy is to make sure JAMS becomes and remains a well-recognized outlet for both meta-analysis and systematic managerial review papers in marketing. Ideally, review papers would come to represent 10%–20% of the papers published by the journal.
Process and structure for review papers
In this section, we review the process and typical structure of a systematic review paper, which lacks any long or established tradition in marketing research. The article by Grewal et al. ( 2018 ) provides a summary of effects-focused review papers (i.e., meta-analyses), so we do not discuss them in detail here.
Systematic literature review process
Some review papers submitted to journals take a “narrative” approach. They discuss current knowledge about a research domain, yet they often are flawed, in that they lack criteria for article inclusion (or, more accurately, article exclusion), fail to discuss the methodology used to evaluate included articles, and avoid critical assessment of the field (Barczak 2017 ). Such reviews tend to be purely descriptive, with little lasting impact.
In contrast, a systematic literature review aims to “comprehensively locate and synthesize research that bears on a particular question, using organized, transparent, and replicable procedures at each step in the process” (Littell et al. 2008 , p. 1). Littell et al. describe six key steps in the systematic review process. The extent to which each step is emphasized varies by paper, but all are important components of the review.
Topic formulation . The author sets out clear objectives for the review and articulates the specific research questions or hypotheses that will be investigated.
Study design . The author specifies relevant problems, populations, constructs, and settings of interest. The aim is to define explicit criteria that can be used to assess whether any particular study should be included in or excluded from the review. Furthermore, it is important to develop a protocol in advance that describes the procedures and methods to be used to evaluate published work.
Sampling . The aim in this third step is to identify all potentially relevant studies, including both published and unpublished research. To this end, the author must first define the sampling unit to be used in the review (e.g., individual, strategic business unit) and then develop an appropriate sampling plan.
Data collection . By retrieving the potentially relevant studies identified in the third step, the author can determine whether each study meets the eligibility requirements set out in the second step. For studies deemed acceptable, the data are extracted from each study and entered into standardized templates. These templates should be based on the protocols established in step 2.
Data analysis . The degree and nature of the analyses used to describe and examine the collected data vary widely by review. Purely descriptive analysis is useful as a starting point but rarely is sufficient on its own. The examination of trends, clusters of ideas, and multivariate relationships among constructs helps flesh out a deeper understanding of the domain. For example, both Hult ( 2015 ) and Huber et al. ( 2014 ) use bibliometric approaches (e.g., examine citation data using multidimensional scaling and cluster analysis techniques) to identify emerging versus declining themes in the broad field of marketing.
Reporting . Three key aspects of this final step are common across systematic reviews. First, the results from the fifth step need to be presented, clearly and compellingly, using narratives, tables, and figures. Second, core results that emerge from the review must be interpreted and discussed by the author. These revelatory insights should reflect a deeper understanding of the topic being investigated, not simply a regurgitation of well-established knowledge. Third, the author needs to describe the implications of these unique insights for both future research and managerial practice.
A new paper by Watson et al. ( 2017 ), “Harnessing Difference: A Capability-Based Framework for Stakeholder Engagement in Environmental Innovation,” provides a good example of a systematic review, starting with a cohesive conceptual framework that helps establish the boundaries of the review while also identifying core constructs and their relationships. The article then explicitly describes the procedures used to search for potentially relevant papers and clearly sets out criteria for study inclusion or exclusion. Next, a detailed discussion of core elements in the framework weaves published research findings into the exposition. The paper ends with a presentation of key implications and suggestions for the next steps. Similarly, “Marketing Survey Research Best Practices: Evidence and Recommendations from a Review of JAMS Articles” (Hulland et al. 2017 ) systematically reviews published marketing studies that use survey techniques, describes recent trends, and suggests best practices. In their review, Hulland et al. examine the entire population of survey papers published in JAMS over a ten-year span, relying on an extensive standardized data template to facilitate their subsequent data analysis.
Structure of systematic review papers
There is no cookie-cutter recipe for the exact structure of a useful systematic review paper; the final structure depends on the authors’ insights and intended points of emphasis. However, several key components are likely integral to a paper’s ability to contribute.
Depth and rigor
Systematic review papers must avoid falling in to two potential “ditches.” The first ditch threatens when the paper fails to demonstrate that a systematic approach was used for selecting articles for inclusion and capturing their insights. If a reader gets the impression that the author has cherry-picked only articles that fit some preset notion or failed to be thorough enough, without including articles that make significant contributions to the field, the paper will be consigned to the proverbial side of the road when it comes to the discipline’s attention.
Authors that fall into the other ditch present a thorough, complete overview that offers only a mind-numbing recitation, without evident organization, synthesis, or critical evaluation. Although comprehensive, such a paper is more of an index than a useful review. The reviewed articles must be grouped in a meaningful way to guide the reader toward a better understanding of the focal phenomenon and provide a foundation for insights about future research directions. Some scholars organize research by scholarly perspectives (e.g., the psychology of privacy, the economics of privacy; Martin and Murphy 2017 ); others classify the chosen articles by objective research aspects (e.g., empirical setting, research design, conceptual frameworks; Cleeren et al. 2017 ). The method of organization chosen must allow the author to capture the complexity of the underlying phenomenon (e.g., including temporal or evolutionary aspects, if relevant).
Replicability
Processes for the identification and inclusion of research articles should be described in sufficient detail, such that an interested reader could replicate the procedure. The procedures used to analyze chosen articles and extract their empirical findings and/or key takeaways should be described with similar specificity and detail.
We already have noted the potential usefulness of well-done review papers. Some scholars always are new to the field or domain in question, so review papers also need to help them gain foundational knowledge. Key constructs, definitions, assumptions, and theories should be laid out clearly (for which purpose summary tables are extremely helpful). An integrated conceptual model can be useful to organize cited works. Most scholars integrate the knowledge they gain from reading the review paper into their plans for future research, so it is also critical that review papers clearly lay out implications (and specific directions) for research. Ideally, readers will come away from a review article filled with enthusiasm about ways they might contribute to the ongoing development of the field.
Helpful format
Because such a large body of research is being synthesized in most review papers, simply reading through the list of included studies can be exhausting for readers. We cannot overstate the importance of tables and figures in review papers, used in conjunction with meaningful headings and subheadings. Vast literature review tables often are essential, but they must be organized in a way that makes their insights digestible to the reader; in some cases, a sequence of more focused tables may be better than a single, comprehensive table.
In summary, articles that review extant research in a domain (topic, theory, or method) can be incredibly useful to the scientific progress of our field. Whether integrating the insights from extant research through a meta-analysis or synthesizing them through a systematic assessment, the promised benefits are similar. Both formats provide readers with a useful overview of knowledge about the focal phenomenon, as well as insights on key dilemmas and conflicting findings that suggest future research directions. Thus, the editorial team at JAMS encourages scholars to continue to invest the time and effort to construct thoughtful review papers.
Barczak, G. (2017). From the editor: writing a review article. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 34 (2), 120–121.
Article Google Scholar
Bem, D. J. (1995). Writing a review article for psychological bulletin. Psychological Bulletin, 118 (2), 172–177.
Bettencourt, L. A., & Houston, M. B. (2001). Assessing the impact of article method type and subject area on citation frequency and reference diversity. Marketing Letters, 12 (4), 327–340.
Cleeren, K., Dekimpe, M. G., & van Heerde, H. J. (2017). Marketing research on product-harm crises: a review, managerial implications. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (5), 593–615.
Grewal, D., Puccinelli, N. M., & Monroe, K. B. (2018). Meta-analysis: error cancels and truth accrues. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (1).
Hanssens, D. M. (2018). The value of empirical generalizations in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (1).
Huber, J., Kamakura, W., & Mela, C. F. (2014). A topical history of JMR . Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (1), 84–91.
Hulland, J., Baumgartner, H., & Smith, K. M. (2017). Marketing survey research best practices: evidence and recommendations from a review of JAMS articles. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0532-y .
Hult, G. T. M. (2015). JAMS 2010—2015: literature themes and intellectual structure. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (6), 663–669.
Knoll, J., & Matthes, J. (2017). The effectiveness of celebrity endorsements: a meta-analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (1), 55–75.
Kozlenkova, I. V., Samaha, S. A., & Palmatier, R. W. (2014). Resource-based theory in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 42 (1), 1–21.
Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta-analysis . New York: Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Martin, K. D., & Murphy, P. E. (2017). The role of data privacy in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 135–155.
Rindfleisch, A., & Heide, J. B. (1997). Transaction cost analysis: past, present, and future applications. Journal of Marketing, 61 (4), 30–54.
Sorescu, A., Warren, N. L., & Ertekin, L. (2017). Event study methodology in the marketing literature: an overview. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 186–207.
Verma, V., Sharma, D., & Sheth, J. (2016). Does relationship marketing matter in online retailing? A meta-analytic approach. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44 (2), 206–217.
Voorhies, C. M., Brady, M. K., Calantone, R., & Ramirez, E. (2016). Discriminant validity testing in marketing: an analysis, causes for concern, and proposed remedies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44 (1), 119–134.
Watson, R., Wilson, H. N., Smart, P., & Macdonald, E. K. (2017). Harnessing difference: a capability-based framework for stakeholder engagement in environmental innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12394 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Foster School of Business, University of Washington, Box: 353226, Seattle, WA, 98195-3226, USA
Robert W. Palmatier
Neeley School of Business, Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX, USA
Mark B. Houston
Terry College of Business, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA
John Hulland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Robert W. Palmatier .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Palmatier, R.W., Houston, M.B. & Hulland, J. Review articles: purpose, process, and structure. J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. 46 , 1–5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0563-4
Download citation
Published : 02 October 2017
Issue Date : January 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0563-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
What is a review article?
Learn how to write a review article.
What is a review article? A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results.
Writing a review of literature is to provide a critical evaluation of the data available from existing studies. Review articles can identify potential research areas to explore next, and sometimes they will draw new conclusions from the existing data.
Why write a review article?
To provide a comprehensive foundation on a topic.
To explain the current state of knowledge.
To identify gaps in existing studies for potential future research.
To highlight the main methodologies and research techniques.
Did you know?
There are some journals that only publish review articles, and others that do not accept them.
Make sure you check the aims and scope of the journal you’d like to publish in to find out if it’s the right place for your review article.
How to write a review article
Below are 8 key items to consider when you begin writing your review article.
Check the journal’s aims and scope
Make sure you have read the aims and scope for the journal you are submitting to and follow them closely. Different journals accept different types of articles and not all will accept review articles, so it’s important to check this before you start writing.
Define your scope
Define the scope of your review article and the research question you’ll be answering, making sure your article contributes something new to the field.
As award-winning author Angus Crake told us, you’ll also need to “define the scope of your review so that it is manageable, not too large or small; it may be necessary to focus on recent advances if the field is well established.”
Finding sources to evaluate
When finding sources to evaluate, Angus Crake says it’s critical that you “use multiple search engines/databases so you don’t miss any important ones.”
For finding studies for a systematic review in medical sciences, read advice from NCBI .
Writing your title, abstract and keywords
Spend time writing an effective title, abstract and keywords. This will help maximize the visibility of your article online, making sure the right readers find your research. Your title and abstract should be clear, concise, accurate, and informative.
For more information and guidance on getting these right, read our guide to writing a good abstract and title and our researcher’s guide to search engine optimization .
Introduce the topic
Does a literature review need an introduction? Yes, always start with an overview of the topic and give some context, explaining why a review of the topic is necessary. Gather research to inform your introduction and make it broad enough to reach out to a large audience of non-specialists. This will help maximize its wider relevance and impact.
Don’t make your introduction too long. Divide the review into sections of a suitable length to allow key points to be identified more easily.
Include critical discussion
Make sure you present a critical discussion, not just a descriptive summary of the topic. If there is contradictory research in your area of focus, make sure to include an element of debate and present both sides of the argument. You can also use your review paper to resolve conflict between contradictory studies.
What researchers say
Angus Crake, researcher
As part of your conclusion, include making suggestions for future research on the topic. Focus on the goal to communicate what you understood and what unknowns still remains.
Use a critical friend
Always perform a final spell and grammar check of your article before submission.
You may want to ask a critical friend or colleague to give their feedback before you submit. If English is not your first language, think about using a language-polishing service.
Find out more about how Taylor & Francis Editing Services can help improve your manuscript before you submit.
What is the difference between a research article and a review article?
| Differences in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| Presents the viewpoint of the author | Critiques the viewpoint of other authors on a particular topic | |
| New content | Assessing already published content | |
| Depends on the word limit provided by the journal you submit to | Tends to be shorter than a research article, but will still need to adhere to words limit |
Before you submit your review article…
Complete this checklist before you submit your review article:
Have you checked the journal’s aims and scope?
Have you defined the scope of your article?
Did you use multiple search engines to find sources to evaluate?
Have you written a descriptive title and abstract using keywords?
Did you start with an overview of the topic?
Have you presented a critical discussion?
Have you included future suggestions for research in your conclusion?
Have you asked a friend to do a final spell and grammar check?
Expert help for your manuscript

