- How to Order
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example

Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Crafting a comprehensive research paper can be daunting. Understanding diverse citation styles and various subject areas presents a challenge for many.
Without clear examples, students often feel lost and overwhelmed, unsure of how to start or which style fits their subject.
Explore our collection of expertly written research paper examples. We’ve covered various citation styles and a diverse range of subjects.
So, read on!
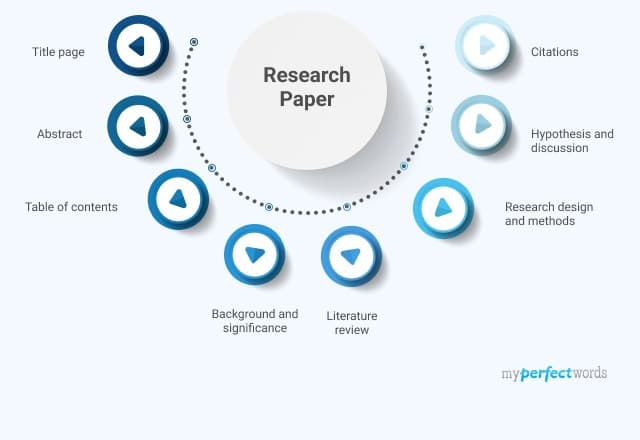
- 1. Research Paper Example for Different Formats
- 2. Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
- 3. Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
- 4. Research Paper Example Outline
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
Following a specific formatting style is essential while writing a research paper . Knowing the conventions and guidelines for each format can help you in creating a perfect paper. Here we have gathered examples of research paper for most commonly applied citation styles :
Social Media and Social Media Marketing: A Literature Review
APA Research Paper Example
APA (American Psychological Association) style is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, and education. This format is recognized for its clear and concise writing, emphasis on proper citations, and orderly presentation of ideas.
Here are some research paper examples in APA style:
Research Paper Example APA 7th Edition
Research Paper Example MLA
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is frequently employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. An MLA research paper might explore literature analysis, linguistic studies, or historical research within the humanities.
Here is an example:
Found Voices: Carl Sagan
Research Paper Example Chicago
Chicago style is utilized in various fields like history, arts, and social sciences. Research papers in Chicago style could delve into historical events, artistic analyses, or social science inquiries.
Here is a research paper formatted in Chicago style:
Chicago Research Paper Sample
Research Paper Example Harvard
Harvard style is widely used in business, management, and some social sciences. Research papers in Harvard style might address business strategies, case studies, or social policies.
View this sample Harvard style paper here:
Harvard Research Paper Sample
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper has different parts. Each part is important for the overall success of the paper. Chapters in a research paper must be written correctly, using a certain format and structure.
The following are examples of how different sections of the research paper can be written.
Research Proposal
The research proposal acts as a detailed plan or roadmap for your study, outlining the focus of your research and its significance. It's essential as it not only guides your research but also persuades others about the value of your study.
Example of Research Proposal
An abstract serves as a concise overview of your entire research paper. It provides a quick insight into the main elements of your study. It summarizes your research's purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions in a brief format.
Research Paper Example Abstract
Literature Review
A literature review summarizes the existing research on your study's topic, showcasing what has already been explored. This section adds credibility to your own research by analyzing and summarizing prior studies related to your topic.
Literature Review Research Paper Example
Methodology
The methodology section functions as a detailed explanation of how you conducted your research. This part covers the tools, techniques, and steps used to collect and analyze data for your study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper
The conclusion summarizes your findings, their significance and the impact of your research. This section outlines the key takeaways and the broader implications of your study's results.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
Research papers can be about any subject that needs a detailed study. The following examples show research papers for different subjects.
History Research Paper Sample
Preparing a history research paper involves investigating and presenting information about past events. This may include exploring perspectives, analyzing sources, and constructing a narrative that explains the significance of historical events.
View this history research paper sample:
Many Faces of Generalissimo Fransisco Franco
Sociology Research Paper Sample
In sociology research, statistics and data are harnessed to explore societal issues within a particular region or group. These findings are thoroughly analyzed to gain an understanding of the structure and dynamics present within these communities.
Here is a sample:
A Descriptive Statistical Analysis within the State of Virginia
Science Fair Research Paper Sample
A science research paper involves explaining a scientific experiment or project. It includes outlining the purpose, procedures, observations, and results of the experiment in a clear, logical manner.
Here are some examples:
Science Fair Paper Format
What Do I Need To Do For The Science Fair?
Psychology Research Paper Sample
Writing a psychology research paper involves studying human behavior and mental processes. This process includes conducting experiments, gathering data, and analyzing results to understand the human mind, emotions, and behavior.
Here is an example psychology paper:
The Effects of Food Deprivation on Concentration and Perseverance
Art History Research Paper Sample
Studying art history includes examining artworks, understanding their historical context, and learning about the artists. This helps analyze and interpret how art has evolved over various periods and regions.
Check out this sample paper analyzing European art and impacts:
European Art History: A Primer
Research Paper Example Outline
Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper.
Here is an outline of a research paper example:
|
Here is a downloadable sample of a standard research paper outline:
Research Paper Outline
Want to create the perfect outline for your paper? Check out this in-depth guide on creating a research paper outline for a structured paper!
Good Research Paper Examples for Students
Here are some more samples of research paper for students to learn from:
Fiscal Research Center - Action Plan
Qualitative Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example Introduction
How to Write a Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example for High School
Now that you have explored the research paper examples, you can start working on your research project. Hopefully, these examples will help you understand the writing process for a research paper.
If you're facing challenges with your writing requirements, you can hire our essay writing help online.
Our team is experienced in delivering perfectly formatted, 100% original research papers. So, whether you need help with a part of research or an entire paper, our experts are here to deliver.
So, why miss out? Place your ‘ write my research paper ’ request today and get a top-quality research paper!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
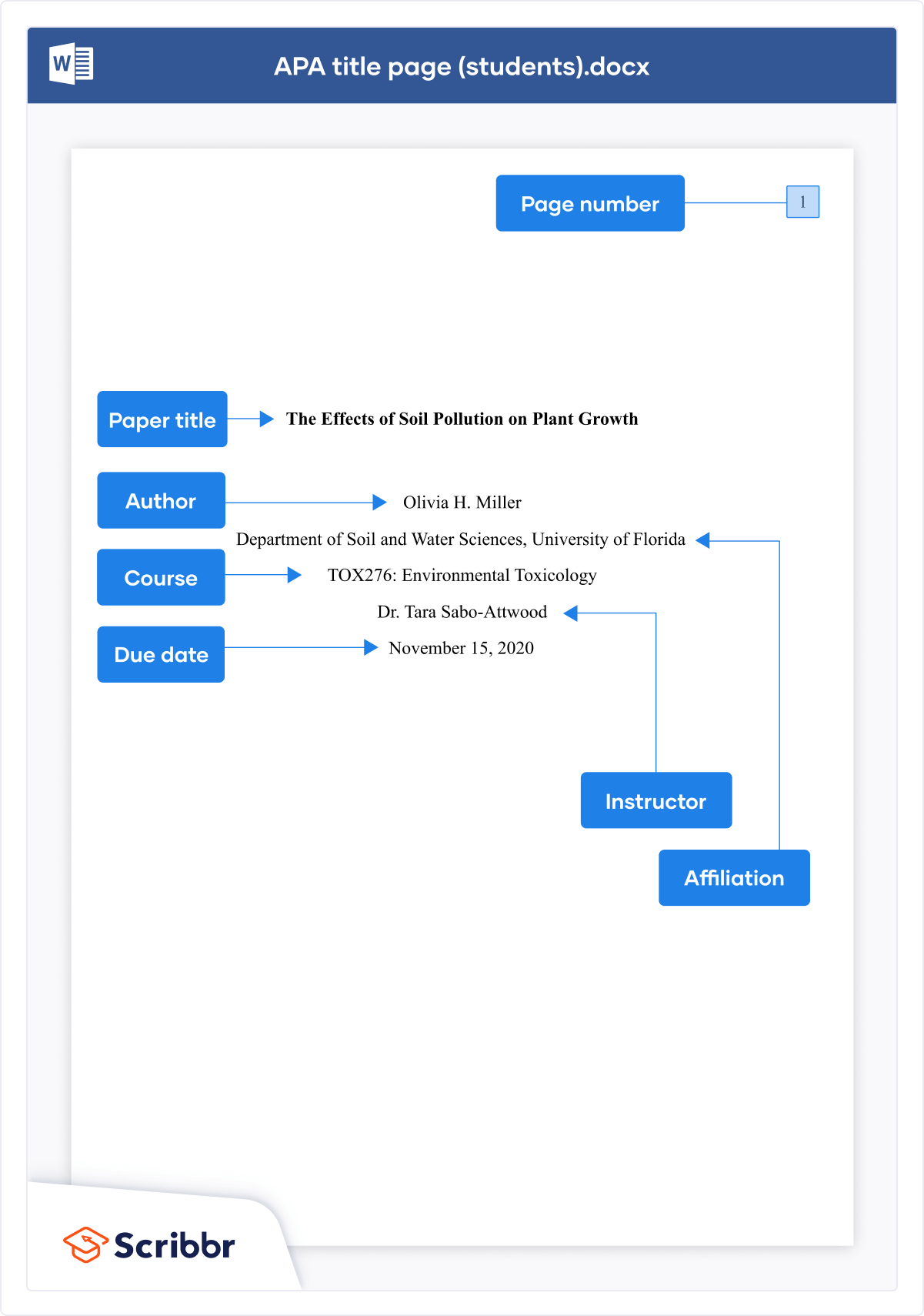
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
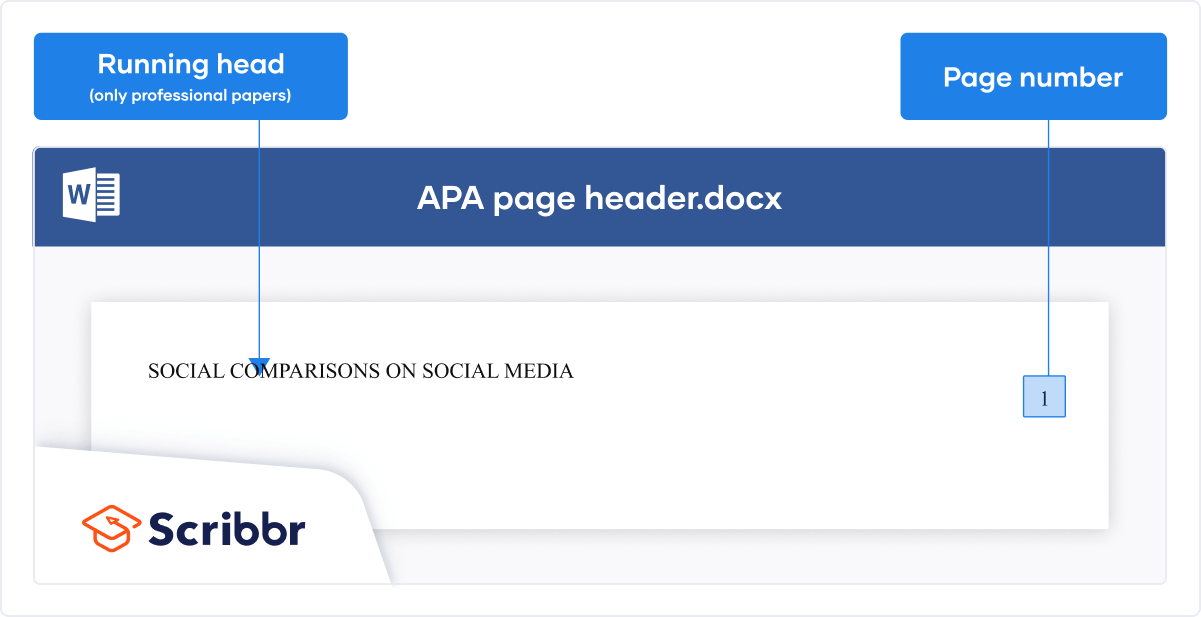
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
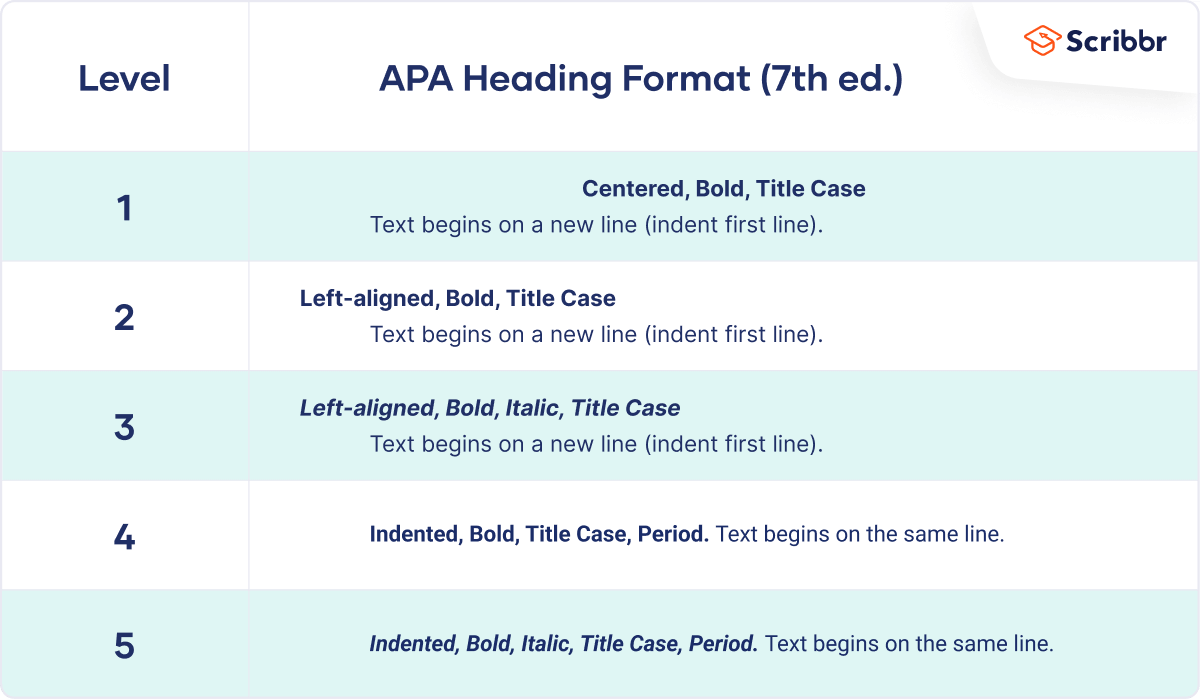
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
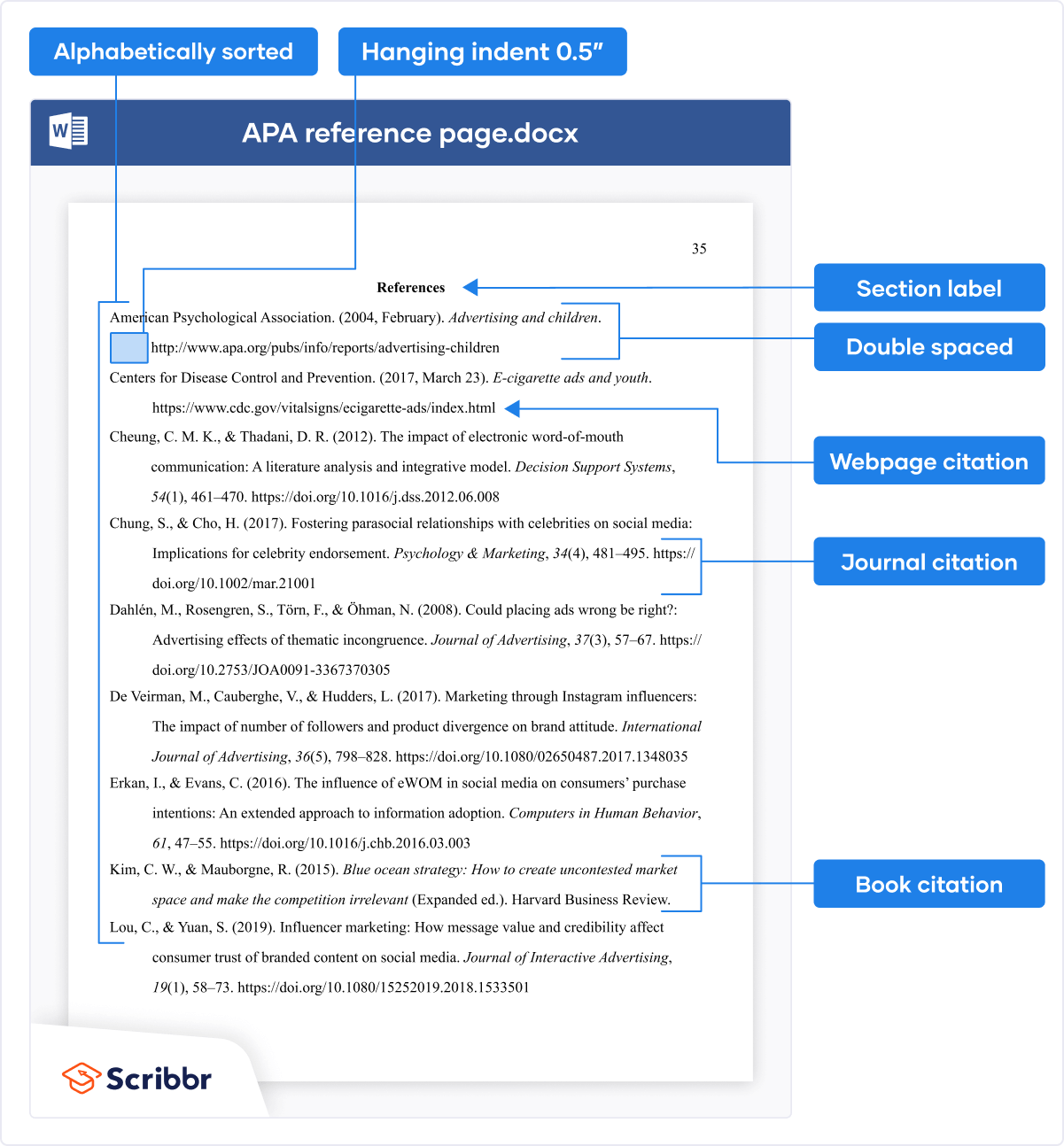
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
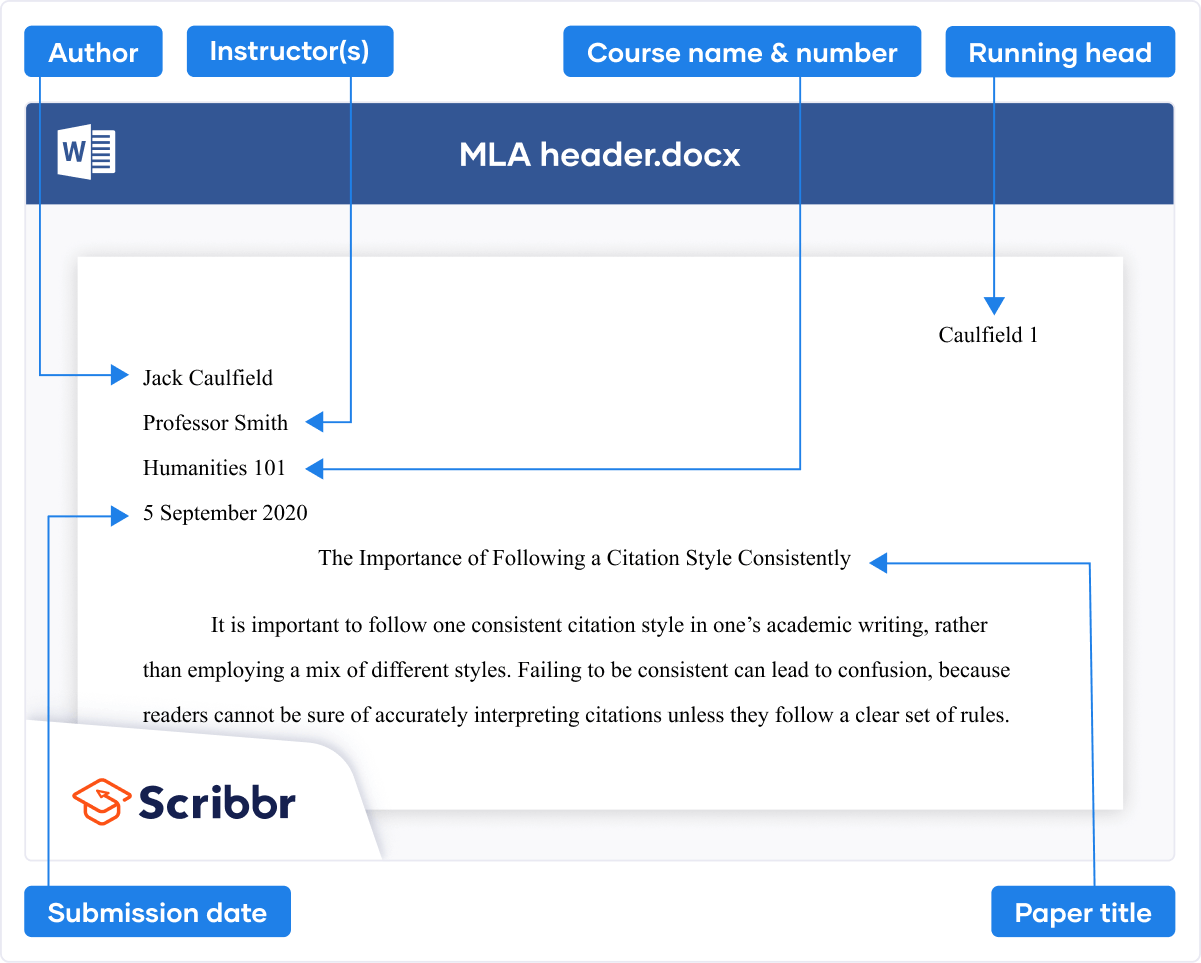
Page header
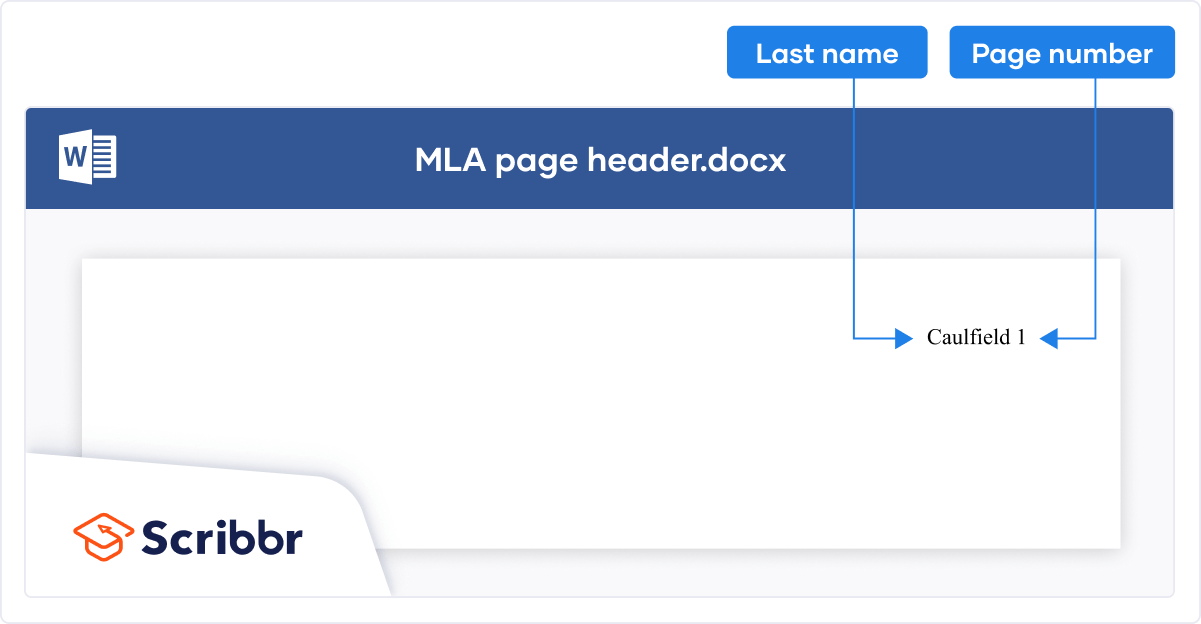
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
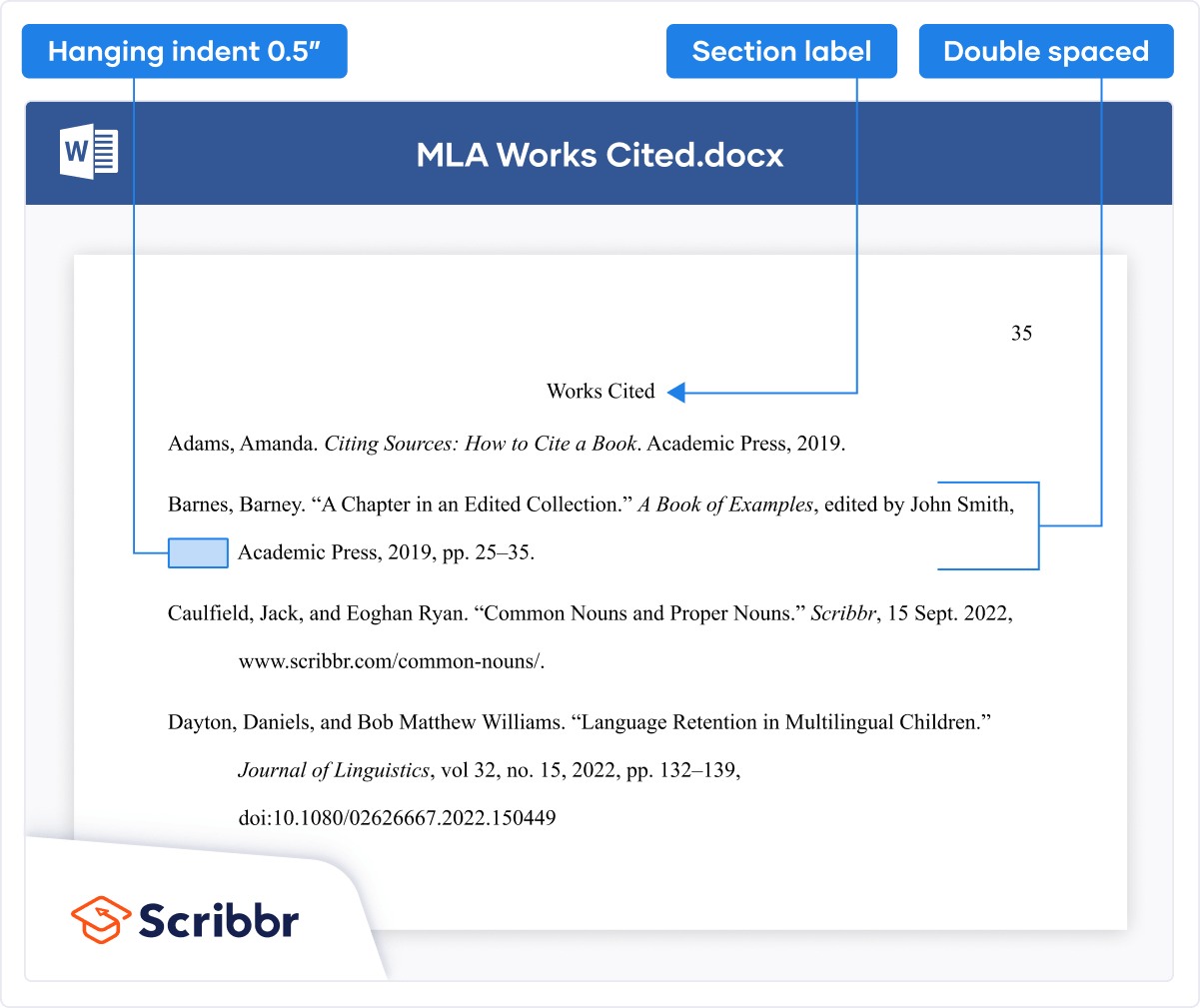
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
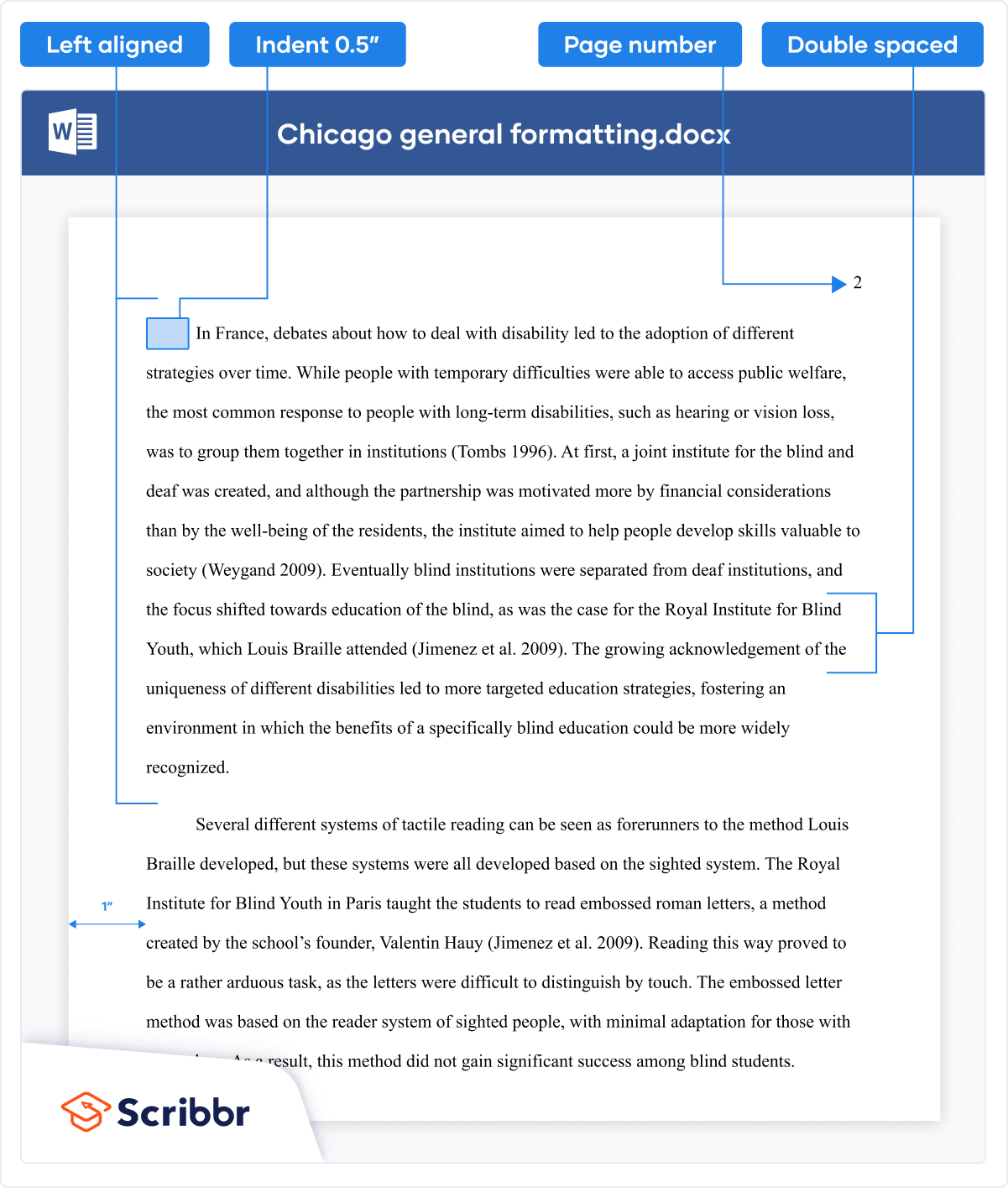
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
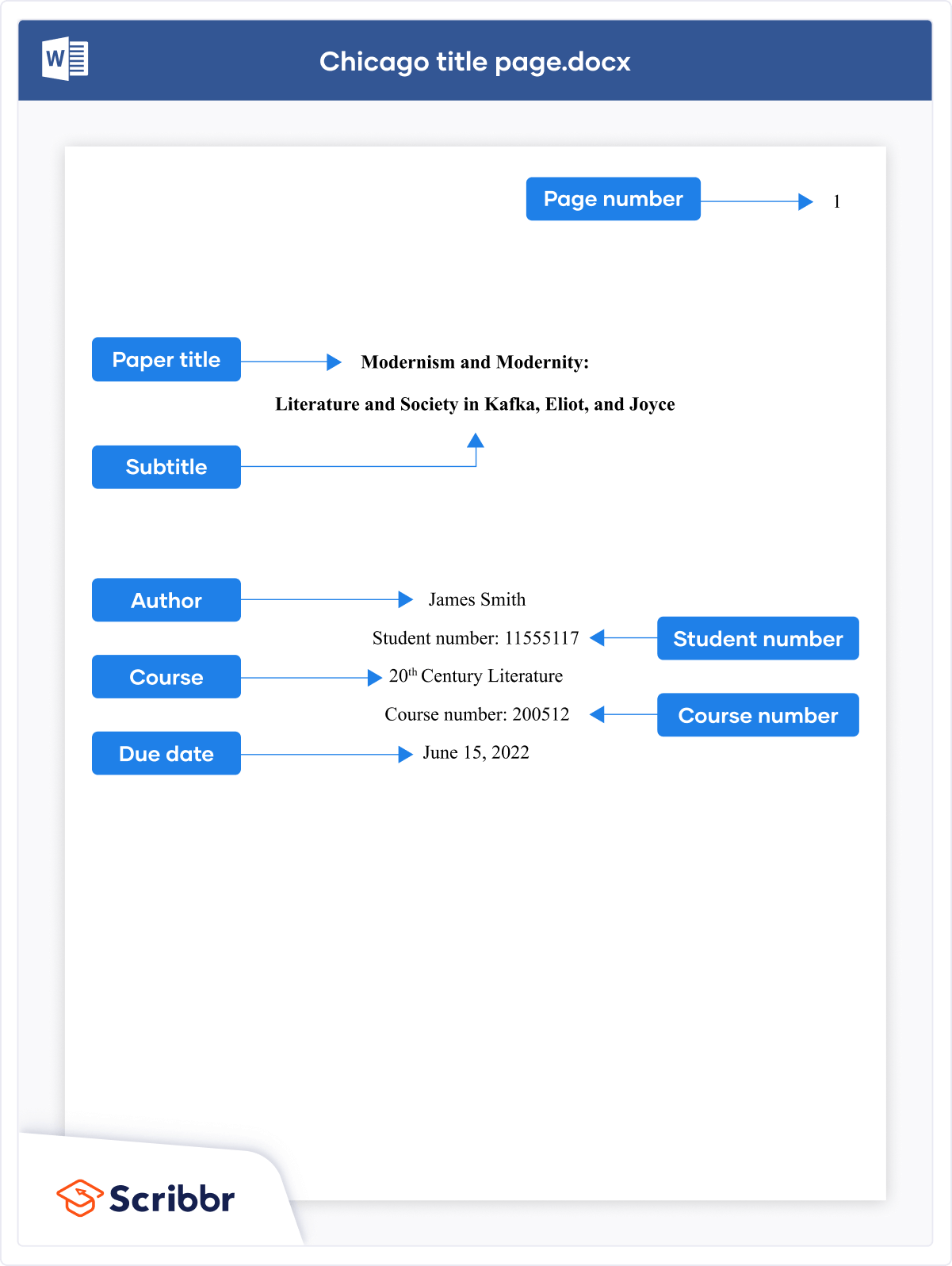
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
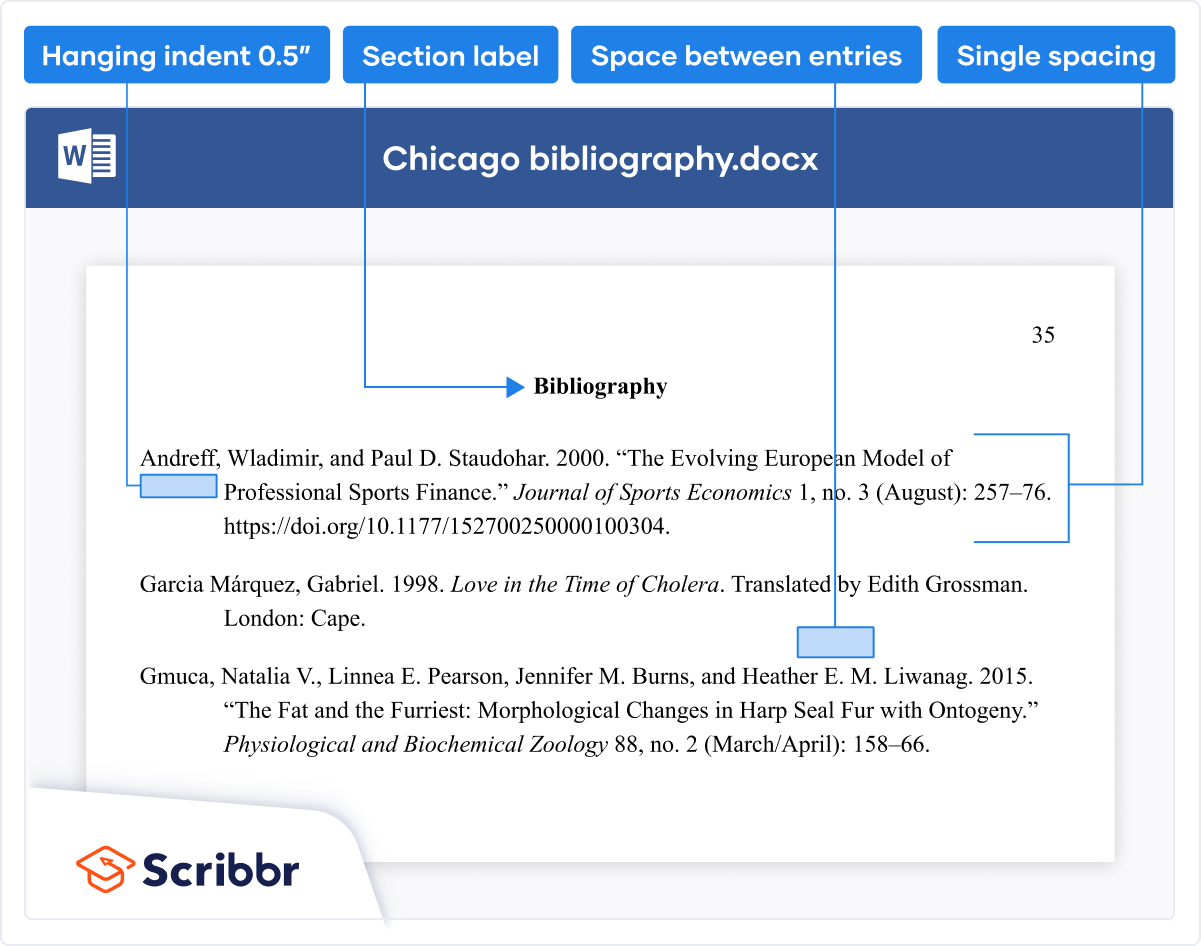
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example
Last updated on: Nov 20, 2023
Research Paper Example: Samples to Write a Research Paper
By: Nathan D.
Reviewed By: Jacklyn H.
Published on: Jun 11, 2019