Taylor & Francis Editing Services offers a full range of pre-submission manuscript preparation services to help you improve the quality of your manuscript and submit with confidence.
Related resources
How to edit your paper
Writing a scientific literature review
How to Write a Review Article
- Types of Review Articles
- Before Writing a Review Article
- Determining Where to Publish
- Searching the Literature
- Citation Management
- Reading a Review Article
What is a Review Article?
The purpose of writing a review article is for knowledge updating concerning a topic.
A review article aims to highlight:
- What has been done?
- What has been found?
- What issues have not been addressed?
- What issues remain to be debated?
- What new issues have been raised?
- What will be the future direction of research?
Similarities and Differences to Original Research Articles
Differences Between Original Research Articles and Review Articles

- An original research article aims to: Provides background information (Intro.) on prior research, Reasons for present study, Issues to be investigated by the present study, Written for experts. Authors describe: Research methods & materials, Data acquisition/analysis tools, Results, Discussion of results.
- Both are Peer-reviewed for: Accuracy, Quality, Biases, Conflict of interest.
- A review article aims to: Extensive survey of published research articles about a specific topic, Critical appraising of research findings, summarize up-to-date research findings, Identify critical issues to be addressed, Written for experts and general audiences, Be a source of original research.
Figure by Zhiyong Han, PhD
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Types of Review Articles >>
- The Interprofessional Health Sciences Library
- 123 Metro Boulevard
- Nutley, NJ 07110
- [email protected]
- Student Services
- Parents and Families
- Career Center
- Web Accessibility
- Visiting Campus
- Public Safety
- Disability Support Services
- Campus Security Report
- Report a Problem
- Login to LibApps
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

Writing a good review article
- 3 minute read
- 86.6K views
Table of Contents
As a young researcher, you might wonder how to start writing your first review article, and the extent of the information that it should contain. A review article is a comprehensive summary of the current understanding of a specific research topic and is based on previously published research. Unlike research papers, it does not contain new results, but can propose new inferences based on the combined findings of previous research.
Types of review articles
Review articles are typically of three types: literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
A literature review is a general survey of the research topic and aims to provide a reliable and unbiased account of the current understanding of the topic.
A systematic review , in contrast, is more specific and attempts to address a highly focused research question. Its presentation is more detailed, with information on the search strategy used, the eligibility criteria for inclusion of studies, the methods utilized to review the collected information, and more.
A meta-analysis is similar to a systematic review in that both are systematically conducted with a properly defined research question. However, unlike the latter, a meta-analysis compares and evaluates a defined number of similar studies. It is quantitative in nature and can help assess contrasting study findings.
Tips for writing a good review article
Here are a few practices that can make the time-consuming process of writing a review article easier:
- Define your question: Take your time to identify the research question and carefully articulate the topic of your review paper. A good review should also add something new to the field in terms of a hypothesis, inference, or conclusion. A carefully defined scientific question will give you more clarity in determining the novelty of your inferences.
- Identify credible sources: Identify relevant as well as credible studies that you can base your review on, with the help of multiple databases or search engines. It is also a good idea to conduct another search once you have finished your article to avoid missing relevant studies published during the course of your writing.
- Take notes: A literature search involves extensive reading, which can make it difficult to recall relevant information subsequently. Therefore, make notes while conducting the literature search and note down the source references. This will ensure that you have sufficient information to start with when you finally get to writing.
- Describe the title, abstract, and introduction: A good starting point to begin structuring your review is by drafting the title, abstract, and introduction. Explicitly writing down what your review aims to address in the field will help shape the rest of your article.
- Be unbiased and critical: Evaluate every piece of evidence in a critical but unbiased manner. This will help you present a proper assessment and a critical discussion in your article.
- Include a good summary: End by stating the take-home message and identify the limitations of existing studies that need to be addressed through future studies.
- Ask for feedback: Ask a colleague to provide feedback on both the content and the language or tone of your article before you submit it.
- Check your journal’s guidelines: Some journals only publish reviews, while some only publish research articles. Further, all journals clearly indicate their aims and scope. Therefore, make sure to check the appropriateness of a journal before submitting your article.
Writing review articles, especially systematic reviews or meta-analyses, can seem like a daunting task. However, Elsevier Author Services can guide you by providing useful tips on how to write an impressive review article that stands out and gets published!