Working on your research paper?
Want to learn the dos and don’ts of writing a research paper? Learn from examples!
We have compiled some examples to help you get started. If you are in need of a research paper example, take a look at these samples and choose one that is best suited for your research paper writing needs.
You can also use these as templates to create your own research papers. There are many different samples available here so please feel free to browse around and find the perfect one for yourself.
Stay with us to learn more.

On this Page
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is different from a usual kind of essay and assignment. It requires more research and explanation than any other assignment and has a set structure for it. It is a complex type of academic paper. Usually, students studying science write them for their coursework and as a degree requirement.
It is generally simpler than high school term papers and a dissertation that students write in humanities and other academic groups. Research papers are common in the academic world, and students, regardless of the field of study, get them as part of their degree requirements.
The research writing skills are invaluable for everyone and not just for the students only. Young professionals and entrepreneurs benefit a lot from these skills. Writing a research paper properly means that you have to study, observe, and choose a topic. The step-by-step guide for writing a research paper will help you find answers to your research questions.

Get Quick AI Research Help!
College Research Paper Example
Examples work great when you are looking to learn something in less time and with more efficiency. Below, we have added some good research paper examples. With them, you could learn about a research paper format and structure.
Moreover, we will also be able to add relevant and credible sources in each section.
APA Style Research Paper
Below is an APA-style sample research paper guide. Each section is explained separately. By going through it, you will know how to format and write each section of your APA research paper successfully.
APA STYLE RESEARCH PAPER
MLA Style Research Paper
This MLA-style research paper explains all the sections and formatting of the paper in detail. This will help you in writing an MLA-style paper successfully.
MLA STYLE RESEARCH PAPER
Subject-Related Research Paper Example
Research papers are not limited to a specific field area. Instead, students need to write research papers for almost every subject. Check out the following research paper examples for several subjects.
Computer Science Research Paper
The research paper is about computer science and how science is a part of it. Scientific research papers are different from what the students do in other disciplines. They are more statistical in nature and often have graphs and visual representations of the data.
COMPUTER SCIENCE RESEARCH PAPER
Chemical Engineering Research Paper
Chemical engineering studies the engineering of different chemicals and how they work together. The following chemical engineering research paper is about the calcium looping cycle for carbon dioxide obtained from different manufacturing processes.
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH PAPER
Nursing Research Paper
The research paper explores the benefits of participating in research. Medical sciences heavily rely on real-life research and results, and therefore, it uses medical professionals as subjects. The paper discusses how the experience contributes to their professional life and helps them work better.
NURSING RESEARCH PAPER
Psychology Research Paper
Psychology is the study of the mind. The paper examines the positive effects of psychology at school. It discusses how it will help in controlling the mental illnesses in adolescents and help in enhancing their health.
PSYCHOLOGY RESEARCH PAPER

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Research Paper Outline Example
A research paper’s outline may consist of different formats and sections based on the research topic. Therefore, you must ask your instructor to go through the research content and guide you.
Before starting to write a research paper, you will need to write and submit a research proposal. A research proposal includes the details of your proposed research, the significance of the research, the impact your research will have on the area of research, and the methodology that you will use. For writing a research proposal , you need to discuss all of these factors.
A research paper follows a set pattern and structure. Just like an essay or any other assignment, it also has some sections that you have to include in it. However, before formatting, make sure that you follow the referencing style that your teacher has provided.
The main research paper outline is given below. Pay attention to the document to get a detailed idea of the writing process.
RESEARCH PAPER OUTLINE EXAMPLE
This outline includes the following sections:
An abstract is usually written after the entire paper. It explains the research question and the expected outcome of the research.
Here, we have added an abstract example to help you see how to write an engaging abstract in no time.
RESEARCH PAPER ABSTRACT EXAMPLE
Introduction
It is the first section of the research. It gives a background of the research, explains the main research topic briefly, and presents the hypothesis.
A strong introduction is essential for a strong research paper because no one will read the paper if the introduction is lousy and weak. Go through the attached example to learn how to write a good research paper example.
RESEARCH PAPER INTRODUCTION EXAMPLE
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement presents the main topic and aim of the research. It is brief and based on a few lines only.
The following downloadable PDF has some great thesis statement examples that are engaging and help to convey the message powerfully.
RESEARCH PAPER THESIS EXAMPLE
This is the meatiest part of the research paper. It includes all the chapters and sections of the research.
The main body of the paper discusses the entire paper in detail. All the main points and arguments of the paper are added in this section. Learn how to add and discuss everything by going through the following downloadable PDF.
EXAMPLE OF DISCUSSION IN RESEARCH PAPER
Literature Review
It is added in the main body section. It includes the study of previous relevant studies and research and discusses their outcome. You will discuss your main topic and draw parallels and contrasts with these existing studies.
EXAMPLE OF A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A RESEARCH PAPER
Research Methodology
Discuss the type of research that you are going to use for the research. Usually, scientific research is based on quantitative research and includes statistical analysis. Theoretical research uses qualitative method and includes studying of theory and other research.
EXAMPLE OF METHODOLOGY IN RESEARCH PAPER
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
This is the closing part of your research paper as you will conclude your research here. Mention your thesis statement and main research findings here and close it.
The conclusion does not mean that you have a chance to add some new ideas or points here; it would be a disaster. To know better, go through the following PDF.
RESEARCH PAPER CONCLUSION EXAMPLE
An appendix is an optional section in the research paper. It contains terms and topics that are too detailed to be added to the main text. It also states the topics and page number, which makes it easier to find relevant topics.
APPENDICES EXAMPLE IN RESEARCH PAPER
Now you must have explored different examples of a research paper. You can generate more examples according to your field of study by using our FREE AI powered paper typer .
However, if you are still wondering how to write it perfectly, consult the best write essay for me? service now.
5StarEssays.com offers high-quality and affordable research paper writing help. Place your order now to get your scientific research paper, or any other type of paper, written by experts.

Education, Literature
Nathan completed his Ph.D. in journalism and has been writing articles for well-respected publications for many years now. His work is carefully researched and insightful, showing a true passion for the written word. Nathan's clients appreciate his expertise, deep understanding of the process, and ability to communicate difficult concepts clearly.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write a Research Paper - Writing Guide & Examples

- 20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Research Papers

- Learn How to Write an Abstract - Steps & Examples

- How to Write a Literature Review: Steps and Outline

- How to Start a Research Paper - 9 Simple Steps

- Psychology Research Topics - 170+ Ideas for Your Paper

- How to Write a Hypothesis - A Step-by-Step Guide

- Writing a Research Proposal - Outline, Format, and Examples

- Good Research Paper Topics & Ideas for Students

- Good History Research Paper Topics For Your Help

- How to Cite a Research Paper with the Help of Examples

- How to Write a Research Methodology in 10 Simple Steps

- Research Paper Outline - Basic Format & Sample

- Great Sociology Research Topics & Ideas (2024)

People Also Read
- article review
- expository essay outline
- narrative essay examples
- writing personal statement
- writing research proposal
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved

APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.) for Student Papers
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Powerpoint Presentations
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 2:22 PM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Example

Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
Published on: Jun 12, 2021
Last updated on: Feb 6, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
Writing a research paper is the most challenging task in a student's academic life. researchers face similar writing process hardships, whether the research paper is to be written for graduate or masters.
A research paper is a writing type in which a detailed analysis, interpretation, and evaluation are made on the topic. It requires not only time but also effort and skills to be drafted correctly.
If you are working on your research paper for the first time, here is a collection of examples that you will need to understand the paper’s format and how its different parts are drafted. Continue reading the article to get free research paper examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
A research paper typically consists of several key parts, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and annotated bibliography .
When writing a research paper (whether quantitative research or qualitative research ), it is essential to know which format to use to structure your content. Depending on the requirements of the institution, there are mainly four format styles in which a writer drafts a research paper:
Letâs look into each format in detail to understand the fundamental differences and similarities.
Research Paper Example APA
If your instructor asks you to provide a research paper in an APA format, go through the example given below and understand the basic structure. Make sure to follow the format throughout the paper.
APA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example MLA
Another widespread research paper format is MLA. A few institutes require this format style as well for your research paper. Look at the example provided of this format style to learn the basics.
MLA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Chicago
Unlike MLA and APA styles, Chicago is not very common. Very few institutions require this formatting style research paper, but it is essential to learn it. Look at the example given below to understand the formatting of the content and citations in the research paper.
Chicago Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Harvard
Learn how a research paper through Harvard formatting style is written through this example. Carefully examine how the cover page and other pages are structured.
Harvard Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper is based on different parts. Each part plays a significant role in the overall success of the paper. So each chapter of the paper must be drafted correctly according to a format and structure.
Below are examples of how different sections of the research paper are drafted.
Research Proposal Example
A research proposal is a plan that describes what you will investigate, its significance, and how you will conduct the study.
Research Proposal Sample (PDF)
Abstract Research Paper Example
An abstract is an executive summary of the research paper that includes the purpose of the research, the design of the study, and significant research findings.
It is a small section that is based on a few paragraphs. Following is an example of the abstract to help you draft yours professionally.
Abstract Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Literature Review Research Paper Example
A literature review in a research paper is a comprehensive summary of the previous research on your topic. It studies sources like books, articles, journals, and papers on the relevant research problem to form the basis of the new research.
Writing this section of the research paper perfectly is as important as any part of it.
Literature Review in Research Sample (PDF)
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
The method section comes after the introduction of the research paper that presents the process of collecting data. Basically, in this section, a researcher presents the details of how your research was conducted.
Methods Section in Research Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Conclusion Example
The conclusion is the last part of your research paper that sums up the writerâs discussion for the audience and leaves an impression. This is how it should be drafted:
Research Paper Conclusion Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
The research papers are not limited to a particular field. They can be written for any discipline or subject that needs a detailed study.
In the following section, various research paper examples are given to show how they are drafted for different subjects.
Science Research Paper Example
Are you a science student that has to conduct research? Here is an example for you to draft a compelling research paper for the field of science.
Science Research Paper Sample (PDF)
History Research Paper Example
Conducting research and drafting a paper is not only bound to science subjects. Other subjects like history and arts require a research paper to be written as well. Observe how research papers related to history are drafted.
History Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Psychology Research Paper Example
If you are a psychology student, look into the example provided in the research paper to help you draft yours professionally.
Psychology Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for Different Levels
Writing a research paper is based on a list of elements. If the writer is not aware of the basic elements, the process of writing the paper will become daunting. Start writing your research paper taking the following steps:
- Choose a topic
- Form a strong thesis statement
- Conduct research
- Develop a research paper outline
Once you have a plan in your hand, the actual writing procedure will become a piece of cake for you.
No matter which level you are writing a research paper for, it has to be well structured and written to guarantee you better grades.
If you are a college or a high school student, the examples in the following section will be of great help.
Research Paper Outline (PDF)
Research Paper Example for College
Pay attention to the research paper example provided below. If you are a college student, this sample will help you understand how a winning paper is written.
College Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for High School
Expert writers of CollegeEssay.org have provided an excellent example of a research paper for high school students. If you are struggling to draft an exceptional paper, go through the example provided.
High School Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples are essential when it comes to academic assignments. If you are a student and aim to achieve good grades in your assignments, it is suggested to get help from CollegeEssay.org .
We are the best writing company that delivers essay help for students by providing free samples and writing assistance.
Professional writers have your back, whether you are looking for guidance in writing a lab report, college essay, or research paper.
Simply hire a writer by placing your order at the most reasonable price. You can also take advantage of our essay writer to enhance your writing skills.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
Example of a Research Paper
What follows is a hypothetical example of a research paper based on an experiment.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
- Example of a Paper 2
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
The experiment: Say you have just conducted the Milgram Study . Now you want to write the research paper for it. (Milgram actually waited two years before writing about his study.)
Here's a shortened example of a research article that MIGHT have been written.
DISCLAIMER: This article is not written by Stanley Milgram, but is intended as an example of a psychology research paper that someone might have written after conducting the first Milgram-study. It's presented here for educational purposes.
Normally you would use double spacing in the paper.
EXAMPLE OF A RESEARCH PAPER

--- START OF EXAMPLE ---
[Page 1 - text aligned in the center and middle of the page]
"Behavioral Study of Obedience"
by [author], [University]
[Page 2 - text starts at the top, left]
There are few facts about the role of obedience when committing acts against one’s personal conscience (1961). Most theories suggest that only very disturbed people are capable of administering pain to an ordinary citizen if they are ordered to do so. Our experiment tested people's obedience to authority. The results showed that most obey all orders given by the authority-figure, despite their unwillingness. The conclusion is that, contrary to common belief, personal ethics mean little when pitted against authority.
[Page 3-X - text starts in the top, left corner, no extra spacing to align text]
Current theories focus on personal characteristics to explain wrong-doing and how someone can intentionally harm others. In a survey, professionals such as doctors, psychologist and laymen predicted that a small proportion of a population (1-3%) would harm others if ordered to do so. In the recent war trial with Adolph Eichmann, he claims to only have been “following orders". The author wanted to test this claim. Can people harm others because they are merely obeying orders? Can people be ordered to act against their moral convictions? The experiment will test whether a person can keep administering painful electric shocks to another person just because they are ordered to do so. The expectation is that very few will keep giving shocks, and that most participants will disobey the order.
Participants There were 30 male participants. They were recruited by advertisement in a newspaper and were paid $4.50. Instruments A "shock generator" was used to trick the participants into thinking that they were giving an electric shock to another person in another room. The shock generator had switches labeled with different voltages, starting at 30 volts and increasing in 15-volt increments all the way up to 450 volts. The switches were also labeled with terms which reminded the participant of how dangerous the shocks were. Procedures The participant met another "participant" in the waiting room before the experiment. The other "participant" was an actor. Each participant got the role as a "teacher" who would then deliver a shock to the actor ("learner") every time an incorrect answer to a question was produced. The participant believed that he was delivering real shocks to the learner. The learner would pretend to be shocked. As the experiment progressed, the teacher would hear the learner plead to be released and complain about a heart condition. Once the 300-volt level had been reached, the learner banged on the wall and demanded to be released. Beyond this point, the learner became completely silent and refused to answer any more questions. The experimenter then instructed the participant to treat this silence as an incorrect response and deliver a further shock. When asking the experimenter if they should stop, they were instructed to continue.
Of the 40 participants in the study, 26 delivered the maximum shocks. 14 persons did not obey the experimenter and stopped before reaching the highest levels. All 40 participants continued to give shocks up to 300 volts.
Discussion/Conclusion
Most of the participants became very agitated, stressed and angry at the experimenter. Many continued to follow orders throughout even though they were clearly uncomfortable. The study shows that people are able to harm others intentionally if ordered to do so. It provides evidence that this dynamic is far more important than previously believed, and that personal ethics are less predictive of such behavior.
[Read more about references here]

--- END OF EXAMPLE ---
The scientific format: a research paper outline:.
Title , Author, Work/School
Abstract : A short summary of the article.
Current theories about the topic. What are the hypothesis for the paper?
What method used.
What were the results obtained?
Discussion and Conclusion
What are our thought about the results compared to other relevant theories.
Through the text there are references, sources of knowledge, which you've used. Citing those will give you more credibility because good research is thought to be based on other knowledge and empirical (observed) evidence .
Tables , Figures , Appendix
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (May 21, 2008). Example of a Research Paper. Retrieved Jul 12, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/example-of-a-research-paper
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to write a high-quality conference paper, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the....
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Paper
Last Updated: February 18, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,193,550 times.
Whether you’re in a history, literature, or science class, you’ll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you’re just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process a breeze. Research your topic, find reliable sources, and come up with a working thesis. Then create an outline and start drafting your paper. Be sure to leave plenty of time to make revisions, as editing is essential if you want to hand in your best work!
Sample Research Papers and Outlines

Researching Your Topic

- For instance, you might start with a general subject, like British decorative arts. Then, as you read, you home in on transferware and pottery. Ultimately, you focus on 1 potter in the 1780s who invented a way to mass-produce patterned tableware.
Tip: If you need to analyze a piece of literature, your task is to pull the work apart into literary elements and explain how the author uses those parts to make their point.