What are Implications in Research?

How to write the results section of a research paper
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Scholarly Sources: What are They and Where can You Find Them?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

How to Review a Journal Article

For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.
The do’s and don’ts of writing review articles
If you (or a global pandemic) take the bench away from the scientist, what do they do? They write reviews of course!
As many of us are now far too familiar with, crafting a review article presents a series of unique challenges. Unlike a manuscript, in which the nature of your data inherently shapes the narrative of the article, a review requires synthesizing one largely from scratch. Reviews are often initiated without a well-defined scope going in, which can often leave us feeling overwhelmed, like we’re faced with covering an entire field.
With these challenges in mind, here are a few tips and tricks to make review writing as painless as possible, for the next time you lose your pipette:
- Defining this viewpoint can be extremely helpful in limiting the scope of your literature search, preventing the overwhelming feeling of having to read every paper ever — focus your time and energy on deep-dives into those papers most important to this motivating viewpoint.
- Ask yourself: Who do you want reading your review? What could you cover that would be most helpful to them?
- This will be an iterative process — the focus of your review will likely change significantly over the writing process, as you read more papers and start organizing your thoughts.
- For each review, ask: What are their take-home messages? How can you differentiate your own from each of these?
- As a member of the field, look out for things you wish they had covered: “I wish they had a figure on this, I wish they discussed this, I wish they clarified this…”
- Are there key papers that they missed?
- Are there key papers that have been published since these reviews have been published?
- Cite other reviews to save yourself some writing! If a tangentially related topic is outside of the scope of your review, it’s commonplace to reference other reviews for the sake of brevity, and to recognize their hard work: “X is outside of the scope of this review, but is covered in-depth here [Ref]”).
- For each paper, ask: What was known before this paper, what did this paper show, and what are its limitations?
- It’s important to accept the fact that it is impossible to read, let alone discuss in-depth, hundreds and hundreds of papers.
- Depending on how each paper will fit into your article’s narrative, it may only be necessary to review specific sections or figures. [ I don’t have to read every word of every paper?! ]
- Given the unstructured nature of a non-data-driven article, this is a hugely important step in the process that will make writing infinitely less painful.
- Which key papers are you going to discuss in which sections?
- Outline subsections and transitions under each major section.
- Engage with your PI early and often in the process of crafting your outline, and try to get explicit approval of the finished product before you start writing — this can save you from a lot of painful backtracking later!
- Writing and structuring your review should be iterative as you continue to refine, read more papers, and start to actually get words down on the page
- The most helpful reviews synthesize the findings of multiple papers into a cohesive take-home message.
- Think about how specific findings relate to your overarching motivation for this article
- Think about how different papers relate to each other — do different studies align, or do they contradict each other?
- Keep in mind how people generally skim articles, by skimming the figures — reviews are no different
- Figures should be included in your structural outline
- For example, many people pull schematics from their own reviews to use directly in background slides of future presentations
- While you cannot avoid citing and discussing major, high impact papers from larger journals, consider that these have likely already been discussed in great depth by other reviews given their high visibility. Good research exists in smaller journals, and you can do your part to cast a light on this work.
- You can provide a fresh perspective by looking outside your field for analogous research, provided you can find a creative way to fit it into the scope of your review’s narrative.
Blog post written by Caleb Perez , with input from Tyler Toth, Viraat Goel , and Prerna Bhargava .
Reviews versus Perspectives- It’s important to draw the distinction between reviews and perspectives here. Although we believe that both should review the field in the context of some overarching scientific viewpoint, perspective articles allow the author much more freedom to craft a more opinionated argument and are generally more forward-thinking. If you have that freedom, definitely use it!
Belonging to a group- Of course, the extent to which you can do this may be limited, depending on how familiar you are with the field. First-year graduate students getting into a new field, for example, may not have as great of a grasp on the gaps in the field — you may have to lean on the advice of your PI and colleagues to help guide you here, especially in the early stages of the process before you start your in-depth literature search.
How to read a paper- There are many situations in which a narrower, targeted paper review is warranted. As one example, imagine a section of a review in which you are comparing different technologies for application X. In this context, you may only need to do a detailed review of the methods sections and any figures they have that benchmark their method for your particular application of interest. The rest of the paper is less relevant, so there’s no need to waste your valuable time and energy.

Review Paper Format: How To Write A Review Article Fast
This guide aims to demystify the review paper format, presenting practical tips to help you accelerate the writing process.
From understanding the structure to synthesising literature effectively, we’ll explore how to create a compelling review article swiftly, ensuring your work is both impactful and timely.
Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a budding scholar, these insights will streamline your writing journey.
Research Paper, Review Paper Format
| Parts | Notes |
|---|---|
| Title & Abstract | Sets the stage with a concise title and a descriptive abstract summarising the review’s scope and findings. |
| Introduction | Lays the groundwork by presenting the research question, justifying the review’s importance, and highlighting knowledge gaps. |
| Methodology | Details the research methods used to select, assess, and synthesise studies, showcasing the review’s rigor and integrity. |
| Body | The core section where literature is summarised, analysed, and critiqued, synthesising evidence and presenting arguments with well-structured paragraphs. |
| Discussion & Conclusion | Weaves together main points, reflects on the findings’ implications for the field, and suggests future research directions. |
| Citation | Acknowledges the scholarly community’s contributions, linking to cited research and enriching the review’s academic discourse. |
What Is A Review Paper?
Diving into the realm of scholarly communication, you might have stumbled upon a research review article.
This unique genre serves to synthesise existing data, offering a panoramic view of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.

Unlike a standard research article that presents original experiments, a review paper delves into published literature, aiming to:
- clarify, and
- evaluate previous findings.
Imagine you’re tasked to write a review article. The starting point is often a burning research question. Your mission? To scour various journals, piecing together a well-structured narrative that not only summarises key findings but also identifies gaps in existing literature.
This is where the magic of review writing shines – it’s about creating a roadmap for future research, highlighting areas ripe for exploration.
Review articles come in different flavours, with systematic reviews and meta-analyses being the gold standards. The methodology here is meticulous, with a clear protocol for selecting and evaluating studies.
This rigorous approach ensures that your review is more than just an overview; it’s a critical analysis that adds depth to the understanding of the subject.
Crafting a good review requires mastering the art of citation. Every claim or observation you make needs to be backed by relevant literature. This not only lends credibility to your work but also provides a treasure trove of information for readers eager to delve deeper.
Types Of Review Paper
Not all review articles are created equal. Each type has its methodology, purpose, and format, catering to different research needs and questions.
Systematic Review Paper
First up is the systematic review, the crème de la crème of review types. It’s known for its rigorous methodology, involving a detailed plan for:
- identifying,
- selecting, and
- critically appraising relevant research.
The aim? To answer a specific research question. Systematic reviews often include meta-analyses, where data from multiple studies are statistically combined to provide more robust conclusions. This review type is a cornerstone in evidence-based fields like healthcare.
Literature Review Paper
Then there’s the literature review, a broader type you might encounter.
Here, the goal is to give an overview of the main points and debates on a topic, without the stringent methodological framework of a systematic review.
Literature reviews are great for getting a grasp of the field and identifying where future research might head. Often reading literature review papers can help you to learn about a topic rather quickly.

Narrative Reviews
Narrative reviews allow for a more flexible approach. Authors of narrative reviews draw on existing literature to provide insights or critique a certain area of research.
This is generally done with a less formal structure than systematic reviews. This type is particularly useful for areas where it’s difficult to quantify findings across studies.
Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews are gaining traction for their ability to map out the existing literature on a broad topic, identifying:
- key concepts,
- theories, and
Unlike systematic reviews, scoping reviews have a more exploratory approach, which can be particularly useful in emerging fields or for topics that haven’t been comprehensively reviewed before.
Each type of review serves a unique purpose and requires a specific skill set. Whether you’re looking to summarise existing findings, synthesise data for evidence-based practice, or explore new research territories, there’s a review type that fits the bill.
Knowing how to write, read, and interpret these reviews can significantly enhance your understanding of any research area.
What Are The Parts In A Review Paper
A review paper has a pretty set structure, with minor changes here and there to suit the topic covered. The format not only organises your thoughts but also guides your readers through the complexities of your topic.

Title & Abstract
Starting with the title and abstract, you set the stage. The title should be a concise indicator of the content, making it easier for others to quickly tell what your article content is about.
As for the abstract, it should act as a descriptive summary, offering a snapshot of your review’s scope and findings.
Introduction
The introduction lays the groundwork, presenting the research question that drives your review. It’s here you:
- justify the importance of your review,
- delineating the current state of knowledge and
- highlighting gaps.
This section aims to articulate the significance of the topic and your objective in exploring it.
Methodology
The methodology section is the backbone of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, detailing the research methods employed to select, assess, and synthesise studies.

This transparency allows readers to gauge the rigour and reproducibility of your review. It’s a testament to the integrity of your work, showing how you’ve minimised bias.
The heart of your review lies in the body, where you:
- analyse, and
- critique existing literature.
This is where you synthesise evidence, draw connections, and present both sides of any argument. Well-structured paragraphs and clear subheadings guide readers through your analysis, offering insights and fostering a deeper understanding of the subject.
Discussion & Conclusion
The discussion or conclusion section is where you weave together the main points, reflecting on what your findings mean for the field.
It’s about connecting the dots, offering a synthesis of evidence that answers your initial research question. This part often hints at future research directions, suggesting areas that need further exploration due to gaps in existing knowledge.
Lastly, the citation list is your nod to the scholarly community, acknowledging the contributions of others. Each citation is a thread in the larger tapestry of academic discourse, enabling readers to delve deeper into the research that has shaped your review.
Tips To Write An Review Article Fast
Writing a review article quickly without sacrificing quality might seem like a tall order, but with the right approach, it’s entirely achievable.
Clearly Define Your Research Question
Clearly define your research question. A focused question not only narrows down the scope of your literature search but also keeps your review concise and on track.
By honing in on a specific aspect of a broader topic, you can avoid the common pitfall of becoming overwhelmed by the vast expanse of available literature. This specificity allows you to zero in on the most relevant studies, making your review more impactful.
Efficient Literature Searching
Utilise databases specific to your field and employ advanced search techniques like Boolean operators. This can drastically reduce the time you spend sifting through irrelevant articles.
Additionally, leveraging citation chains—looking at who has cited a pivotal paper in your area and who it cites—can uncover valuable sources you might otherwise miss.
Organise Your Findings Systematically
Developing a robust organisation strategy is key. As you gather sources, categorize them based on themes or methodologies. This not only aids in structuring your review but also in identifying areas where research is lacking or abundant.
Tools like citation management software can be invaluable here, helping you keep track of your sources and their key points. We list out some of the best AI tools for academic research here.

Build An Outline Before Writing
Don’t underestimate the power of a well-structured outline. A clear blueprint of your article can guide your writing process, ensuring that each section flows logically into the next.
This roadmap not only speeds up the writing process by providing a clear direction but also helps maintain coherence, ensuring your review article delivers a compelling narrative that advances understanding in your field.
Start Writing With The Easiest Sections
When it’s time to write, start with sections you find easiest. This might be the methodology or a particular thematic section where you feel most confident.
Getting words on the page can build momentum, making it easier to tackle more challenging sections later.
Remember, your first draft doesn’t have to be perfect; the goal is to start articulating your synthesis of the literature.
Learn How To Write An Article Review
Mastering the review paper format is a crucial step towards efficient academic writing. By adhering to the structured components outlined, you can streamline the creation of a compelling review article.
Embracing these guidelines not only speeds up the writing process but also enhances the clarity and impact of your work, ensuring your contributions to scholarly discourse are both valuable and timely.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

NFS 4021 Contemporary Topics in Nutrition: Research Articles vs Review Articles
- Research Articles vs Review Articles
- Citation Help
Agriculture Support Librarian

Research Articles and Review Articles Defined Review
"A research article is a primary source ...that is, it reports the methods and results of an original study performed by the authors . The kind of study may vary (it could have been an experiment, survey, interview, etc.), but in all cases, raw data have been collected and analyzed by the authors, and conclusions drawn from the results of that analysis.
A review article is a secondary source ...it is written about other articles, and does not report original research of its own. Review articles are very important, as they draw upon the articles that they review to suggest new research directions, to strengthen support for existing theories and/or identify patterns among existing research studies. For student researchers, review articles provide a great overview of the existing literature on a topic. If you find a literature review that fits your topic, take a look at its references/works cited list for leads on other relevant articles and books!"
From https://apus.libanswers.com/faq/2324 , "What's the difference between a research and a review article?"
- Example of a RESEARCH Article Lin CL, Huang LC, Chang YT, Chen RY, Yang SH. Effectiveness of Health Coaching in Diabetes Control and Lifestyle Improvement: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 29;13(11):3878.
- Example of a REVIEW Article Ojo O, Ojo OO, Adebowale F, Wang XH. The Effect of Dietary Glycaemic Index on Glycaemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2018 Mar 19;10(3):373.
Difference between Reviews and Research Articles

Research Article Break Down Review
Research articles follow a particular format. Look for:
- A brief introduction will often include a review of the existing literature on the topic studied, and explain the rationale of the author's study.
- A methods section, where authors describe how they collected and analyzed data. Statistical analysis are included.
- A results section describes the outcomes of the data analysis. Charts and graphs illustrating the results are typically included.
- In the discussion , authors will explain their interpretation of their results and theorize on their importance to existing and future research.
- References or works cited are always included. These are the articles and books that the authors drew upon to plan their study and to support their discussion.
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Databases >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.lsu.edu/NFS4021
Provide Website Feedback Accessibility Statement

How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Author Interviews
- Research Curations
- Author Guidelines
- Open Access
- Submission Site
- Why Submit?
- About Journal of Consumer Research
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Why and How Consumers Perform Online Reviewing Differently
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Gwarlann de Kerviler, Catherine Demangeot, Pierre-Yann Dolbec, Why and How Consumers Perform Online Reviewing Differently, Journal of Consumer Research , 2024;, ucae040, https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucae040
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Reviewing products and services is a widespread consumer activity in which millions engage. Why and how do consumers review differently from one another? Prior work assumes that consumers commonly understand what reviewing is. Consequently, it attributes differences in reviewing to individual variations in psychological, motivational, and sociodemographic characteristics, consumption experiences, and expertise. This central assumption is problematic because it fails to consider that differences in how consumers understand reviewing may explain why they approach and perform reviewing differently. To address this gap, we analyze a large qualitative data set composed of reviews and interviews with their authors. Our insights complement prior work by theorizing the sociocultural shaping of reviewing. We answer why consumers review differently by inductively theorizing the concept of reviewing orientation—a cultural model comprising a set of interconnected characteristics that shapes how consumers review and translates into a distinct reviewer voice—a reviewer’s standpoint expressed within a review. We answer how consumers review differently by developing three reviewing orientations: communal sharing, systemic evaluation, and competitive punditry. Finally, we discuss the transferability of the findings, the role of institutional dynamics in reviewing, and recommendations for online review platforms and marketers.
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| July 2024 | 21 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1537-5277
- Print ISSN 0093-5301
- Copyright © 2024 Journal of Consumer Research Inc.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Clinics (Sao Paulo)
Approaching literature review for academic purposes: The Literature Review Checklist
Debora f.b. leite.
I Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetricia, Faculdade de Ciencias Medicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, BR
II Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
III Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
Maria Auxiliadora Soares Padilha
Jose g. cecatti.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field. Unfortunately, little guidance is available on elaborating LRs, and writing an LR chapter is not a linear process. An LR translates students’ abilities in information literacy, the language domain, and critical writing. Students in postgraduate programs should be systematically trained in these skills. Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist. By clearly stating the desired achievements, this checklist allows Masters and Ph.D. students to continuously assess their own progress in elaborating an LR. Institutions aiming to strengthen students’ necessary skills in critical academic writing should also use this tool.
INTRODUCTION
Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer’s block and procrastination ( 1 ) in postgraduate life. Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs ( 2 ) may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR. Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any academic work, despite the more recent trend of producing scientific articles rather than classical theses.
The LR is not an isolated section of the thesis/dissertation or a copy of the background section of a research proposal. It identifies the state-of-the-art knowledge in a particular field, clarifies information that is already known, elucidates implications of the problem being analyzed, links theory and practice ( 3 - 5 ), highlights gaps in the current literature, and places the dissertation/thesis within the research agenda of that field. Additionally, by writing the LR, postgraduate students will comprehend the structure of the subject and elaborate on their cognitive connections ( 3 ) while analyzing and synthesizing data with increasing maturity.
At the same time, the LR transforms the student and hints at the contents of other chapters for the reader. First, the LR explains the research question; second, it supports the hypothesis, objectives, and methods of the research project; and finally, it facilitates a description of the student’s interpretation of the results and his/her conclusions. For scholars, the LR is an introductory chapter ( 6 ). If it is well written, it demonstrates the student’s understanding of and maturity in a particular topic. A sound and sophisticated LR can indicate a robust dissertation/thesis.
A consensus on the best method to elaborate a dissertation/thesis has not been achieved. The LR can be a distinct chapter or included in different sections; it can be part of the introduction chapter, part of each research topic, or part of each published paper ( 7 ). However, scholars view the LR as an integral part of the main body of an academic work because it is intrinsically connected to other sections ( Figure 1 ) and is frequently present. The structure of the LR depends on the conventions of a particular discipline, the rules of the department, and the student’s and supervisor’s areas of expertise, needs and interests.