- Authoritative, credible sources include scholarly articles (especially those other authors reference), government websites, scientific studies, and reputable news bureaus. Additionally, check your sources' dates, and make sure the information you gather is up to date.
- Evaluate how other scholars have approached your topic. Identify authoritative sources or works that are accepted as the most important accounts of the subject matter. Additionally, look for debates among scholars, and ask yourself who presents the strongest evidence for their case. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- You’ll most likely need to include a bibliography or works cited page, so keep your sources organized. List your sources, format them according to your assigned style guide (such as MLA or Chicago ), and write 2 or 3 summary sentences below each one. [4] X Research source

- Imagine you’re a lawyer in a trial and are presenting a case to a jury. Think of your readers as the jurors; your opening statement is your thesis and you’ll present evidence to the jury to make your case.
- A thesis should be specific rather than vague, such as: “Josiah Spode’s improved formula for bone china enabled the mass production of transfer-printed wares, which expanded the global market for British pottery.”
Drafting Your Essay

- Your outline is your paper’s skeleton. After making the outline, all you’ll need to do is fill in the details.
- For easy reference, include your sources where they fit into your outline, like this: III. Spode vs. Wedgewood on Mass Production A. Spode: Perfected chemical formula with aims for fast production and distribution (Travis, 2002, 43) B. Wedgewood: Courted high-priced luxury market; lower emphasis on mass production (Himmelweit, 2001, 71) C. Therefore: Wedgewood, unlike Spode, delayed the expansion of the pottery market.

- For instance, your opening line could be, “Overlooked in the present, manufacturers of British pottery in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries played crucial roles in England’s Industrial Revolution.”
- After presenting your thesis, lay out your evidence, like this: “An examination of Spode’s innovative production and distribution techniques will demonstrate the importance of his contributions to the industry and Industrial Revolution at large.”
Tip: Some people prefer to write the introduction first and use it to structure the rest of the paper. However, others like to write the body, then fill in the introduction. Do whichever seems natural to you. If you write the intro first, keep in mind you can tweak it later to reflect your finished paper’s layout.

- After setting the context, you'd include a section on Josiah Spode’s company and what he did to make pottery easier to manufacture and distribute.
- Next, discuss how targeting middle class consumers increased demand and expanded the pottery industry globally.
- Then, you could explain how Spode differed from competitors like Wedgewood, who continued to court aristocratic consumers instead of expanding the market to the middle class.
- The right number of sections or paragraphs depends on your assignment. In general, shoot for 3 to 5, but check your prompt for your assigned length.

- If you bring up a counterargument, make sure it’s a strong claim that’s worth entertaining instead of ones that's weak and easily dismissed.
- Suppose, for instance, you’re arguing for the benefits of adding fluoride to toothpaste and city water. You could bring up a study that suggested fluoride produced harmful health effects, then explain how its testing methods were flawed.

- Sum up your argument, but don’t simply rewrite your introduction using slightly different wording. To make your conclusion more memorable, you could also connect your thesis to a broader topic or theme to make it more relatable to your reader.
- For example, if you’ve discussed the role of nationalism in World War I, you could conclude by mentioning nationalism’s reemergence in contemporary foreign affairs.
Revising Your Paper

- This is also a great opportunity to make sure your paper fulfills the parameters of the assignment and answers the prompt!
- It’s a good idea to put your essay aside for a few hours (or overnight, if you have time). That way, you can start editing it with fresh eyes.
Tip: Try to give yourself at least 2 or 3 days to revise your paper. It may be tempting to simply give your paper a quick read and use the spell-checker to make edits. However, revising your paper properly is more in-depth.

- The passive voice, such as “The door was opened by me,” feels hesitant and wordy. On the other hand, the active voice, or “I opened the door,” feels strong and concise.
- Each word in your paper should do a specific job. Try to avoid including extra words just to fill up blank space on a page or sound fancy.
- For instance, “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is better than “The author utilizes pathos to make an appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”

- Read your essay out loud to help ensure you catch every error. As you read, check for flow as well and, if necessary, tweak any spots that sound awkward. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- It’s wise to get feedback from one person who’s familiar with your topic and another who’s not. The person who knows about the topic can help ensure you’ve nailed all the details. The person who’s unfamiliar with the topic can help make sure your writing is clear and easy to understand.
Community Q&A
- Remember that your topic and thesis should be as specific as possible. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0
- Researching, outlining, drafting, and revising are all important steps, so do your best to budget your time wisely. Try to avoid waiting until the last minute to write your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evaluating-print-sources/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/research_overview/index.html
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/writing/graduate-writing-lab/writing-through-graduate-school/working-sources
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-5-putting-the-pieces-together-with-a-thesis-statement/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/developing_an_outline/index.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/counterarguments
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/formandstyle/writing/scholarlyvoice/activepassive
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/index.html
About This Article

To write a research paper, start by researching your topic at the library, online, or using an academic database. As you conduct your research and take notes, zero in on a specific topic that you want to write about and create a 1-2 sentence thesis to state the focus of your paper. Then, create an outline that includes an introduction, 3 to 5 body paragraphs to present your arguments, and a conclusion to sum up your main points. Once you have your paper's structure organized, draft your paragraphs, focusing on 1 argument per paragraph. Use the information you found through your research to back up your claims and prove your thesis statement. Finally, proofread and revise your content until it's polished and ready to submit. For more information on researching and citing sources, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Private And Discrete
Aug 2, 2020
Did this article help you?
Jan 3, 2018
Oct 29, 2016
Maronicha Lyles
Jul 24, 2016
Maxwell Ansah
Nov 22, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings . The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing , and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall presentation and coherence. Adhering to the appropriate research paper format is vital for ensuring that the research is accurately and effectively communicated to the intended audience. In this era of information, it is essential to understand the different research paper formats and their guidelines to communicate research effectively, accurately, and with the required level of detail. This post aims to provide an overview of some of the common research paper formats used in academic writing.
Research Paper Formats
Research Paper Formats are as follows:
- APA (American Psychological Association) format
- MLA (Modern Language Association) format
- Chicago/Turabian style
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format
- AMA (American Medical Association) style
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- ACS (American Chemical Society) style
- ASA (American Sociological Association) style
- APSA (American Political Science Association) style
APA (American Psychological Association) Format
Here is a general APA format for a research paper:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your institutional affiliation. It should also include a running head, which is a shortened version of the title, and a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, typically 150-250 words. It should include the purpose of your research, the main findings, and any implications or conclusions that can be drawn.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on your topic, state the purpose of your research, and present your research question or hypothesis. It should also include a brief literature review that discusses previous research on your topic.
- Methods: The methods section should describe the procedures you used to collect and analyze your data. It should include information on the participants, the materials and instruments used, and the statistical analyses performed.
- Results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and concise manner. Use tables and figures to help illustrate your results.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret your results and relate them back to your research question or hypothesis. It should also discuss the implications of your findings and any limitations of your study.
- References : The references section should include a list of all sources cited in your paper. Follow APA formatting guidelines for your citations and references.
Some additional tips for formatting your APA research paper:
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font throughout the paper.
- Double-space all text, including the references.
- Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use a hanging indent for the references (the first line should be flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines should be indented).
- Number all pages, including the title page and references page, in the upper right-hand corner.
APA Research Paper Format Template
APA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Institutional affiliation
- A brief summary of the main points of the paper, including the research question, methods, findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be no more than 250 words.
Introduction:
- Background information on the topic of the research paper
- Research question or hypothesis
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the research methods and design
- Brief summary of the main findings
- Participants: description of the sample population, including the number of participants and their characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.)
- Materials: description of any materials used in the study (e.g., survey questions, experimental apparatus)
- Procedure: detailed description of the steps taken to conduct the study
- Presentation of the findings of the study, including statistical analyses if applicable
- Tables and figures may be included to illustrate the results
Discussion:
- Interpretation of the results in light of the research question and hypothesis
- Implications of the study for the field
- Limitations of the study
- Suggestions for future research
References:
- A list of all sources cited in the paper, in APA format
Formatting guidelines:
- Double-spaced
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Page numbers in the top right corner
- Headings and subheadings should be used to organize the paper
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented
- Quotations of 40 or more words should be set off in a block quote with no quotation marks
- In-text citations should include the author’s last name and year of publication (e.g., Smith, 2019)
APA Research Paper Format Example
APA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
University of XYZ
This study examines the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Data was collected through a survey of 500 students at the University of XYZ. Results suggest that social media use is significantly related to symptoms of depression and anxiety, and that the negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users.
Social media has become an increasingly important aspect of modern life, especially among young adults. While social media can have many positive effects, such as connecting people across distances and sharing information, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This study aims to examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students.
Participants: Participants were 500 college students at the University of XYZ, recruited through online advertisements and flyers posted on campus. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 25, with a mean age of 20.5 years. The sample was 60% female, 40% male, and 5% identified as non-binary or gender non-conforming.
Data was collected through an online survey administered through Qualtrics. The survey consisted of several measures, including the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression symptoms, the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) for anxiety symptoms, and questions about social media use.
Procedure :
Participants were asked to complete the online survey at their convenience. The survey took approximately 20-30 minutes to complete. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis.
Results indicated that social media use was significantly related to symptoms of depression (r = .32, p < .001) and anxiety (r = .29, p < .001). Regression analysis indicated that frequency of social media use was a significant predictor of both depression symptoms (β = .24, p < .001) and anxiety symptoms (β = .20, p < .001), even when controlling for age, gender, and other relevant factors.
The results of this study suggest that social media use is associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety among college students. The negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users. These findings have important implications for mental health professionals and educators, who should consider addressing the potential negative effects of social media use in their work with young adults.
References :
References should be listed in alphabetical order according to the author’s last name. For example:
- Chou, H. T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(2), 117-121.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Note: This is just a sample Example do not use this in your assignment.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format is as follows:
- Page Layout : Use 8.5 x 11-inch white paper, with 1-inch margins on all sides. The font should be 12-point Times New Roman or a similar serif font.
- Heading and Title : The first page of your research paper should include a heading and a title. The heading should include your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date. The title should be centered and in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- In-Text Citations : Use parenthetical citations to indicate the source of your information. The citation should include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source. For example: (Smith 23).
- Works Cited Page : At the end of your paper, include a Works Cited page that lists all the sources you used in your research. Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the medium of publication.
- Formatting Quotations : Use double quotation marks for short quotations and block quotations for longer quotations. Indent the entire quotation five spaces from the left margin.
- Formatting the Body : Use a clear and readable font and double-space your text throughout. The first line of each paragraph should be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
MLA Research Paper Template
MLA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
- Use 8.5 x 11 inch white paper.
- Use a 12-point font, such as Times New Roman.
- Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper, including the title page and works cited page.
- Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Use page numbers in the upper right corner, beginning with the first page of text.
- Include a centered title for the research paper, using title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- Include your name, instructor’s name, course name, and date in the upper left corner, double-spaced.
In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing information from sources, include an in-text citation within the text of your paper.
- Use the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence, before the punctuation mark.
- If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only include the page number in parentheses.
Works Cited Page
- List all sources cited in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
- Each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and medium of publication.
- Use italics for book and journal titles, and quotation marks for article and chapter titles.
- For online sources, include the date of access and the URL.
Here is an example of how the first page of a research paper in MLA format should look:
Headings and Subheadings
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your paper and make it easier to read.
- Use numerals to number your headings and subheadings (e.g. 1, 2, 3), and capitalize the first letter of each word.
- The main heading should be centered and in boldface type, while subheadings should be left-aligned and in italics.
- Use only one space after each period or punctuation mark.
- Use quotation marks to indicate direct quotes from a source.
- If the quote is more than four lines, format it as a block quote, indented one inch from the left margin and without quotation marks.
- Use ellipses (…) to indicate omitted words from a quote, and brackets ([…]) to indicate added words.
Works Cited Examples
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
- Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, publication date, page numbers.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website, publication date, URL. Accessed date.
Here is an example of how a works cited entry for a book should look:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing Research Papers. Penguin, 2021.
MLA Research Paper Example
MLA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
Your Professor’s Name
Course Name and Number
Date (in Day Month Year format)
Word Count (not including title page or Works Cited)
Title: The Impact of Video Games on Aggression Levels
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment among people of all ages. However, the impact of video games on aggression levels has been a subject of debate among scholars and researchers. While some argue that video games promote aggression and violent behavior, others argue that there is no clear link between video games and aggression levels. This research paper aims to explore the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults.
Background:
The debate on the impact of video games on aggression levels has been ongoing for several years. According to the American Psychological Association, exposure to violent media, including video games, can increase aggression levels in children and adolescents. However, some researchers argue that there is no clear evidence to support this claim. Several studies have been conducted to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels, but the results have been mixed.
Methodology:
This research paper used a quantitative research approach to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults. A sample of 100 young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 was selected for the study. The participants were asked to complete a questionnaire that measured their aggression levels and their video game habits.
The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between video game habits and aggression levels among young adults. The participants who reported playing violent video games for more than 5 hours per week had higher aggression levels than those who played less than 5 hours per week. The study also found that male participants were more likely to play violent video games and had higher aggression levels than female participants.
The findings of this study support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to note that the study only examined the impact of video games on aggression levels and did not take into account other factors that may contribute to aggressive behavior. It is also important to note that not all video games promote violence and aggression, and some games may have a positive impact on cognitive and social skills.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, this research paper provides evidence to support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to conduct further research to examine the impact of video games on other aspects of behavior and to explore the potential benefits of video games. Parents and educators should be aware of the potential impact of video games on aggression levels and should encourage young adults to engage in a variety of activities that promote cognitive and social skills.
Works Cited:
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Violent Video Games: Myths, Facts, and Unanswered Questions. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2017/08/violent-video-games
- Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do Angry Birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(5), 646-666.
- Gentile, D. A., Swing, E. L., Lim, C. G., & Khoo, A. (2012). Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1(1), 62-70.
- Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106(4), 530-548.
Chicago/Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian Formate is as follows:
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Font : Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size.
- Page numbering : Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner, beginning with the first page of text. Use Arabic numerals.
- Title page: Include a title page with the title of the paper, your name, course title and number, instructor’s name, and the date. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
- Headings: Use headings to organize your paper. The first level of headings should be centered and in boldface or italics. The second level of headings should be left-aligned and in boldface or italics. Use as many levels of headings as necessary to organize your paper.
- In-text citations : Use footnotes or endnotes to cite sources within the text of your paper. The first citation for each source should be a full citation, and subsequent citations can be shortened. Use superscript numbers to indicate footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Include a bibliography at the end of your paper, listing all sources cited in your paper. The bibliography should be in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, and each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date of publication.
- Formatting of quotations: Use block quotations for quotations that are longer than four lines. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin, and do not use quotation marks. Single-space the quotation, and double-space between paragraphs.
- Tables and figures: Use tables and figures to present data and illustrations. Number each table and figure sequentially, and provide a brief title for each. Place tables and figures as close as possible to the text that refers to them.
- Spelling and grammar : Use correct spelling and grammar throughout your paper. Proofread carefully for errors.
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template is as folows:
Title of Paper
Name of Student
Professor’s Name
I. Introduction
A. Background Information
B. Research Question
C. Thesis Statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of Existing Literature
B. Analysis of Key Literature
C. Identification of Gaps in Literature
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Presentation of Findings
B. Analysis of Findings
C. Discussion of Implications
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Implications for Future Research
C. Conclusion
VI. References
A. Bibliography
B. In-Text Citations
VII. Appendices (if necessary)
A. Data Tables
C. Additional Supporting Materials
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Example
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Political Engagement
Name: John Smith
Class: POLS 101
Professor: Dr. Jane Doe
Date: April 8, 2023
I. Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with friends and family, share their opinions, and stay informed about current events. With the rise of social media, there has been a growing interest in understanding its impact on various aspects of society, including political engagement. In this paper, I will examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, specifically focusing on how social media influences political participation and political attitudes.
II. Literature Review:
There is a growing body of literature on the impact of social media on political engagement. Some scholars argue that social media has a positive effect on political participation by providing new channels for political communication and mobilization (Delli Carpini & Keeter, 1996; Putnam, 2000). Others, however, suggest that social media can have a negative impact on political engagement by creating filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue (Pariser, 2011; Sunstein, 2001).
III. Methodology:
To examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, I conducted a survey of 500 college students. The survey included questions about social media use, political participation, and political attitudes. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Iv. Results:
The results of the survey indicate that social media use is positively associated with political participation. Specifically, respondents who reported using social media to discuss politics were more likely to have participated in a political campaign, attended a political rally, or contacted a political representative. Additionally, social media use was found to be associated with more positive attitudes towards political engagement, such as increased trust in government and belief in the effectiveness of political action.
V. Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that social media has a positive impact on political engagement, by providing new opportunities for political communication and mobilization. However, there is also a need for caution, as social media can also create filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between social media and political engagement, and develop strategies to harness the potential benefits of social media while mitigating its potential negative effects.
Vii. References:
- Delli Carpini, M. X., & Keeter, S. (1996). What Americans know about politics and why it matters. Yale University Press.
- Pariser, E. (2011). The filter bubble: What the Internet is hiding from you. Penguin.
- Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon & Schuster.
- Sunstein, C. R. (2001). Republic.com. Princeton University Press.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Format
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Research Paper Format is as follows:
- Title : A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the paper.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the paper, typically no more than 250 words, that includes the purpose of the study, the methods used, the key findings, and the main conclusions.
- Introduction : An overview of the background, context, and motivation for the research, including a clear statement of the problem being addressed and the objectives of the study.
- Literature review: A critical analysis of the relevant research and scholarship on the topic, including a discussion of any gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Methodology : A detailed description of the methods used to collect and analyze data, including any experiments or simulations, data collection instruments or procedures, and statistical analyses.
- Results : A clear and concise presentation of the findings, including any relevant tables, graphs, or figures.
- Discussion : A detailed interpretation of the results, including a comparison of the findings with previous research, a discussion of the implications of the results, and any recommendations for future research.
- Conclusion : A summary of the key findings and main conclusions of the study.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to IEEE guidelines.
In addition to these elements, an IEEE research paper should also follow certain formatting guidelines, including using 12-point font, double-spaced text, and numbered headings and subheadings. Additionally, any tables, figures, or equations should be clearly labeled and referenced in the text.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) Style Research Paper Format:
- Title Page: This page includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any acknowledgments or disclaimers.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the paper that outlines the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. It is typically limited to 250 words or less.
- Introduction: The introduction provides a background of the research problem, defines the research question, and outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
- Methods: The methods section describes the research design, participants, procedures, and instruments used to collect and analyze data.
- Results: The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and charts where appropriate.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, explains their significance, and relates them to previous research in the field.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points of the paper, discusses the implications of the findings, and suggests future research directions.
- References: The reference list includes all sources cited in the paper, listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name.
In addition to these sections, the AMA format requires that authors follow specific guidelines for citing sources in the text and formatting their references. The AMA style uses a superscript number system for in-text citations and provides specific formats for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites.
Harvard Style
Harvard Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should outline the main points of your research and highlight your findings.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your research topic, provide background information, and outline your research question or thesis statement.
- Literature review: This section should review the relevant literature on your topic, including previous research studies, academic articles, and other sources.
- Methodology : This section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including any data collection methods, research instruments, and sampling techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids if necessary.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and relate them to the broader research question or thesis statement. You should also discuss the implications of your research and suggest areas for future study.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and provide a final statement on the significance of your research.
- References : This is a list of all the sources you cited in your paper, presented in alphabetical order by author name. Each citation should include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, and other relevant information.
In addition to these sections, a Harvard Style research paper may also include a table of contents, appendices, and other supplementary materials as needed. It is important to follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or academic institution when preparing your research paper in Harvard Style.
Vancouver Style
Vancouver Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The Vancouver citation style is commonly used in the biomedical sciences and is known for its use of numbered references. Here is a basic format for a research paper using the Vancouver citation style:
- Title page: Include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your research paper, usually no more than 250 words.
- Introduction : Provide some background information on your topic and state the purpose of your research.
- Methods : Describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including the study design, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables and figures as needed.
- Discussion : Interpret your results and explain their significance. Also, discuss any limitations of your study and suggest directions for future research.
- References : List all of the sources you cited in your paper in numerical order. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the article or book, the name of the journal or publisher, the year of publication, and the page numbers.
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The American Chemical Society (ACS) Style is a citation style commonly used in chemistry and related fields. When formatting a research paper in ACS Style, here are some guidelines to follow:
- Paper Size and Margins : Use standard 8.5″ x 11″ paper with 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Font: Use a 12-point serif font (such as Times New Roman) for the main text. The title should be in bold and a larger font size.
- Title Page : The title page should include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the date of submission. The title should be centered on the page and written in bold font. The authors’ names should be centered below the title, followed by their affiliations and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract should be a brief summary of the paper, no more than 250 words. It should be on a separate page and include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the text of the abstract.
- Main Text : The main text should be organized into sections with headings that clearly indicate the content of each section. The introduction should provide background information and state the research question or hypothesis. The methods section should describe the procedures used in the study. The results section should present the findings of the study, and the discussion section should interpret the results and provide conclusions.
- References: Use the ACS Style guide to format the references cited in the paper. In-text citations should be numbered sequentially throughout the text and listed in numerical order at the end of the paper.
- Figures and Tables: Figures and tables should be numbered sequentially and referenced in the text. Each should have a descriptive caption that explains its content. Figures should be submitted in a high-quality electronic format.
- Supporting Information: Additional information such as data, graphs, and videos may be included as supporting information. This should be included in a separate file and referenced in the main text.
- Acknowledgments : Acknowledge any funding sources or individuals who contributed to the research.
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page of an ASA style research paper should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, and the institutional affiliation. The title should be centered and should be in title case (the first letter of each major word should be capitalized).
- Abstract: An abstract is a brief summary of the paper that should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page. The abstract should be no more than 200 words in length and should summarize the main points of the paper.
- Main Body: The main body of the paper should begin on a new page following the abstract page. The paper should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins on all sides, and should be written in 12-point Times New Roman font. The main body of the paper should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology section, results, and a discussion.
- References : The reference section should appear on a separate page at the end of the paper. All sources cited in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the date of publication.
- Appendices : Appendices are optional and should only be included if they contain information that is relevant to the study but too lengthy to be included in the main body of the paper. If you include appendices, each one should be labeled with a letter (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) and should be referenced in the main body of the paper.
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the name of the course or instructor, and the date.
- Abstract : An abstract is typically not required in APSA style papers, but if one is included, it should be brief and summarize the main points of the paper.
- Introduction : The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the research question, and the main argument or thesis of the paper.
- Literature Review : The literature review should summarize the existing research on the topic and provide a context for the research question.
- Methods : The methods section should describe the research methods used in the paper, including data collection and analysis.
- Results : The results section should present the findings of the research.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret the results and connect them back to the research question and argument.
- Conclusion : The conclusion should summarize the main findings and implications of the research.
- References : The reference list should include all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to APSA style guidelines.
In-text citations in APSA style use parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) if applicable. For example, (Smith 2010, 25).
About the author

Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide...
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Find top study documents
Top 300+ Ideas For Research Paper Topics in 2024
Updated 05 Jul 2024

Some say the most difficult part of writing a text – is to start. But topic selection even precedes this starting point. This activity takes off a lot of time, and sometimes, imagination just doesn’t work in your favor. That’s where our list of best research paper topics will be useful.
Our research paper writing service collected the most unhacked and powerful ideas to turn the average piece of writing into a research paper. Discover what is a research paper and how to choose suitable and interesting research topics with our help.
Writing a research topic on your own requires either producing one from scratch (based on your interests and goals and potentially, on some brainstorming) or getting inspiration from a number of sources, like preassembled topic lists, course material, teachers, real life, news headlines, published research in the respective field, etc.
What are the 3 Types of Research Questions?
Before formulating your research questions ideas, note that there are 3 important types of research questions:
- Descriptive – these employ careful and comprehensive observation of a phenomenon/ event, subject, trait, etc. in order to characterize it in detail and to reveal important/ interesting/ undescribed aspects or patterns potentially.
- Causal – these investigate whether altering some variables leads to changes in other variables, suggesting a causal relationship.
- Comparative – these look into similarities and differences between two or more entities
What is a Good Research Paper Topic?
Features that tend to characterize good research questions are as follows:
- specific and concrete – investigation goals and (expected results) have to be clear and focused
- original – investigating aspects/ entities/ relationships that have not been researched before
- highly important/ impactful for community/ society/ a professional field.
- highly relevant for potential readers/ reviewers
- trending – emerging disciplines/ topics spark more interest due to their novelty and yet unexplored potential
College Research Paper Topics
- The bias in the selection of the college internships and scholarships
- The problems of reverse discrimination in post-college employment
- Should multicultural education concepts be implemented at a greater depth?
- The drug and alcohol abuse on college campuses
- Does social media help students to find appropriate information and learn?
- The psychological disorders and the support groups in modern colleges
- Should people with ADHD and Autism be separated from the other students?
- The art of college political campaigns
- Pros and cons of religious colleges
- Should college athletes be paid and provided with additional advantages?
- The Influence of Social Media on College Students' Academic Performance and Well-being
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms in Higher Education
- The Role of College Education in Fostering Entrepreneurial Skills
- The Impact of Student Loan Debt on Career Choices Among Graduates
- Analyzing the Shift in College Admissions Criteria in the Post-COVID Era
Health Research Paper Topics
- The challenges of deafness and communication difficulties among special needs students
- The concept of global health security
- The ways to decrease household air pollution
- How the information about infectious diseases is distributed online
- Should people be allowed to know more about climate change issues?
- The privacy factor and the personal health issues
- The role of fitness ads in exercising practices
- The healthy food standards are not always unbiased
- The role of social media in the medical care system
- The psychological aspect in the perception of allergies
- The Long-term Effects of COVID-19 on Respiratory Health
- Mental Health Outcomes of Prolonged Social Media Use Among Adolescents
- The Efficacy of Plant-based Diets in Preventing Chronic Diseases
- The Role of Telemedicine in Improving Accessibility to Healthcare
- Analyzing the Impact of Sleep Quality on Daily Cognitive Functioning
Research Paper Topics on Medicine
- Is life-sustaining therapy needed when it’s futile?
- The role of placebo treatment
- How to avoid animal testing?
- Pros and contras of medical marijuana
- Is being a vegetarian useful for child’s health?
- How obesity affects our health?
- Vaccines for kids: their usefulness or damage
- Should prescription drugs be advertised directly to consumers?
- Do doctors turn their patients into drug addicts?
- Advancements in Gene Editing: Ethical Implications and Future Prospects
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Medicine
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Drug Therapies to Genetic Profiles
- The Impact of Microbiome Diversity on Human Health
- Stem Cell Therapy: Current Applications and Ethical Considerations
- The Challenges and Successes of Vaccine Development in the 21st Century
Need more writing assistance?
Connect with our top writers and receive writing sample crafted to your needs.
Education Research Paper Topics
- How can standardized tests improve education?
- Does college graduates make more money?
- Should education be cheaper?
- How will modern technologies change the way of teaching in the future?
- The creation of particular learning methods for blind children
- Social networking and school
- Metal detectors at schools
- The effects of contemporary teaching methods
- The role of technology in lesson planning
- How to manage bullies and take actions against bullying at education institutions?
- The Effects of Bilingual Education on Cognitive Development in Children
- Evaluating the Long-term Impact of Early Childhood Education Programs
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Special Education
- Standardized Testing: Measuring Intelligence or Memorization?
- The Influence of Teacher-Student Relationships on Academic Achievement
Read also: 150+ Best Sociology Research Topics
Environmental Research Paper Topics
- How to reduce global warming?
- How to stop wasting paper and save trees?
- Can overpopulation be managed?
- Should more films about environmental issues be produced?
- Human impacts on forests
- Underground effects of earthquakes
- How to elaborate the optimal adaptation of buildings threatened by hurricanes?
- Is it possible to predict hurricane impacts?
- Is nuclear power safe for humans?
- How dangerous is GMO food?
- Assessing the Impact of Urban Sprawl on Local Ecosystems
- The Effectiveness of Plastic Ban Policies on Ocean Health
- Carbon Capture Technology: Viability and Potential in Mitigating Climate Change
- The Role of Indigenous Knowledge in Biodiversity Conservation
- Analyzing the Environmental Consequences of Fast Fashion
Research Topics on Entertainment and Sport
- Are social networks good for our society?
- Do violent video games make kids angry and cruel?
- Is it necessary to forbid using animals for entertainment?
- Do beauty contests set the non-achievable beauty standards?
- Are newspapers going to be replaced by online sources of information?
- How gaming consoles influence the youth?
- Should women be allowed to compete against men?
- What television programs should be banned?
- How tv shows impose fake moral standards?
- Can the use of social media, such as Facebook, lower teens’ self-esteem?
- The Psychological Impact of Competitive Sports on Young Athletes
- The Influence of Celebrity Endorsements on Consumer Behavior
- E-Sports: The Rise of Competitive Gaming and Its Recognition as a Legitimate Sport
- The Role of Sports in Promoting Intercultural Dialogue and Understanding
- The Economic Impact of Major Sporting Events on Host Cities
Research Paper Topics on Media and Communication
- Should the media programming of ads aimed at children be made illegal?
- The role of mediation in the media
- Should bloggers be considered as journalists?
- The ethical side of modern news reports
- The freedom of speech online
- The copyright law restrictions and the vague concepts
- The importance of psychology and communicative skills in journalism
- The role of gender in interpersonal communication
- The modern standards of nonverbal communication
- The negative influence of Instagram and body image distortion
- The Evolution of News Consumption: Impact of Social Media on Traditional Media
- The Role of Media in Shaping Public Opinion During Political Campaigns
- The Ethics of Surveillance and Privacy in Digital Communication
- The Effects of Smartphone Usage on Face-to-Face Communication Skills
- Virtual Reality: The Future of Immersive Journalism
Research Paper Topics on Politics
- Should the drinking age be lowered?
- Should adults have the right to carry a concealed handgun?
- More gun control laws should be enacted
- How can the international community prevent Iran from developing nuclear weapons?
- How can ethnic killings be stopped?
- Current prospect for peace between Israel and the Palestinians
- What world would be like without wars?
- How to avoid workforce reduction?
- Should the death penalty be allowed?
- Is socialism possible?
- The Influence of Social Media on Political Mobilization and Public Protests
- Campaign Finance Reform: The Effects on Political Representation and Elections
- The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) in Shaping Global Policy
- The Impact of Populism on Traditional Political Party Systems
- Cybersecurity in Elections: Protecting the Integrity of Democracy
Psychology Research Paper Topics
- Is autism a disease or a development idiosyncrasy?
- How to forecast and shape behavioral patterns?
- How to manage child violence?
- How to deal with a mental breakdown?
- The impact of classical music on the work of the brain
- How insomnia affects our health?
- How bad dreams influence our mood?
- Is stress really harmful?
- How depression impacts the immune system?
- Intellectually gifted people: how is it possible?
- The Psychological Effects of Social Isolation in the Digital Age
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs. Mindfulness: Comparative Outcomes in Treating Anxiety
- The Role of Resilience in Recovery from Trauma
- The Impact of Parenting Styles on Child Personality Development
- Neuroplasticity: How Learning and Experience Shape Brain Function
Get plagiarism-free papers in just 3 hours
- Zero AI - 100% human-crafted content
- Tailored to your writing style
- Sourced from the latest, reliable sources
Guaranteed Turnitin success ✌️
Science & Technology Research Paper Ideas
- How is light being used to treat cancer and other diseases?
- What is the current evidence that Mars has had water and maybe life?
- Can nanomedicine potentially extend the human lifespan?
- What is the future of computing and artificial intelligence?
- The role cryogenics may play in future
- Can alternative energy effectively replace fossil fuels?
- Is it beneficial for wild animals to have interactions with people?
- What evidence do we have that CMB is the result of the big bang?
- How will self-driving cars change the way people live?
- Can using system like bitcoin help protect identity theft?
- The Potential of CRISPR and Gene Therapy in Curing Genetic Diseases
- Nanotechnology in Medicine: The Next Frontier for Drug Delivery Systems
- The Role of Quantum Computing in the Future of Cybersecurity
- The Ethical Implications of Humanoid Robots in Society
- Renewable Energy Technologies: Assessing the Efficiency and Sustainability of Solar Power Solutions
Research Topics Ideas on Culture
- A new comprehension of past events
- The origin of racial discrimination
- The roots of antisemitism
- The impact of advertisements and commercials on modern art
- The most remarkable cultural achievements of the 20th century and their influence on our society
- Cultural revolutions throughout history
- How pop culture trends influence youth?
- Should pregnant celebrities be exposed on magazine’s covers?
- Why was Greek cultural influence so important for the ancient Mediterranean world?
- Why was the Victorian period a time of cultural change?
- Cultural Impact on Climate Change Response: A Comparative Study
- The Preservation of Folklore and Oral Traditions in the Digital Age
- Cross-Cultural Communication: Overcoming Language and Ethical Barriers
- The Influence of Globalization on Indigenous Cultures
- Cultural Diplomacy and Its Role in International Relations
Research Paper Topics on Math
- The influence of algorithms
- Is it possible to build a winning monopoly strategy?
- Why is 'x' the unknown?
- How math changed the world?
- What's the solution to the McDonald's math problem?
- How do math geniuses understand extremely hard math concepts so quickly?
- Should high school math contests be banned?
- What is the relationship between music and math?
- Are math formulas ever used in real life?
- What are some of the most confusing math problems ever?
- The Role of Mathematics in Cryptography and Cybersecurity
- Mathematical Models in Predicting Pandemic Outcomes: A Case Study of COVID-19
- The Application of Game Theory in Economic and Social Decision Making
- Chaos Theory and Its Implications in Weather Forecasting and Climate Science
- The Impact of Big Data on the Evolution of Statistical Methods and Theories
Research Paper Topics on Business
- How do dirty business tactics work?
- Can business be started without money?
- Notorious business leaders
- Entrepreneurship and family business
- Ethical decision making in everyday work situations
- What are the most effective strategies for promoting a small business?
- Is it worth it to expand the business into a new region or country?
- How to build a successful startup
- The role of international business and sustainable development
- The impact of climate change on international business strategies
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Measuring the Impact on Business Performance
- The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for the Modern Workforce
- Innovative Business Models in the Age of Sustainable Development
- The Influence of Organizational Culture on Employee Productivity and Satisfaction
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Shaping Consumer Behavior and Marketing Strategies
Research Paper Topics For Middle School
- Is going vegan the healthiest choice for you?
- Is the greenhouse effect artificial or natural?
- The causes, effects, and consequences of earthquakes
- How much computer games can one play without getting addicted
- Princess Diana and her dynasty
- Why is competition so critical for humans?
- How did poetry evolve?
- Methods used by ancient sailors to navigate the globe
- Gender roles in children’s books and cartoons
- Who is the greatest general who has lived on the planet?
- The Science Behind Video Games: How Gaming Affects Reflexes and Learning
- The History and Cultural Significance of a Popular Holiday
- The Impact of Recycling Programs in Schools
- Animal Habitats: How Urban Development Affects Local Wildlife
- The Role of Social Media in Modern Communication Among Teens
High School Research Paper Ideas
- The ways to address drug addiction cases in high school
- The physical vs digital communications
- The body image and the K-Pop culture
- The importance of school volunteering and social work
- The changes to the academic process due to Covid-19
- The legacy of the Trail of Tears
- The role of motivation in becoming a better student
- The role of books in print and the libraries
- The ways to improve school safety
- The role of parental involvement in school work
- Exploring the Psychological Effects of Social Media on Teen Self-Esteem
- The Physics of Sports: Analyzing the Science Behind Athletic Performance
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Local Ecosystems
- The Evolution of Language in the Digital Age
- The Rise of Cryptocurrency: Economic Education and the Future of Money
History Research Paper Topics
- What were the impacts of World War II on the rights of women?
- What factors initiated the WWII
- Is liberalism the most optimal solution?
- What were the consequences of women suffrage movements
- What was the impact of Martin Luther King’s protest against the Catholic church
- What is the most effective military strategy of all time
- How has Asian art influenced contemporary art
- How have different monetary systems affected the development of humanity
- What is the correlation between the Roman and Greek culture?
- Aztec empire and its architecture
- The Role of Women in World War II and Its Impact on Gender Roles
- The Influence of the Silk Road on the Cultural Exchange between East and West
- The Effects of the Cold War on Space Exploration Competition
- The Historical Accuracy of Popular Historical Films: A Case Study
- The Impact of the Printing Press on the Renaissance and European Society
Art Research Paper Ideas
- The reasons why digital museums must be present and made available
- The peculiarities of the Flemish artists
- Should Japanese anime be considered as a separate art form?
- The role of Photoshop and similar digital solutions in the perception of modern art
- The history of photography and the artistic expression forms
- The challenges of the modern artists during social distancing times
- The Middle Eastern perception of color and the light
- Ancient Rome's role in the creation of the sculptures
- Should the artists be allowed to represent their works in public parks?
- The importance of art education in middle schools
- The Evolution of Street Art and Its Acceptance into Mainstream Art Culture
- The Influence of Digital Media on Traditional Painting Techniques
- The Role of Patronage in the Development of Renaissance Art
- The Psychological Impact of Color in Abstract Art
- Cultural Representation and Diversity in Modern Art Museums
Literature Research Paper Topics
- The American dream literature
- How does harry potter reflects the ideal of the time
- Can you show a new aspect of prose based on the independent investigation
- The prose of women suffrage movements
- The dawn of literature on modern society
- Why do authors use metaphors and similes
- Evaluate and discuss the allegory of 2 random novels
- What factors are helpful in allowing you to identify the genre of a novel you are reading
- Is fanfiction considered an independent literature
- Romance and sex in Renaissance
- Fiction as an instrument of propaganda
- The Representation of Gender Roles in Victorian Literature
- Postcolonial Voices: How Literature Has Shaped National Identity
- The Journey Motif in Classic American Road Novels
- Dystopian Visions: What Modern Dystopian Literature Tells Us About Today's Society
Law Research Paper Topics
- How is the Islamic law perceived around the globe
- Is ECOLEX a pathway to environmental law
- Why is it critical to learn the GATT documents?
- What does the European patent office do?
- Mass communication law
- Impact of women’s authority in different countries on the planet
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the international criminal law court tools
- Detailed analysis and report of the comparative criminal procedure
- Exciting outtakes from the inter-American human rights library
- Does the US copyright office really help writers defend their businesses?
- The Impact of International Law on Human Rights Practices in Developing Countries
- Cyber Law: The Challenges of Regulating Online Behavior and Privacy
- Intellectual Property Rights in the Digital Age: Balancing Innovation and Protection
- The Effectiveness of Rehabilitation in Juvenile Justice Systems
- Comparative Analysis of Gun Control Legislation and Its Impact on Violent Crime Rates
Religion Research Paper Topics
- The Role of Religion in Modern Secular Societies
- Interfaith Dialogue: Benefits and Challenges in a Pluralistic Society
- The Influence of Religious Beliefs on Ethical Decision-Making in Business
- Religion and Politics: An Analysis of Their Intersections in Contemporary World Affairs
- The Impact of Religious Education on Tolerance and Cultural Understanding
- The Evolution of Religious Practices and Their Adaptation in the Digital Age
- The Psychological Effects of Religious Rituals and Traditions
- Comparative Study of Creation Myths Across Different Cultures
- The Role of Women in Organized Religions: A Historical Perspective
- Secularization: The Decline of Religious Influence in Western Societies
- Religious Extremism: Understanding the Causes and Seeking Solutions
- The Impact of Pilgrimage on Religious and Spiritual Life
- Religious Symbols in Public Spaces: Freedom of Expression or a Call for Regulation?
- The Relationship Between Religion and Morality in Contemporary Ethical Debates
- The Effects of Globalization on Indigenous Religions and Spiritual Practices
Argumentative Research Paper Topics
- Should education be made free for everyone?
- The influencers and bloggers cannot be considered as a job
- The role of military service is the way towards maturity
- Should Internet access be limited during college lectures?
- The death penalty service is not an ethical solution
- Fashion industry creates a bad influence on young people
- The Fairplay concept should be rewarded financially
- Should tobacco be made illegal indoors?
- Religious differences often become the cause of wars
- The majority of mobile applications represent the invasion of privacy
- Universal Basic Income: Economic Savior or Road to Dependency?
- Mandatory Vaccinations: Public Health Requirement or Personal Choice Infringement?
- The Death Penalty: A Necessary Deterrent or a Violation of Human Rights?
- Climate Change Policies: Economic Hindrance or Long-term Investment?
- Animal Testing in Medical Research: Ethical Consideration or Scientific Necessity?
These are the 200+ topics on various subjects, which you might find useful when creating your own. In case you need help aside from creating topics, you can also order the original research on Politics, Media & Communication, to do my Math homework , Law, and even Nursing papers for sale on nursing essay writing service Edubirdie.
Get professional fact-checking and editing!
Ensure accuracy and enhance quality in your papers. Our experts provide thorough fact-checking and editing for just $7/page.
How to Choose a Good Research Paper Topic?
While it may seem challenging to come up with a good research paper topic as you try your best to narrow things down, the trick is to choose something that influences you because you know it well and can support your arguments with relevant evidence. The subject should be well-structured and relevant to your thesis statement. Always take time to research the list of sources to compose your topic sentences as well to make them relate to your thesis part. It’s always best to check a good research paper introduction example before you start working on the paper and choosing your topic, or contact our essay writing service for help. Here are the steps to consider:
- Start With Observing Your Interests.
If you are confused with a variety of interesting topics for writing a creative essay, it’s better to decide what interests you the most. Don’t stick to easy research paper topics just to complete the task fast. If you are allowed to freely choose what to write an essay about, use the opportunity to create something unique. Write down the list of your interests and break down every idea into small certain topics. When you have a list in front of your eyes, it will be easier to make up your mind and start considering a particular issue.
Then you should examine what aspect of the topic is preferable for you to outline in your research paper . A list will save you here again. Use pros/cons template to include all the arguments and objections to the issues.
- Come Up With an Argumentative Research Question.
The most challenging part of choosing a competitive research paper topic is finding an aspect that poses some importance for your course and the subject per se. While it may seem that it is sufficient to make a general statement, your argumentation should include a clear research question. Consider asking yourself why you have chosen a particular topic and how your research will make it clearer or provide innovative solutions.
- Study Available Research Topic Ideas.
Since we have already mentioned the dangers of choosing something too broad, it is vital to narrow things down and brainstorm the list of possible research paper ideas that deal with the same subject. In other words, you can write down at least five different subjects and see whether you can find sufficient information to support them with the sources or statistical data. Remember the importance of your topic’s wording!
- Compose Strong Thesis Statement.
It must be done at the same time as you choose your research paper topic because these two concepts must be interconnected. Your subject must reflect your main idea of the thesis statement. Make sure that you have the list of sources prepared in advance to incorporate relevant information in your body paragraphs. As always, they must be the supporting evidence for your thesis statement’s idea and the research purpose.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by David Kidwell
David is one of those experienced content creators from the United Kingdom who has a high interest in social issues, culture, and entrepreneurship. He always says that reading, blogging, and staying aware of what happens in the world is what makes a person responsible. He likes to learn and share what he knows by making things inspiring and creative enough even for those students who dislike reading.
Related Blog Posts
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper.
Though introduction to any writing is frequently associated with beginning, it's not that simple for an introduction to a research paper. Here you ...
200+ Fascinating Biology Research Topics for Students in 2024
Table of contents A List of Researchable Topics for Biology Abortion, Human cloning, Genetic Researches Biology Topics Behaviour and ...
150 Fascinating Astronomy Research Topics: Explore the Wonders of the Universe
The Significance of Astronomy Research Topics Astronomy research topics hold a significant place in the academic curriculum due to their profoun...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most