Interestingly, many postgraduate students choose to submit their LR to peer-reviewed journals. As LRs are critical evaluations of current knowledge, they are indeed publishable material, even in the form of narrative or systematic reviews. However, systematic reviews have specific patterns 1 ( 8 ) that may not entirely fit with the questions posed in the dissertation/thesis. Additionally, the scope of a systematic review may be too narrow, and the strict criteria for study inclusion may omit important information from the dissertation/thesis. Therefore, this essay discusses the definition of an LR is and methods to develop an LR in the context of an academic dissertation/thesis. Finally, we suggest a checklist to evaluate an LR.
WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A THESIS?
Conducting research and writing a dissertation/thesis translates rational thinking and enthusiasm ( 9 ). While a strong body of literature that instructs students on research methodology, data analysis and writing scientific papers exists, little guidance on performing LRs is available. The LR is a unique opportunity to assess and contrast various arguments and theories, not just summarize them. The research results should not be discussed within the LR, but the postgraduate student tends to write a comprehensive LR while reflecting on his or her own findings ( 10 ).
Many people believe that writing an LR is a lonely and linear process. Supervisors or the institutions assume that the Ph.D. student has mastered the relevant techniques and vocabulary associated with his/her subject and conducts a self-reflection about previously published findings. Indeed, while elaborating the LR, the student should aggregate diverse skills, which mainly rely on his/her own commitment to mastering them. Thus, less supervision should be required ( 11 ). However, the parameters described above might not currently be the case for many students ( 11 , 12 ), and the lack of formal and systematic training on writing LRs is an important concern ( 11 ).
An institutional environment devoted to active learning will provide students the opportunity to continuously reflect on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the postgraduate student and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ). Postgraduate students will be interpreting studies by other researchers, and, according to Hart (1998) ( 3 ), the outcomes of the LR in a dissertation/thesis include the following:
- To identify what research has been performed and what topics require further investigation in a particular field of knowledge;
- To determine the context of the problem;
- To recognize the main methodologies and techniques that have been used in the past;
- To place the current research project within the historical, methodological and theoretical context of a particular field;
- To identify significant aspects of the topic;
- To elucidate the implications of the topic;
- To offer an alternative perspective;
- To discern how the studied subject is structured;
- To improve the student’s subject vocabulary in a particular field; and
- To characterize the links between theory and practice.
A sound LR translates the postgraduate student’s expertise in academic and scientific writing: it expresses his/her level of comfort with synthesizing ideas ( 11 ). The LR reveals how well the postgraduate student has proceeded in three domains: an effective literature search, the language domain, and critical writing.
Effective literature search
All students should be trained in gathering appropriate data for specific purposes, and information literacy skills are a cornerstone. These skills are defined as “an individual’s ability to know when they need information, to identify information that can help them address the issue or problem at hand, and to locate, evaluate, and use that information effectively” ( 14 ). Librarian support is of vital importance in coaching the appropriate use of Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) and other tools for highly efficient literature searches (e.g., quotation marks and truncation), as is the appropriate management of electronic databases.
Language domain
Academic writing must be concise and precise: unnecessary words distract the reader from the essential content ( 15 ). In this context, reading about issues distant from the research topic ( 16 ) may increase students’ general vocabulary and familiarity with grammar. Ultimately, reading diverse materials facilitates and encourages the writing process itself.
Critical writing
Critical judgment includes critical reading, thinking and writing. It supposes a student’s analytical reflection about what he/she has read. The student should delineate the basic elements of the topic, characterize the most relevant claims, identify relationships, and finally contrast those relationships ( 17 ). Each scientific document highlights the perspective of the author, and students will become more confident in judging the supporting evidence and underlying premises of a study and constructing their own counterargument as they read more articles. A paucity of integration or contradictory perspectives indicates lower levels of cognitive complexity ( 12 ).
Thus, while elaborating an LR, the postgraduate student should achieve the highest category of Bloom’s cognitive skills: evaluation ( 12 ). The writer should not only summarize data and understand each topic but also be able to make judgments based on objective criteria, compare resources and findings, identify discrepancies due to methodology, and construct his/her own argument ( 12 ). As a result, the student will be sufficiently confident to show his/her own voice .
Writing a consistent LR is an intense and complex activity that reveals the training and long-lasting academic skills of a writer. It is not a lonely or linear process. However, students are unlikely to be prepared to write an LR if they have not mastered the aforementioned domains ( 10 ). An institutional environment that supports student learning is crucial.
Different institutions employ distinct methods to promote students’ learning processes. First, many universities propose modules to develop behind the scenes activities that enhance self-reflection about general skills (e.g., the skills we have mastered and the skills we need to develop further), behaviors that should be incorporated (e.g., self-criticism about one’s own thoughts), and each student’s role in the advancement of his/her field. Lectures or workshops about LRs themselves are useful because they describe the purposes of the LR and how it fits into the whole picture of a student’s work. These activities may explain what type of discussion an LR must involve, the importance of defining the correct scope, the reasons to include a particular resource, and the main role of critical reading.
Some pedagogic services that promote a continuous improvement in study and academic skills are equally important. Examples include workshops about time management, the accomplishment of personal objectives, active learning, and foreign languages for nonnative speakers. Additionally, opportunities to converse with other students promotes an awareness of others’ experiences and difficulties. Ultimately, the supervisor’s role in providing feedback and setting deadlines is crucial in developing students’ abilities and in strengthening students’ writing quality ( 12 ).
HOW SHOULD A LITERATURE REVIEW BE DEVELOPED?
A consensus on the appropriate method for elaborating an LR is not available, but four main steps are generally accepted: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, and writing ( 6 ). We suggest a fifth step: reflecting on the information that has been written in previous publications ( Figure 2 ).