Chicago Research Paper Formatting
Chicago manual of style (cmos - 17th edition).
- Finding Sources for Your Paper
- Additional Resources
- Sample Papers
You are going to love this! Save this template somewhere safe or e-mail it to yourself. Then resave it immediately with the name of your new document. This will keep your template safe and ready to reuse again for future assignments.
The templates provided will be sufficient for most student Chicago Style papers. For more information on formatting, please check out The Chicago Manual of Style Online Resources for Students page at https://www.chicagomanualofstyle.org/help-tools/Resources-for-Students.html .

- Purdue Owl Author Date Sample Paper Sample paper is downloadable.
- Purdue Owl Notes Bibliography Sample Paper Sample paper is downloadable.
- Turabian: Student Paper-Writing Tip Sheets Official Chicago style, in easy-to-use, printable PDF paper-writing tip sheets for students, teachers, and librarians. Guidelines are per Kate L. Turabian, A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (9th ed.) and are fully compatible with The Chicago Manual of Style (17th ed.).
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Finding Sources for Your Paper >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 11:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.polk.edu/chicago
Polk State College is committed to equal access/equal opportunity in its programs, activities, and employment. For additional information, visit polk.edu/compliance .

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
113 Great Research Paper Topics
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Research Paper
- STEP 1. How to start research topic?
- STEP 2. Find information
- STEP 3. Make your thesis statement
- STEP 4. Make research paper outline
- STEP 5. Oganize your notes
- STEP 6. Literature review
STEP 7. The research question(s)
Step 8. research methodology.
- STEP 9. Writing the results, analysis, discussion, and conclusion
STEP 10. The process of writing a research paper
- STEP 11. Write your first draft
- Checklist One
- Checklist Two
- STEP 13. Tools for research paper help
- STEP 14. Some words of encouragement
When an average student hears about writing a research paper, apprehension and anxiety always arise. Contrary to popular belief, it’s easier than writing an average college assignment. Essentially, what is a research paper in basic terms? It is a type of academic writing that must follow instructions to the letter and adhere to certain standards. Since writing a research paper is based on the original research already done by another person, your task involves analysis, processing, and interpretation of research outcomes.
Since it’s a time-consuming process, it’s only natural to feel stressed without clear knowledge regarding where to start. If you write a research paper for the first time, things can become even more difficult. As students need to learn more about research paper structure peculiarities, they often write hastily and skip through all the essential elements that make research papers accurate.
This helpful guide will provide advice and assistance as you navigate the challenges of research paper writing. The article on how to write a research paper will include all the recommended steps that must be followed to earn the best grades. We shall also provide helpful tips and 14 steps to help you choose a good topic, write without stress and collect all the necessary information. It is precisely what helps to start up research work and achieve success.
You will also learn more about citation basics and free online tools that can help you check certain things and achieve clarity in your tone and the writing flow as you write. Read on to learn how to compose an A+ research paper!
STEP 1. How to start research and find a good topic?
The most challenging part is knowing how to start a research paper by narrowing things down. You must start by choosing a subject that interests and motivates you the most. Your motivation and general attitude will always differ when you feel inspired by the research problem. It will also help determine things you might already know regarding the subject.
Stay focused on keeping your content narrowed down. If you are talking about social conflicts, specify what types of problems it represents by talking about location and the sample group. When unsure, always talk to your academic advisor and seek topic approval first to ensure you are on the right track. It will always help you to avoid confusion in the future!
Finding a suitable topic problem or how to make your paper stand out!
When you have several research topics that inspire you, focus on those you know better and think about subjects that can be supported with solid argumentative evidence. Invest your time in a preliminary study of the subject and pay attention to detail because it will help you to see the shortcomings and advantages of choosing a particular subject.
Once you can achieve this goal for your paper, you will also meet most grading rubric requirements. As you choose your research paper writing topic, try to determine research questions early, as it will help you to see how to work with the methods section, analysis, and discussion, among other vital elements. Make sure you look at similar research paper topics by checking what else is available online.
This type of exploration is always essential because you must make your research paper stand out from the rest by offering something unique. You must do relevant explorations to see what other authors have done so you do not repeat the same work. Outline the objectives you wish to follow and develop the thesis or a hypothesis for your future work. Ask yourself what kind of work has already been done as you focus on your chosen topic.
Ask yourself whether some bits and pieces have yet to be explored. This way, you can shed some light on a subject and provide a new research method that has yet to be explored. Moreover, it will help you to publish your work in the future and present it at various academic venues! When your professor sees that you have done your homework correctly, it will become a cornerstone in your academic career!
Narrowing things down!
The most common mistake most college students make is taking a narrow approach when starting with research work. The trick here is to narrow things down and focus on the vital information you have obtained. Consider the statistical data, literature reviews, and facts supporting your main arguments. It means you do not have to choose all the available information and write it down in your work. Such an approach will only make your paper sound generic and take the research part away.
Think about choosing another method by focusing on elements that interest you the most! Seek the value in every sentence and add your author’s voice as you process information and present something of your vision. It will also help to explain why your research paper is important as you talk about the significance of your work.
STEP 2. Finding credible sources of information
One of the first elements of proper research work is finding the information required for an outline. Consider finding relevant general information online by visiting libraries or university resources. You may also use search engines and approach online resources such as Britannica . Still, try to implement Google Scholar as well by checking relevant publications.
It will be a good starting point to consider! Ensure you look at the domain extensions representing educational institutions, the .edu or .org domains (non-profit organizations). Likewise, you can locate accurate and verified information at .gov extension websites. Just remember that there may be a certain political bias, depending on the government.
Be careful with commercial .com websites as you write research papers. Many such websites can be excellent for research purposes, yet many tend to contain poor quality or advertisements that may make them less relevant. You can look at Network Solutions websites to learn more about what extensions this or that type stand for. Quality sources are not easy to find, so you must learn how to evaluate websites critically and eliminate those sources that are not peer-reviewed. If you are looking for sources in print or seek digital books for your academic paper, consider checking the Online Public Access Catalog (OPAC) library.
Conduct preliminary research based on a chosen subject!
When you are visiting a library online to write a research paper or considering visiting one in person, make sure to check the following as you write and take notes:
- Almanacs, atlases, and scientific catalogs;
- Government publications, guides, and reports;
- Vertical files;
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries;
- Magazines and Newspapers;
- Yellow Pages.
Speaking of online resources, you can safely consider web-based information as long as you can check the original or consider multimedia sources in audio and/or video format:
- Online reference materials at SIRS, ProQuest, or eLibrary;
- Indexing is done for periodicals and newspapers (onlinenewspapers.com);
- Newspapers and scientific magazines;
- Answers.com;
- International Public Libraries;
- Wall Street Executive Library;
- Online Encyclopedias like Britannica or Canadian Encyclopedia;
- Google Scholar.
Remember to check public and university libraries, read business press releases related to your subject, or check governmental agencies as you write. You can also talk to people by hosting interviews for the primary sources. Always document your sources, and do not use anything without a solid reason. When collecting your research paper writing resources, take notes of all the citing and/or bibliographical information.
It must include the author’s name, full title, place of publication, information about the publisher, publication date, and page numbers. Include the URL, DOI, or ISBN, depending on the publication’s type and the paper type you must write. As a rule, information not providing sufficient bibliographical data is virtually useless for citation purposes. If you are unsure of some source, it’s better to avoid it.
Try the new AI Essay Writer to make writing easier. It’s free and a great solution for moments when creativity seems out of reach!
STEP 3. Make your thesis statement clear
A thesis statement is the heart of every research paper because they deliver the main thesis or an assumption that is made. As a rule, the thesis must be created when you work on your paper’s outline. While some research papers may not require a thesis, the list of objectives must be presented in any case to help your target audience understand what they might expect. A thesis is the main idea of your research and a central point that should be outlined after your introduction part. The arguments must be clear and related to your chosen subject and topic.
In most cases, a thesis statement should present one sentence only. You can approach it as a declaration of your vision and the message that you wish to deliver. This is how you defend your point!
Developing a thesis statement before you do all the rest is recommended. A thesis usually appears at the end of your introduction paragraph and can be placed in italics. Starting with your thesis statement when you already have certain arguments written down is not recommended, as it will require post-adjustment work.
Likewise, your thesis statement must be supported by the evidence and literature sources you have obtained. Take your time to analyze available materials and come up with a clearly formulated statement for your research paper. It will help you to develop your ideas further as you move to the body parts of your research.
Do your best to avoid generic or vague statements and always focus on the subject and keywords included in your main subject. Your paper should inspire the audience and reflect the main idea presented in your introduction. Remember to avoid placing citations in the same paragraph with your thesis. It is precisely where your unique ideas and vision must be offered instead!
Your thesis statement should achieve the following as you write:
- Outline and explain how you approach a particular research subject.
- Address the research questions you have been given to write a research paper.
- Explain what to expect from your research work.
- Present various claims and set up a dispute.
Your thesis statement should be valid and possible to achieve. It is recommended to share it with your academic advisor as you may receive brief revision comments and address all the weak points. If it’s impossible, proofread it aloud and check if it can be supported.
Here is a list of questions to consider as you write a scientific paper:
- Does my thesis address the main problem of my research paper?
- Can I support my thesis with sufficient evidence?
- Does my thesis provide interesting and inspiring data?
- Is my statement clear and precise to present academic value?
- Can my thesis position be disputed and challenged? As a rule, the answer should be “yes”.
Remember that changing your thesis’s wording is possible as you work on your assignment. It will help you shape better ideas and increase your precision. Speaking of helpful research paper tips based on writing a powerful paper, you should focus on the credibility of your writing by checking things twice. Your strong and clear thesis shows that you have done your homework correctly and know the subject well!
STEP 4. Creating a research paper outline
Let’s continue with the basic research paper outline template that can be used further for research paper writing purposes. Here is the research paper outline format with universal elements:
I. INTRODUCTION
a) Provide a brief overview of a problem or issue you plan to research. Include your main assumption or an argument outlined in your thesis statement.
b) Include a justification of your research work. It is basically a reason why your readers should care and follow your research paper. Also known as the study importance, you must write it clearly and explain why your subject is meaningful.
c) Write down a brief outline of the paper’s range and the planned methods you will use to approach your issue or problem.
II. RESEARCH PROBLEM
a) Provide a background history of a problem.
b) How does your issue impact society and/or the academic environment?
c) Critical factors related to your research problem.
d) Possible solutions that will be explored in your paper.
III. LITERATURE REVIEW
a) A list of theories and concepts (textbooks, journal articles, or other relevant publications.
i. Offer a description of how these theories help to explain your problem and represent a solution.
ii. How were these concepts of theories explained by others?
iii. Describe how these theories help to explain your research problem.
b) Empirical research literature (mostly journal articles)
i. Provide an overview of relevant empirical studies based on chronology.
ii. Offer a summary of the methodology.
iii. Talk about major findings.
iv. What were the limitations you faced?
c) Talk about what has been discovered in a literature review
i. Talk about concepts and definitions you plan to use based on other authors.
ii. Describe all the unique concepts you have faced.
iii. Describe what method fits your research best and based on what reading(s).
a. Offer specific research questions that you address.
b. Describe your research method and data collection processes.
c. Justify your method’s rationale and explain why you have chosen it.
V. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
a. Write down your major findings.
b. Write about statistical information and facts to explain your research outcomes.
c. Discuss and write about the relevance of findings based on prior studies.
d. Was there anything unusual or not-so-common? Write about unusual discoveries.
e. The discovered limitations of your study as you wrote a research paper.
VI. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
a. Provide a brief overview of the issue examined and outline major findings.
b. Remind your readers (briefly) about the goals of your study and write down your accomplishments.
c. Offer recommendations and talk about how other researchers can benefit from your findings.
Depending on the type of research you have to write, you can write a scientific paper with an outline that can be formal or informal. The authors use an informal outline to narrow down and organize their ideas. You can revise, add, edit, or remove certain bits mentioned in your paper without keeping it strictly focused. You can use it as a writer who wants to keep on track.
Now, things are totally different when you are asked to present a formal outline and research paper. A formal outline always uses a clear structure by following numbers, letters, and logic. Every paper heading is essential here, along with sub-headings that must be grouped exactly as they appear in your research paper. The capital Roman numerals are usually used for coordination purposes.
An example of an outline to help you write a research paper:
Paper Title: Open Scouting Movement in Flanders, Belgium. An Analysis of Scouting Branches
a. Importance of Open Scouting Movement in Belgium.
b. Define the major differences between Open Scouting and the National Scouting Movement.
c. A brief history of Open Scouting in Belgium.
d. Examination of statistical data to determine the involvement of scouting branches.
e) Justification of the study’s importance.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
a. Analysis of popular theories in youth movements in Belgium: Chiro, KSA, and Vrije-school movements.
b. Review of youth studies done based on local coverage and accessibility.
c. Gaps and areas that lack coverage and discussion in literature and the media.
III. METHOD
a. Visiting Open Scouting branches in person.
b. Behavior codes across branches to compare the rules.
c. Data collection methods: staff surveys and group interviews.
IV. RESULTS, DISCUSSION, AND ANALYSIS
a. Differences and similarities of scouting branches review.
b. Analysis of practical differences of Open Scouting in Belgium (write a research paper based on observations).
c. Outcomes of surveys.
d. Usefulness and accuracy of relevant methods (write research paper points related to your methodology).
e. Limitations of the implemented methods.
V. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
a. Main points mastered by the research.
b. The importance of Open Scouting in practice.
c. Further recommendations for parents, educators, and camp leaders.
As you do a research paper, it is recommended to narrow things down and keep your outline to the point based on what data you have obtained for your paper. When you have an outline, you can avoid being vague and keep your structure relevant to a certain logic. When you have a good outline and write a research paper correctly, it is essential to write an excellent one. Remember to follow our templates and that an outline should include an introduction, body content, and a conclusion.
Writing an introduction and other elements for your research paper structure
- INTRODUCTION: This is where you have to introduce your research problem and include a clear thesis. Ask yourself about the main reason why you are researching something and outline it here. Explain how you plan to approach an issue in your research paper. Depending on the research type, you can focus on the facts, review relevant literature, or offer an analysis of a problem. This is also where you must explain all the major points mentioned in your paper and why they matter!
- BODY CONTENT: Present your strongest to weakest arguments by supporting your thesis statement. This section is also divided into several parts. It will always depend on your academic discipline, requirements issued by your professors, subject, and many other things. To write a good research paper, your body parts usually contain elements like a literature review, methodology or methods section, analysis, research outcomes (results), sample analysis, and a discussion section.
- A CONCLUSION: This is where you must state your thesis and research question in simpler terms. Do not introduce any new ideas. Try your best to summarize existing arguments. Explain why you came up with a specific conclusion. Your paper must represent at least 15% of the final part. Explain again why your research matters and how the results can be replicated or used for future research.
STEP 5. Organize your notes
Keeping your notes organized is essential as you have to ensure that every vital point has been mentioned as it is presented in your outline. As you write a research paper, evaluate your research data critically and check for accuracy. If some information has not been updated in a while and has missing citation data, it’s always better to skip it as you work on your paper. If some beliefs or views oppose your main thesis, write a research essay section that mentions them in a counter-arguments paragraph.
It is one of the most important stages to consider when writing a research paper. It is where you must sort, analyze, and evaluate your available data. It will help you to learn new things and determine the main purpose of your objectives. Think about eliminating less important aspects as you take notes of your ideas, thoughts, concepts, and research findings.
As you write a research paper, avoid information that is not relevant to your research issue! Do not include facts that cannot be supported by a clear piece of evidence or a direct citation. At the same time, using only up to three citations per 300 words is recommended to avoid possible plagiarism risks. As you write a research paper, use paraphrasing instead whenever possible! If an idea is not yours, always provide a reference and document it accurately.
When you sort and classify your notes as you make a research paper stand out, do your best to provide detailed bibliographic data for each citation before you create a References or Works Cited page. As you work on the notes, you have prepared to write a research paper, use different outline codes or colors to mark the types of sources, depending if they are in print or online, related to the first, second, third argument, and so on.
STEP 6. A literature review or learning of available resources
This part basically stands for knowing what data is available out there. It is precisely where you have to do all the research work and a reason why it differs from most other assignment types you might encounter as a college or university student. The purpose here is not simply to list all the information available on a particular subject but to contribute something based on your vision and thoughts.
One of the ways to do that is to go through the literature review process and narrow things down as you look for background information related to a particular subject. As you start with a literature review for your paper, you automatically determine what is already known about an issue you plan to explore. A comprehensive literature review for a professional research paper will help you save time and discover what aspects of a subject have yet to be reviewed. Likewise, you will know what has been done before.
- Internet research based on keywords. It’s one of the easiest methods to start with as you look for information online and use specific keywords that reflect your chosen topic. You can consider the information available on various websites or general publications. Most students who write research papers will turn to academic research and scientific databases. Finding peer-reviewed sources and sorting out unnecessary social media websites or blogs is safe. Remember that places like PubMed or ScienceDirect are more trustworthy for an academic research paper than a post on Twitter, even though the latter may represent a primary source.
- Checking prior research on the topic. The next step worth taking is exploring all the prior work that other researchers have done. You can visit official organizations that work in the field of your research. This way, you can collect statistical information and see what they have found before and what information has been made available. Focus on whether research work is funded publicly or done privately. If the research is affiliated with a certain company, consider checking things twice for possible bias, especially if your paper must be neutral. Always check for credibility and try to locate information about the author(s)
- Visiting the university library. As a rule, if you are enrolled in Automotive Industry at MIT, you will have access to unique materials at the local library. The chances are high that your academic advisor may already provide you with a recommended or even obligatory reading list. As you brainstorm various steps in writing a research paper, take your time to research what’s available at the university or college library. Turn to research databases and look through the online index by entering keywords related to your paper. Most of them will have available citation info to save you valuable time.
- Using academic sources. These include peer-reviewed journals that you can access either in print or online. As a rule, such publications receive the highest level of credibility from most professors and should be considered first. It is partially because of the unbiased review and cross-linked publications. If you are dealing with a citation from someone who knows the subject well, you will increase the credibility of your research paper. Likewise, if your research paper becomes published or you present it publicly, you increase your chances of being cited and quoted by others in the chosen scientific field.
Once you complete a detailed literature review and are ready to pursue the next steps to write a research paper, you will receive sufficient background information to understand your subject’s peculiarities. Much of this work will help you shape your research paper thesis much better because you will automatically address numerous objectives and know all the limitations and research gaps. You will learn what must be done to keep the research accessible and clear based on the chosen topic.
Before moving to the Methodology section, exploring the answers that address your research objectives is crucial. Most importantly, you must keep your research paper data within the scope and timeframe of the issue. When dealing with scientific research, you must keep information clear to a certain point. It must be possible to replicate and measure your actions. Whether using quantitative or qualitative methods (or both), it should be trustworthy and possible to replicate.
Always consider what methods to use and what sources to put forward, depending on your subject. If you are talking about the violence of video games and their effect on teenagers, the best solution to write such a paper would be to use surveys or other methods in your research paper guidelines to determine your sampling method and avoid bias. Likewise, you may use various means and technical tools to receive answers to your research questions , depending on the strengths and weaknesses of each.
It’s one of the most challenging steps to consider as you have to choose a particular research method based on your research paper subject, the type of research, and the sources you have obtained. Here are the most popular research methods that you may consider:
- Focus group. It can be a suitable method if the author’s goal is to obtain information from a small group of people. It might be a safe choice for your research paper if you cannot invest time and funds. It usually comes to asking questions and taking notes as you determine a limited sample group. While it can be convenient, findings from a focus group method might not fit those cases where you need to be more careful with a selection. It means that you must avoid it for legal or medical studies. After all, as you write a research paper based on that, a fellow researcher can make a limited conclusion regarding the findings because of the limited sampling approach.
- Survey. It’s another popular method that can be used for a large sample group where participants are chosen randomly. Such a method is often recommended when dealing with peer-reviewed research sources. When writing a scientific paper, remember that most paper surveys you can write down also have weaknesses since participants may not provide honest opinions or politically correct answers. Numerous factors also influence them, so a certain bias is always possible.
- Field experiments . These are also helpful when you wish to experience information in practice and explore a certain community. The methods used here include field analysis, lab experiments, direct observation, participant control, case study replication, and many non-conventional methods that researchers can use to address their research objectives. The same is true for the technical equipment tools you can use to determine the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
- A word on replication: It must be noted that writing down the methods section for your research paper must be precise and accurate. Other researchers should be able to replicate your method and come up with the same findings and outcomes. Replication is critical in the research process, as your results must be valid!