First step: Defining the main topic
Planning an LR is directly linked to the research main question of the thesis and occurs in parallel to students’ training in the three domains discussed above. The planning stage helps organize ideas, delimit the scope of the LR ( 11 ), and avoid the wasting of time in the process. Planning includes the following steps:
- Reflecting on the scope of the LR: postgraduate students will have assumptions about what material must be addressed and what information is not essential to an LR ( 13 , 18 ). Cooper’s Taxonomy of Literature Reviews 2 systematizes the writing process through six characteristics and nonmutually exclusive categories. The focus refers to the reviewer’s most important points of interest, while the goals concern what students want to achieve with the LR. The perspective assumes answers to the student’s own view of the LR and how he/she presents a particular issue. The coverage defines how comprehensive the student is in presenting the literature, and the organization determines the sequence of arguments. The audience is defined as the group for whom the LR is written.
- Designating sections and subsections: Headings and subheadings should be specific, explanatory and have a coherent sequence throughout the text ( 4 ). They simulate an inverted pyramid, with an increasing level of reflection and depth of argument.
- Identifying keywords: The relevant keywords for each LR section should be listed to guide the literature search. This list should mirror what Hart (1998) ( 3 ) advocates as subject vocabulary . The keywords will also be useful when the student is writing the LR since they guide the reader through the text.
- Delineating the time interval and language of documents to be retrieved in the second step. The most recently published documents should be considered, but relevant texts published before a predefined cutoff year can be included if they are classic documents in that field. Extra care should be employed when translating documents.
Second step: Searching the literature
The ability to gather adequate information from the literature must be addressed in postgraduate programs. Librarian support is important, particularly for accessing difficult texts. This step comprises the following components:
- Searching the literature itself: This process consists of defining which databases (electronic or dissertation/thesis repositories), official documents, and books will be searched and then actively conducting the search. Information literacy skills have a central role in this stage. While searching electronic databases, controlled vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Headings, or MeSH, for the PubMed database) or specific standardized syntax rules may need to be applied.
In addition, two other approaches are suggested. First, a review of the reference list of each document might be useful for identifying relevant publications to be included and important opinions to be assessed. This step is also relevant for referencing the original studies and leading authors in that field. Moreover, students can directly contact the experts on a particular topic to consult with them regarding their experience or use them as a source of additional unpublished documents.
Before submitting a dissertation/thesis, the electronic search strategy should be repeated. This process will ensure that the most recently published papers will be considered in the LR.
- Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information. However, since these materials are not peer-reviewed, we recommend that they are carefully added to the LR.
This task is an important exercise in time management. First, students should read the title and abstract to understand whether that document suits their purposes, addresses the research question, and helps develop the topic of interest. Then, they should scan the full text, determine how it is structured, group it with similar documents, and verify whether other arguments might be considered ( 5 ).
Third step: Analyzing the results
Critical reading and thinking skills are important in this step. This step consists of the following components:
- Reading documents: The student may read various texts in depth according to LR sections and subsections ( defining the main topic ), which is not a passive activity ( 1 ). Some questions should be asked to practice critical analysis skills, as listed below. Is the research question evident and articulated with previous knowledge? What are the authors’ research goals and theoretical orientations, and how do they interact? Are the authors’ claims related to other scholars’ research? Do the authors consider different perspectives? Was the research project designed and conducted properly? Are the results and discussion plausible, and are they consistent with the research objectives and methodology? What are the strengths and limitations of this work? How do the authors support their findings? How does this work contribute to the current research topic? ( 1 , 19 )
- Taking notes: Students who systematically take notes on each document are more readily able to establish similarities or differences with other documents and to highlight personal observations. This approach reinforces the student’s ideas about the next step and helps develop his/her own academic voice ( 1 , 13 ). Voice recognition software ( 16 ), mind maps ( 5 ), flowcharts, tables, spreadsheets, personal comments on the referenced texts, and note-taking apps are all available tools for managing these observations, and the student him/herself should use the tool that best improves his/her learning. Additionally, when a student is considering submitting an LR to a peer-reviewed journal, notes should be taken on the activities performed in all five steps to ensure that they are able to be replicated.
Fourth step: Writing
The recognition of when a student is able and ready to write after a sufficient period of reading and thinking is likely a difficult task. Some students can produce a review in a single long work session. However, as discussed above, writing is not a linear process, and students do not need to write LRs according to a specific sequence of sections. Writing an LR is a time-consuming task, and some scholars believe that a period of at least six months is sufficient ( 6 ). An LR, and academic writing in general, expresses the writer’s proper thoughts, conclusions about others’ work ( 6 , 10 , 13 , 16 ), and decisions about methods to progress in the chosen field of knowledge. Thus, each student is expected to present a different learning and writing trajectory.
In this step, writing methods should be considered; then, editing, citing and correct referencing should complete this stage, at least temporarily. Freewriting techniques may be a good starting point for brainstorming ideas and improving the understanding of the information that has been read ( 1 ). Students should consider the following parameters when creating an agenda for writing the LR: two-hour writing blocks (at minimum), with prespecified tasks that are possible to complete in one section; short (minutes) and long breaks (days or weeks) to allow sufficient time for mental rest and reflection; and short- and long-term goals to motivate the writing itself ( 20 ). With increasing experience, this scheme can vary widely, and it is not a straightforward rule. Importantly, each discipline has a different way of writing ( 1 ), and each department has its own preferred styles for citations and references.
Fifth step: Reflecting on the writing
In this step, the postgraduate student should ask him/herself the same questions as in the analyzing the results step, which can take more time than anticipated. Ambiguities, repeated ideas, and a lack of coherence may not be noted when the student is immersed in the writing task for long periods. The whole effort will likely be a work in progress, and continuous refinements in the written material will occur once the writing process has begun.
LITERATURE REVIEW CHECKLIST
In contrast to review papers, the LR of a dissertation/thesis should not be a standalone piece or work. Instead, it should present the student as a scholar and should maintain the interest of the audience in how that dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A checklist for evaluating an LR is convenient for students’ continuous academic development and research transparency: it clearly states the desired achievements for the LR of a dissertation/thesis. Here, we present an LR checklist developed from an LR scoring rubric ( 11 ). For a critical analysis of an LR, we maintain the five categories but offer twelve criteria that are not scaled ( Figure 3 ). The criteria all have the same importance and are not mutually exclusive.

First category: Coverage
1. justified criteria exist for the inclusion and exclusion of literature in the review.
This criterion builds on the main topic and areas covered by the LR ( 18 ). While experts may be confident in retrieving and selecting literature, postgraduate students must convince their audience about the adequacy of their search strategy and their reasons for intentionally selecting what material to cover ( 11 ). References from different fields of knowledge provide distinct perspective, but narrowing the scope of coverage may be important in areas with a large body of existing knowledge.
Second category: Synthesis
2. a critical examination of the state of the field exists.
A critical examination is an assessment of distinct aspects in the field ( 1 ) along with a constructive argument. It is not a negative critique but an expression of the student’s understanding of how other scholars have added to the topic ( 1 ), and the student should analyze and contextualize contradictory statements. A writer’s personal bias (beliefs or political involvement) have been shown to influence the structure and writing of a document; therefore, the cultural and paradigmatic background guide how the theories are revised and presented ( 13 ). However, an honest judgment is important when considering different perspectives.
3. The topic or problem is clearly placed in the context of the broader scholarly literature
The broader scholarly literature should be related to the chosen main topic for the LR ( how to develop the literature review section). The LR can cover the literature from one or more disciplines, depending on its scope, but it should always offer a new perspective. In addition, students should be careful in citing and referencing previous publications. As a rule, original studies and primary references should generally be included. Systematic and narrative reviews present summarized data, and it may be important to cite them, particularly for issues that should be understood but do not require a detailed description. Similarly, quotations highlight the exact statement from another publication. However, excessive referencing may disclose lower levels of analysis and synthesis by the student.
4. The LR is critically placed in the historical context of the field
Situating the LR in its historical context shows the level of comfort of the student in addressing a particular topic. Instead of only presenting statements and theories in a temporal approach, which occasionally follows a linear timeline, the LR should authentically characterize the student’s academic work in the state-of-art techniques in their particular field of knowledge. Thus, the LR should reinforce why the dissertation/thesis represents original work in the chosen research field.
5. Ambiguities in definitions are considered and resolved
Distinct theories on the same topic may exist in different disciplines, and one discipline may consider multiple concepts to explain one topic. These misunderstandings should be addressed and contemplated. The LR should not synthesize all theories or concepts at the same time. Although this approach might demonstrate in-depth reading on a particular topic, it can reveal a student’s inability to comprehend and synthesize his/her research problem.
6. Important variables and phenomena relevant to the topic are articulated
The LR is a unique opportunity to articulate ideas and arguments and to purpose new relationships between them ( 10 , 11 ). More importantly, a sound LR will outline to the audience how these important variables and phenomena will be addressed in the current academic work. Indeed, the LR should build a bidirectional link with the remaining sections and ground the connections between all of the sections ( Figure 1 ).
7. A synthesized new perspective on the literature has been established
The LR is a ‘creative inquiry’ ( 13 ) in which the student elaborates his/her own discourse, builds on previous knowledge in the field, and describes his/her own perspective while interpreting others’ work ( 13 , 17 ). Thus, students should articulate the current knowledge, not accept the results at face value ( 11 , 13 , 17 ), and improve their own cognitive abilities ( 12 ).
Third category: Methodology
8. the main methodologies and research techniques that have been used in the field are identified and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed.
The LR is expected to distinguish the research that has been completed from investigations that remain to be performed, address the benefits and limitations of the main methods applied to date, and consider the strategies for addressing the expected limitations described above. While placing his/her research within the methodological context of a particular topic, the LR will justify the methodology of the study and substantiate the student’s interpretations.
9. Ideas and theories in the field are related to research methodologies
The audience expects the writer to analyze and synthesize methodological approaches in the field. The findings should be explained according to the strengths and limitations of previous research methods, and students must avoid interpretations that are not supported by the analyzed literature. This criterion translates to the student’s comprehension of the applicability and types of answers provided by different research methodologies, even those using a quantitative or qualitative research approach.
Fourth category: Significance
10. the scholarly significance of the research problem is rationalized.
The LR is an introductory section of a dissertation/thesis and will present the postgraduate student as a scholar in a particular field ( 11 ). Therefore, the LR should discuss how the research problem is currently addressed in the discipline being investigated or in different disciplines, depending on the scope of the LR. The LR explains the academic paradigms in the topic of interest ( 13 ) and methods to advance the field from these starting points. However, an excess number of personal citations—whether referencing the student’s research or studies by his/her research team—may reflect a narrow literature search and a lack of comprehensive synthesis of ideas and arguments.
11. The practical significance of the research problem is rationalized
The practical significance indicates a student’s comprehensive understanding of research terminology (e.g., risk versus associated factor), methodology (e.g., efficacy versus effectiveness) and plausible interpretations in the context of the field. Notably, the academic argument about a topic may not always reflect the debate in real life terms. For example, using a quantitative approach in epidemiology, statistically significant differences between groups do not explain all of the factors involved in a particular problem ( 21 ). Therefore, excessive faith in p -values may reflect lower levels of critical evaluation of the context and implications of a research problem by the student.
Fifth category: Rhetoric
12. the lr was written with a coherent, clear structure that supported the review.
This category strictly relates to the language domain: the text should be coherent and presented in a logical sequence, regardless of which organizational ( 18 ) approach is chosen. The beginning of each section/subsection should state what themes will be addressed, paragraphs should be carefully linked to each other ( 10 ), and the first sentence of each paragraph should generally summarize the content. Additionally, the student’s statements are clear, sound, and linked to other scholars’ works, and precise and concise language that follows standardized writing conventions (e.g., in terms of active/passive voice and verb tenses) is used. Attention to grammar, such as orthography and punctuation, indicates prudence and supports a robust dissertation/thesis. Ultimately, all of these strategies provide fluency and consistency for the text.
Although the scoring rubric was initially proposed for postgraduate programs in education research, we are convinced that this checklist is a valuable tool for all academic areas. It enables the monitoring of students’ learning curves and a concentrated effort on any criteria that are not yet achieved. For institutions, the checklist is a guide to support supervisors’ feedback, improve students’ writing skills, and highlight the learning goals of each program. These criteria do not form a linear sequence, but ideally, all twelve achievements should be perceived in the LR.
CONCLUSIONS
A single correct method to classify, evaluate and guide the elaboration of an LR has not been established. In this essay, we have suggested directions for planning, structuring and critically evaluating an LR. The planning of the scope of an LR and approaches to complete it is a valuable effort, and the five steps represent a rational starting point. An institutional environment devoted to active learning will support students in continuously reflecting on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the writer and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ).
The completion of an LR is a challenging and necessary process for understanding one’s own field of expertise. Knowledge is always transitory, but our responsibility as scholars is to provide a critical contribution to our field, allowing others to think through our work. Good researchers are grounded in sophisticated LRs, which reveal a writer’s training and long-lasting academic skills. We recommend using the LR checklist as a tool for strengthening the skills necessary for critical academic writing.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Leite DFB has initially conceived the idea and has written the first draft of this review. Padilha MAS and Cecatti JG have supervised data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read the draft and agreed with this submission. Authors are responsible for all aspects of this academic piece.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all of the professors of the ‘Getting Started with Graduate Research and Generic Skills’ module at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, for suggesting and supporting this article. Funding: DFBL has granted scholarship from Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) to take part of her Ph.D. studies in Ireland (process number 88881.134512/2016-01). There is no participation from sponsors on authors’ decision to write or to submit this manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
1 The questions posed in systematic reviews usually follow the ‘PICOS’ acronym: Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Study design.
2 In 1988, Cooper proposed a taxonomy that aims to facilitate students’ and institutions’ understanding of literature reviews. Six characteristics with specific categories are briefly described: Focus: research outcomes, research methodologies, theories, or practices and applications; Goals: integration (generalization, conflict resolution, and linguistic bridge-building), criticism, or identification of central issues; Perspective: neutral representation or espousal of a position; Coverage: exhaustive, exhaustive with selective citations, representative, central or pivotal; Organization: historical, conceptual, or methodological; and Audience: specialized scholars, general scholars, practitioners or policymakers, or the general public.
Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Recent progress in non-lithium rechargeable batteries with micro to macro 3d engineered electrode architecture.
The increasing demand for flexible and wearable energy storage devices, particularly in the field of 3D printed macrobatteries and microbatteries necessitates extensive research worldwide. While lithium-based batteries have traditionally dominated on electronics market, recent challenges such as lithium scarcity and uneven distribution on earth’s surface have driven up the costs and created an alarming situation. Therefore, there is a critical need to shift focus towards the development of non-lithium-based technologies. This review underscores the urgency of advancing non-lithium-based low-cost technologies for 3D printed batteries, specially focusing on microbatteries. These microbatteries will play a pivotal role in on-board microelectronic applications, including but not limited to medical implants, hearing aids, wireless sensor networks, earbuds, wearable sensors, and IoT sensors. The freedom of electrode architectures provided by 3D printing enhances the potential for innovation in this field. Each section of this comprehensive review delves into the complex details of various non-lithium battery technologies, highlighting their unique materials and recent developments in components. By prioritizing the exploration and development of non-lithium alternatives, the scientific community can contribute to the creation of sustainable and cost-effective solutions for the ever-expanding landscape of microelectronic applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
A. Parida and S. Giri, J. Mater. Chem. A , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D4TA02146K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Speed Matters When Companies Respond to Social Issues
- Alison Wood Brooks,
- Maya Balakrishnan,
- Julian De Freitas

An analysis of Instagram posts by Fortune 500 companies after George Floyd’s murder found that customers were skeptical of those who waited too long to make a statement.
Companies and their leaders face new pressures to make public statements about controversial and sometimes divisive social and political issues. New research shows that timing matters: consumers perceive a relationship between speed and authenticity, and discount statements from companies that wait too long to respond. Leaders can use four questions to understand when and how they should shape their response.
In the wake of George Floyd’s killing by Minneapolis police officers in 2020, individuals began protesting racial injustice both in person and online. But it wasn’t just individuals — many well-known companies in corporate America seemed to publicly align themselves with protestors, rather than staying silent or neutral.
- Alison Wood Brooks is the O’Brien Associate Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School.
- JN Jimin Nam is a doctoral candidate in marketing at Harvard Business School.
- MB Maya Balakrishnan is a doctoral candidate in technology and operations management at Harvard Business School.
- Julian De Freitas is an assistant professor in the marketing unit at Harvard Business School.
Partner Center
- Research into trans medicine has been manipulated
Court documents offer a window into how this happens