STEP 9. Addressing a research paper’s results, analysis, discussion, and conclusion sections
Once you finish the data collection and methods section for your research assignment, it’s high time to move to the results part of your paper and do analysis work. You must use this space as a researcher when dealing with results, analysis, discussion, and conclusion.
The main purpose is to interpret your findings and explain what you could achieve. You can compare your research paper results to prior findings and discuss potential limitations and implications for other researchers.
- Results . Start this section by discussing the findings you could obtain from your research work. Address what research paper questions have been addressed. If you created a series of hypothesis statements or made certain educated guesses in your research paper, state if they have been supported or rejected. It will help if you include tables, graphs, statistical data, and other visual elements to help your readers understand the results.
- Analysis. As a researcher and analyst, you must interpret and explain your findings based on the thesis statement. You have to state whether your research is significant and showcase if your findings support (or reject) prior research findings. Remember to provide a piece of evidence for every fact that you have obtained. Talking in context, explain by comparing and contrasting the facts. It’s also necessary to explain how your findings hold up against other findings conducted by researchers in your field.
- Discussion . Once done with the analytical part, this section should outline and discuss your findings in an accessible way. Remember to mention your research work’s main benefits and limitations. Focus on transparency and allow your readers to determine the weaknesses and specifics of your research. Speaking of tips for writing a research paper analysis part, try to be self-critical but do not overdo it! This part must not introduce any new ideas as you write but help future researchers come up with new methods and try out other things to address the shortcomings of your study.
- Conclusion . This section allows you to summarize and state your thesis again, with a brief overview of the research findings. A conclusion should discuss the main points, starting with the main research questions, the list of methods you have used, the results, and your findings. A research paper’s conclusion should be sufficient to understand the type of work done. Imagine that a reader has no time to read the entire paper and include all the important bits in your conclusion. The key is to write and help everyone understand your content well by reading the conclusion alone!
We are finally ready to write it all down, which will be easier since we already have all the necessary information. As you write a paper for college, the most important thing is to keep the flow and remember to look into your outline. Your research paper must be structured per every section mentioned in your grading rubric and the outline (if you have one!).
Consider starting with an introduction and thinking about starting with the background information bit to present your thesis statement. As you proceed with your writing, a thesis statement should be the last sentence of the introduction part that will help to proceed with the further sections.
Remember the importance of having an outline? If you have been listening and creating one, supporting your thesis with relevant arguments and organizing your content from strong to weak will be easier. Just follow your writing with the sections already mentioned in your outline! Using topic sentences at the beginning that instantly explain your research and include bullet point structures to guide your readers will be helpful.
It also helps to narrow things down and outline the most important ideas and/or facts. A good paper outline will also help you work in chunks and save time, as you only have to grasp some research work simultaneously. It is recommended to allocate at least 2-3 hours to write a research paper to ensure you do not exhaust yourself by spending more as you deal with a lengthy research paper!
A good research paper can be finished, so taking one step at a time for each section will help you see what is left and what is already done. Do your best to avoid procrastination! Meanwhile, as you create a research paper, do not try to reach perfection, as it’s barely possible! Keep yourself disciplined and have a writing schedule, as it will help you to overcome the usual writer’s block issue. It is the best way to meet your deadline and stay on topic! See below for the essential 9 steps that are worth knowing:
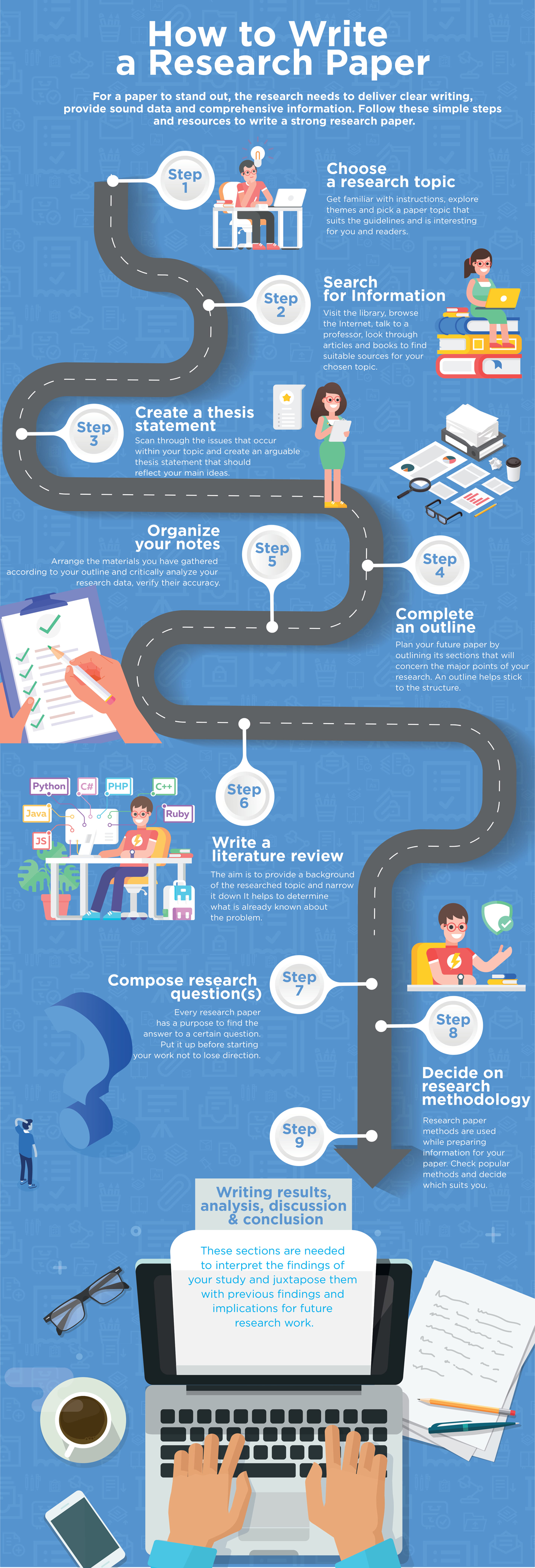
STEP 11. The importance of writing your first draft
It must start with the first aspect of your research paper outline. It means that background information and the relevance of your topic must come first. Make sure to include all your notes and avoid citations unless it’s statistical information that you need to explain the importance of your research. Try to summarize the available information and alternate between paraphrasing and direct quotes as you write a research paper to decrease plagiarism risks.
An ideal scenario would be introducing an issue and continuing with the direct quote, followed by your analysis. Alternatively, writing a science research paper can use various techniques that fit you, like summaries, quotes, tables, or comparisons. Since it’s your first draft, do not spend too much time editing things yet!
Once you are ready with the first draft, remember that it does not have to be perfect because it is not meant for submission. As a rule, most students go through at least three different revisions until they submit the final paper version. Always follow your thesis statement to guarantee that you do not touch upon other subjects.
If you have an opportunity, ask a good friend or even a professional researcher to listen to your draft and help you identify the weaknesses or entire passages to change and improve. It has to be accessible and easy to understand. Always give your first draft enough time, and remember to take a break from your paper and get outside before you get back to it and continue with the revision.
STEP 12. Editing your paper
We are finally at the stage where it is necessary to review the research paper draft and ensure that everything is correct, adheres to the writing standards, and follows existing instructions and/or grading rubrics. To simplify things for any research project, we have created several checklists for you. These include helpful tips and tricks for writing research papers well. They allow you to save time and impress even the most demanding professors.
The main purpose of reviewing your work is to check your paper for any content and logical mistakes. Double-check all the facts and figures. Check your outline and arrange or rearrange ideas based on your notes. You must keep things logical and clear as you edit your paper for repetitions but remember to include all the necessary bibliography and additional notes when and if necessary.
First checklist for writing an excellent paper:
- Is my thesis statement clear and concise for the audience?
- Is the outline followed? Has anything been missed?
- Are arguments presented from strong to weak in a logical way?
- Are all in-text citations corresponding with the Bibliography page?
- Is the thesis supported with strong statements?
- Are intentions and methodology parts clear as to research objectives?
Note: Remember the importance of editing your paper for grammar and spelling mistakes. You can use a dictionary to check spelling and consult a thesaurus if necessary. MS Word and Google Docs allow you to check your spelling for typos and punctuation issues. Take your time to correct the mistakes and proofread your content aloud to ensure it is accessible. If possible, have another person proofread and check your paper, as you may have missed certain weak points. It’s only natural as you write a research paper and edit it repeatedly!
Second checklist for writing:
- Does every body’s paragraph start with a relevant topic sentence?
- Are my arguments supported with evidence and practical examples?
- Have run-on or odd sentences been eliminated?
- Have repetition issues been removed?
- Is the length of sentences normal?
- Is there an easy flow of ideas?
- Has the content been checked for grammar and spelling?
- Are citations accurate and in the correct citation style?
- Is my research paper unbiased and objective?
- Does the paper provide a strong sense of completion?
Note: It is recommended to use “cannot” instead of “can’t” as you write a research paper, as well as “do not” instead of “don’t”. A research paper must be written in the third person unless specified otherwise.
Keeping your writing in style
If you wish to improve your English composition skills, check out “The Elements of Style” by William Strunk for an example of a classic book that addresses style issues in writing. The book’s contents focus on the main grammar rules, elementary principles of composition, useful words and expressions that are usually misused, and important reminders. The book teaches how to revise and rewrite the odd parts. It helps to learn how to avoid all the fancy words. See details of the book by checking The Elements of Style by William Strunk, Jr. , which is partially available online free of charge.
Correct citation and formatting issues
As you might already know, every research paper is written in an academic style like APA , MLA , Chicago , or Harvard. Students majoring in Healthcare will likely use AMA (American Medical Association) citation style. It will depend on your discipline or the style specified in your grading rubric. The most common styles are APA and MLA. The research paper styles that are uncommon are Harvard, Chicago Manual of Style, APSA (American Political Science Association), and the IEEE, which stands for the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. You can check style guides before you check your formatting aspect.
- APA (American Psychological Association) style is mostly used for social sciences subjects. Make sure to check your grading rubric and university templates for more information.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) style is the most common for Liberal Arts and Humanities. The most recent is MLA 8th Handbook style. Remember to check information on parenthetical citations in MLA to ensure that your research paper follows all the rules. If you are new to this style, check relevant examples for printed books, online sources, etc.
STEP 13. Tools for research paper writing help and accuracy
Once you are done with the editing part and review your draft more than once, it’s time to apply another evaluation method, also known as copy-editing. Thanks to AI-based tools, copy editing is now a more expensive and demanding task. Of course, it will work differently than professional editing because you should still check all the false corrections. Still, since it’s possible free of charge, there is little to complain about when you can write a research paper correctly. You can easily find These types of tools online:
- Grammar checkers. They mostly correct issues like grammar, spelling, typos, and punctuation. It will also address lexical issues, a saving grace for most ESL learners. Remember that poor grammar may seriously ruin your paper, so check grammar checkers and enable them in Google Docs and MS Word.
- Plagiarism checkers . It provides excellent help because you can scan your paper for similarities and balance direct citations and paraphrasing. It does not take more than five minutes to check things, so do yourself a favor and check one of the free or commercial ones. As a researcher, remember to cite your paper completely and give credit where it’s due.
- Citation generators. These are helpful for cases when you cannot find ready-made citation information. When you compose your Works Cited or Bibliography pages, you must double-check the accuracy of citations with all the spaces, punctuation, and indents. The most common research paper styles such tools support are APA, Harvard citations, MLA, Chicago, Vancouver, and more. Free research paper tools also make it possible to convert your sources from one style to another automatically. It is helpful when you have found a complete citation in Chicago but need it in MLA or Vancouver.
- Title page generators. These are useful when brainstorming ideas for a good and inspiring title. After all, a title is what your professor will see first as you submit your paper. Many college students feel challenged as they work with all the indents and ideas, title case problems, and other formatting issues. Title generators help with this problem and will follow the relevant style.
Note: if you plan to get your research paper ready for publishing, read the eligibility rules twice and submit it for peer review. It is also necessary when you plan to attend a scientific conference. As a researcher, you must read and follow all the editorial guidelines before you submit a publication. If you fail to follow the guidelines, you may get rejected even if your paper is an excellent example of academic research.
STEP 14. Final words of encouragement
As we have reached the end of our guide to writing a research paper in 14 easy steps, we sincerely hope that you do not see it as a daunting and frustrating task any longer. Follow every section of our guide and take one step at a time to make things easier. The most important is choosing an inspiring topic you know well, as it’s already half of the task done. Take your time and research the subject that motivates you the most, as it will help you develop a message that makes a difference.
Once again, always pay attention to the literature review part and online research! It will help you to learn what subjects are popular and which need more effort and additional research. It always helps to narrow things down and find something you know well to occupy a research niche.