Your browser does not support the <audio> element.
I N APRIL HILARY CASS , a British paediatrician, published her review of gender-identity services for children and young people, commissioned by NHS England. It cast doubt on the evidence base for youth gender medicine. This prompted the World Professional Association for Transgender Health ( WPATH ), the leading professional organisation for the doctors and practitioners who provide services to trans people, to release a blistering rejoinder. WPATH said that its own guidelines were sturdier, in part because they were “based on far more systematic reviews”.
Systematic reviews should evaluate the evidence for a given medical question in a careful, rigorous manner. Such efforts are particularly important at the moment, given the feverish state of the American debate on youth gender medicine, which is soon to culminate in a Supreme Court case challenging a ban in Tennessee. The case turns, in part, on questions of evidence and expert authority.
Court documents recently released as part of the discovery process in a case involving youth gender medicine in Alabama reveal that WPATH ’s claim was built on shaky foundations. The documents show that the organisation’s leaders interfered with the production of systematic reviews that it had commissioned from the Johns Hopkins University Evidence-Based Practice Centre ( EPC ) in 2018.
From early on in the contract negotiations, WPATH expressed a desire to control the results of the Hopkins team’s work. In December 2017, for example, Donna Kelly, an executive director at WPATH , told Karen Robinson, the EPC ’s director, that the WPATH board felt the EPC researchers “cannot publish their findings independently”. A couple of weeks later, Ms Kelly emphasised that, “the [ WPATH ] board wants it to be clear that the data cannot be used without WPATH approval”.
Ms Robinson saw this as an attempt to exert undue influence over what was supposed to be an independent process. John Ioannidis of Stanford University, who co-authored guidelines for systematic reviews, says that if sponsors interfere or are allowed to veto results, this can lead to either biased summaries or suppression of unfavourable evidence. Ms Robinson sought to avoid such an outcome. “In general, my understanding is that the university will not sign off on a contract that allows a sponsor to stop an academic publication,” she wrote to Ms Kelly.
Months later, with the issue still apparently unresolved, Ms Robinson adopted a sterner tone. She noted in an email in March 2018 that, “Hopkins as an academic institution, and I as a faculty member therein, will not sign something that limits academic freedom in this manner,” nor “language that goes against current standards in systematic reviews and in guideline development”.
Not to reason XY
Eventually WPATH relented, and in May 2018 Ms Robinson signed a contract granting WPATH power to review and offer feedback on her team’s work, but not to meddle in any substantive way. After wpath leaders saw two manuscripts submitted for review in July 2020, however, the parties’ disagreements flared up again. In August the WPATH executive committee wrote to Ms Robinson that WPATH had “many concerns” about these papers, and that it was implementing a new policy in which WPATH would have authority to influence the EPC team’s output—including the power to nip papers in the bud on the basis of their conclusions.
Ms Robinson protested that the new policy did not reflect the contract she had signed and violated basic principles of unfettered scientific inquiry she had emphasised repeatedly in her dealings with WPATH . The Hopkins team published only one paper after WPATH implemented its new policy: a 2021 meta-analysis on the effects of hormone therapy on transgender people. Among the recently released court documents is a WPATH checklist confirming that an individual from WPATH was involved “in the design, drafting of the article and final approval of [that] article”. (The article itself explicitly claims the opposite.) Now, more than six years after signing the agreement, the EPC team does not appear to have published anything else, despite having provided WPATH with the material for six systematic reviews, according to the documents.
No one at WPATH or Johns Hopkins has responded to multiple inquiries, so there are still gaps in this timeline. But an email in October 2020 from WPATH figures, including its incoming president at the time, Walter Bouman, to the working group on guidelines, made clear what sort of science WPATH did (and did not) want published. Research must be “thoroughly scrutinised and reviewed to ensure that publication does not negatively affect the provision of transgender health care in the broadest sense,” it stated. Mr Bouman and one other coauthor of that email have been named to a World Health Organisation advisory board tasked with developing best practices for transgender medicine.
Another document recently unsealed shows that Rachel Levine, a trans woman who is assistant secretary for health, succeeded in pressing wpath to remove minimum ages for the treatment of children from its 2022 standards of care. Dr Levine’s office has not commented. Questions remain unanswered, but none of this helps WPATH ’s claim to be an organisation that bases its recommendations on science. ■
Stay on top of American politics with The US in brief , our daily newsletter with fast analysis of the most important electoral stories, and Checks and Balance , a weekly note from our Lexington columnist that examines the state of American democracy and the issues that matter to voters.
Explore more
This article appeared in the United States section of the print edition under the headline “Marking their own homework”
United States June 29th 2024
- Young voters strongly favour Joe Biden, but will they turn out?
- True-crime fans are banding together online to try to solve cases
- Przekrój, an iconic Polish magazine, relaunches in America
- Non-white American parents are embracing AI faster than white ones
- What to make of the US Supreme Court’s latest abortion ruling
- In New York, the Democratic establishment strikes back

From the June 29th 2024 edition
Discover stories from this section and more in the list of contents
More from United States

Joe Biden’s ABC interview will not quell doubts about his future
Nor will it resolve the Democratic Party’s dilemma

Jill Biden; Defender-in-chief
What happens next in the Democratic leadership saga may depend on the First Lady

Will IVF really be the next frontier in America’s culture wars?
Banning it would be political suicide. But it could get harder to find in conservative states
What the Chevron ruling means for the next US president
The Supreme Court weakened regulators and created uncertainty, inviting a “tsunami of lawsuits”
The unsteady comeback of the California condor
The bird’s plight is a study in unintended consequences
The Supreme Court’s term ends with a rash of divisive rulings
Big decisions arrived on guns, abortion, homelessness, presidential power—and more

COMMENTS
2. Benefits of Review Articles to the Author. Analysing literature gives an overview of the "WHs": WHat has been reported in a particular field or topic, WHo the key writers are, WHat are the prevailing theories and hypotheses, WHat questions are being asked (and answered), and WHat methods and methodologies are appropriate and useful [].For new or aspiring researchers in a particular ...
A Review Article is a secondary source that summarizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic or research question. These articles provide an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic, including a critical analysis of the strengths and limitations of previous research.
The fundamental rationale of writing a review article is to make a readable synthesis of the best literature sources on an important research inquiry or a topic. This simple definition of a review article contains the following key elements: The question (s) to be dealt with.
3. Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.
A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer's knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits.
Finding Review and Research Papers in PubMed. Many databases have special features that allow the searcher to restrict results to articles that match specific criteria. In other words, only articles of a certain type will be displayed in the search results. These "limiters" can be useful when searching for research or review articles.
Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate; Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic. Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We've written a step-by-step ...
A well-written review article must summarize key research findings, reference must-read articles, describe current areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates, point out gaps in current knowledge, depict unanswered questions, and suggest directions for future research ( 1 ). During the last decades, there has been a great expansion ...
Many research disciplines feature high-impact journals that are dedicated outlets for review papers (or review-conceptual combinations) (e.g., Academy of Management Review, Psychology Bulletin, Medicinal Research Reviews).The rationale for such outlets is the premise that research integration and synthesis provides an important, and possibly even a required, step in the scientific process.
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
Differences Between Original Research Articles and Review Articles. An original research article aims to: Provides background information (Intro.) on prior research, Reasons for present study, Issues to be investigated by the present study, Written for experts.Authors describe: Research methods & materials, Data acquisition/analysis tools, Results, Discussion of results.
22 Sep 2016. By Elisabeth Pain. Share: A good peer review requires disciplinary expertise, a keen and critical eye, and a diplomatic and constructive approach. Credit: dmark/iStockphoto. As junior scientists develop their expertise and make names for themselves, they are increasingly likely to receive invitations to review research manuscripts.
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
A review article is a comprehensive summary of the current understanding of a specific research topic and is based on previously published research. Unlike research papers, it does not contain new results, but can propose new inferences based on the combined findings of previous research. Types of review articles
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating, and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings ...
Infographic: 5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper. There are different types of scholarly literature. Some of these require researchers to conduct an original study, whereas others can be based on previously published research. Understanding each of these types and also how they differ from one another can be rather ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Don't: Be discouraged if your outline keeps changing as you get further into the writing process. Writing and structuring your review should be iterative as you continue to refine, read more papers, and start to actually get words down on the page. Don't: Summarize the results and rehash the discussion of papers you are citing.
Tips To Write An Review Article Fast. Writing a review article quickly without sacrificing quality might seem like a tall order, but with the right approach, it's entirely achievable. Clearly Define Your Research Question. Clearly define your research question. A focused question not only narrows down the scope of your literature search but ...
Research articles follow a particular format. Look for: A brief introduction will often include a review of the existing literature on the topic studied, and explain the rationale of the author's study.; A methods section, where authors describe how they collected and analyzed data.Statistical analysis are included. A results section describes the outcomes of the data analysis.
Research Article Review. Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed ...
One could easily make the argument that literature review research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches; therefore, literature review research is a mixed method type of research. Methodological congruence refers to an analysis process that all those evaluating any study use. It is a determination of how the elements of the study (e ...
We answer how consumers review differently by developing three reviewing orientations: communal sharing, systemic evaluation, and competitive punditry. Finally, we discuss the transferability of the findings, the role of institutional dynamics in reviewing, and recommendations for online review platforms and marketers.
Science and research integrity has been facing a growing crisis. Mass retractions, manipulated peer review, authorship for sale, and complicit guest editors have shaken the publishing system and risk undermining public trust in the scientific record. Meanwhile, there have been huge advances in the development of generative artificial intelligence (AI).
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
The increasing demand for flexible and wearable energy storage devices, particularly in the field of 3D printed macrobatteries and microbatteries necessitates extensive research worldwide. While lithium-based batteries have traditionally dominated on electronics market, recent challenges such as lithium scar Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles
Companies and their leaders face new pressures to make public statements about controversial and sometimes divisive social and political issues. New research shows that timing matters: consumers ...
Research must be "thoroughly scrutinised and reviewed to ensure that publication does not negatively affect the provision of transgender health care in the broadest sense," it stated.