If you want to contribute something special, consider choosing something not widely researched. Once you are set on a topic for your research paper, think of a strong thesis statement and create an outline. It will help you see the entire picture and clearly understand what steps to take and in what order. It will eventually lead you to an excellent research paper!
If you face any challenges or feel lost when writing a research paper, our trained writers and editors are always ready to help you 24/7!

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research
Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
Art Research Paper

This sample art research paper features: 6600 words (approx. 22 pages) and a bibliography with 52 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
The Sociology of Art
The arts and sociology, as Pierre Bourdieu (1980:207) observed, make uneasy bedfellows. It is an unease that pervades American sociology even more than he imagined. We should bear in mind that barely two decades have elapsed since a handful of American Sociological Association members succeeded in convincing a necessary quorum of colleagues to sign the petition required to set up a new Section. The Culture Section’s growth since then must have come as a surprise even to some of those early supporters.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, more art research papers:.
- Performing Arts Research Paper
- Music Research Paper
- Architecture Research Paper
- Theater Research Paper
- Visual Arts Research Paper
Culture and the arts have become increasingly visible in sociological publications (Peterson 1976; Becker 1982; Crane 1987; Balfe 1993), disciplinary recognition (Griswold 2000), and professional organizations, both in the United States and elsewhere (Zolberg 1990). But despite the richly textured potential that the arts afford for social science disciplines, it appears that American sociologists continue to devote relatively little attention to them. The success of culture’s reentry as a domain of considerable significance in American sociological investigation provides an opportune moment to reexamine the standing of the arts in what should be the most hospitable field of the discipline. This research paper provides an account of the persistent hesitancy to recognize the arts as central rather than peripheral in the social scientific field even in the face of the extraordinary promise that artistic transformations in the past century would seem to offer. The theme is that despite the increasing prominence of culture in the profession, the standing of the arts in American sociology appears to have changed less than might have been expected. 232
Staging the Sociology of the Arts in America
Less than a half century ago, a survey of the sociology of art would have begun and ended with contentiously worded assertions concerning the relationships of the arts and society. Certainly, many scholars affirmed that in some ways art mirrors society, but at that point consensus would end. Some insisted that art reflects societal production relationships, serving largely as an ideological tool to maintain dominant groups in favorable situations. Deriving from the materialist orientation of Karl Marx, who actually wrote little about the arts, that perspective provides the foundation of Arnold Hauser’s (1951) massive analysis of artistic creativity through the ages, The Social History of Art. Other scholars, with equal certainty, maintained that great art should be treated as part of an autonomous sphere, surmounting material constraints, but in some way reflecting the spirit of its age. Certain versions of reflection analysis see art reaching for higher values, foretelling cultural and societal tendencies. Of the many anti-Marxist variants on this idea, the one elaborated by Pitirim Sorokin (1937), a work that preceded Hauser’s by more than a decade, was nearly as massive.
As divergent as they are in their foundations, these interpretations of the relations of the arts and society aim to unearth hidden postulates of art in relation to broad social structural processes. Whether from the standpoint of Marxist analysis or anti-Marxist idealism, these are universalizing conceptions of art, representing a Western European, hierarchical scheme of cultural classification (Bourdieu 2000:73, 105). Sorokin embraced 2,500 years of civilization; Hauser starts from the even earlier point— prehistoric cave painting—and both ended their analyses with their own artistic contemporaries. Neither passes muster in the face of modern anthropological perspectives, which see art as part of a cultural system, embedded in its cultural context (Geertz 1973). Regardless of the political or intellectual stance of individual scholars today, their ambitions are far more modest. They rarely undertake to encompass such magisterial breadth entailing so speculative an outlook. This does not necessarily result in a narrowing of vision, however, since the types of art that contemporary researchers consider worthy of analysis are far more varied than what their predecessors documented. Neither Hauser nor Sorokin paid much attention to nonWestern civilizations, barely any at all to primitive and folk forms, and, except disparagingly, to commercial art and entertainment (Hauser 1982). Neither considered the absence of women artists a question worthy of scrutiny. Even within the domain of fine art, both shared a largely unexamined but generally unfavorable opinion of avantgarde art. Finally, like most of their more aesthetically oriented peers, although they dealt with changing genres and stylistic modes, they accepted extant categories of art as unproblematic givens, without considering that other creative forms might be valid for inclusion in the aesthetic field (Zolberg 1997). Yet beyond their ambitious reach, what is remarkable about the Hauser and Sorokin studies is that they were truly exceptional, since on the whole social scientists gave short shrift to the subject of art.
On the Sociological Periphery
Early work in sociology of art.
Even though American sociology had its origins in, and continued to look toward European theoretical formulations, aside from literary and aesthetic scholars who sometimes touched ever so lightly on the social contexts or cultural history surrounding the arts, in the first half of the twentieth century, the sociology of art was largely the concern of a few European scholars. A single major work by Max Weber (1958) dealt directly with a specific art form— music—as a case of his theory of cultural rationalization in the West. When Émile Durkheim founded his important publication, Annales, he situated what he termed “aesthetic sociology” within the sociology that he was trying to establish but only under the residual rubric “ divers ” and beyond considering it as part of the “elementary forms of the religious life” of aboriginal society, he himself did no study of it (Zolberg 1990:38). Only Georg Simmel (1968) wrote frequently about the arts, although less as a social scientist than as a literary and art critic, philosopher, or fashionable essayist (Coser 1965).
By the end of World War II, American sociology, along with American science more generally, became the most dynamic and expansive in the world. This growth was a counterpart to the prominence of the United States on the international scene as the champion of Western humanist values during the war, and defender of freedom during the cold war (Guilbaut 1983; Saunders 1999).
American social scientific scholarship, however, hardly acknowledged the arts as a legitimate object of study. This stance had its nearly symmetrical correlative in the opposing and equally intransigent stance on the part of humanistic scholarship, including literature, aesthetics, art theory, musicology, and history of culture, toward what seemed the threat of the social sciences. The increasing preeminence of the exact sciences during and after the war had drawn many social scientists to adopt the presuppositions, techniques, and methodologies of these disciplines, an orientation that cast a shadow over humanistic subjects such as the arts, and qualitative interpretive methods that art calls for. Still, as higher education was expanded, despite official emphasis on the exact sciences, all university studies were made to grow, including the social sciences and the humanities.
A New Moment in Late-20th Century Sociology
Until the post–World War II period, in the United States, the few scholars who did social studies of the arts were emigré scholars, especially members of the Frankfurt School, such as Theodor Adorno ([1962] 1976), who were escaping persecution by totalitarian states. Straddling the intersection of the humanities and social sciences, these exiles often remained marginal to mainstream intellectual life, were treated as outsiders, and saw themselves in that light (Wilson 1964:v). Their marginality was enhanced by the Marxist orientation to which some adhered, combined more generally with their critical views on American sociology’s “scientistic empiricism,” and, in many cases, contempt for what they took to be its intellectual shallowness (Zolberg 1990:72). Most of them deplored the development of “mass society” and its impact on individual autonomy. Their insistence on taking an evaluative position in their social analysis, rejecting what they regarded as a fictive scientific objectivity, reinforced the exclusion they suffered from the academic mainstream of American sociology. Nevertheless, some of them attracted a following of American scholars, intrigued by and sympathetic to their inquiry in the spheres both of high culture and their critique of culture industries. Although the legacy of earlier misgiving persists, in recent times, it has become considerably muted because of changes in both sets of disciplines that have produced convergences in their orientations (Zolberg 1990).
Foundations for a New Social Study of the Arts
Although in many European countries a considerable body of scholarship was devoted to aesthetics, it was only in the post–World War II period that an autonomous field of sociology of art, distinct from philosophy, history, or criticism materialized. This was the case in France, as the sociologists Pierre Bourdieu ([1979] 1984) and Raymonde Moulin ([1967] 1987, 1992) provided important intellectual leadership and the French state gave institutional support. German philosophical, musicological, and art historical scholarship continued to straddle the social domain as successors to the Frankfurt School tradition for whom the arts, both fine and commercial, were foci of critical study. English literary and historical scholarship infused Raymond Williams’s social analysis of what he saw as the hegemonic role of the arts and served to underpin the development of British culture studies. Williams led the way to open up the social study of the arts by introducing popular forms, such as the movies, radio, jazz, and more popular forms. In the United States, students and faculty who considered the university an agent of government policy, especially through its involvement in the Vietnam War, challenged what they suspected were biases of the social sciences.
Simultaneously, in relation to some of the same developments, the art world itself was undergoing transformation. The trend that had begun much earlier, for the center of the international art market to shift from Paris to New York became a reality in the immediate post–World War II period. As happened during World War I, when the arts were challenged by Marcel Duchamp’s gathering of “found objects”—bathroom plumbing, snow shovels, bicycle wheels—and “assisting” them to the status of art by supplying them with titles and signatures by purported artists, in the 1950s the arts “exploded.” Artists introduced new media, broke the barriers separating genres, and challenged conventional hierarchies, routinely wreaking havoc with artistic traditions, including even the historical avant-garde.
The material conditions that encouraged the entry of large numbers of aspiring artists into the avant-garde art world included growing foundation, corporate, and government support for the arts (Crane 1987). Political ideology played an important role in the form of cold war strategy by American advocates of government support for the arts, who successfully argued for creating a hospitable environment for artistic originality to serve as evidence of the creative freedom that was anathema under authoritarian regimes (Guilbaut 1983; Saunders 1999). Besides providing an opportunity structure for artists, indirectly, it opened the path for social scientists interested in culture, whose forays into studies of the arts gained some legitimacy.
On the basis of what had become “normal sociology” of the 1950s and 1960s, it would have been difficult to predict the efflorescence in the sociology of art that was in the offing. Prior to that time, aside from a few articles, no major sociological works had increased the small, pre-1950s bookshelf. An indication of the new trend appeared in the exploratory work, The Arts in Society a reader edited by Robert Wilson (1964), who wrote a number of its essays and solicited additional ones. Justifying his choices by taking as his point of departure the fairly orthodox idea that artists could “often see what is going on in the society or the psyche a good bit earlier than other men do” (p. vi), he was unabashedly “concerned with the products and producers of high culture.” Only a few years later, another collection of essays heralded an “institutional” approach that examines the functions of the arts in meeting human needs and maintaining social stability (Albrecht, Barnett, and Griff 1970). The editors included studies of the relationship of forms and styles to various social institutions; artists’ careers and their interactions in a variety of artistic milieus; distribution and reward systems; the roles of critics, dealers, and the public in recognizing artists and works.
They were generously open to divergent views that encompassed even Marxian analysts. At the same time, however, these essays demonstrated the infancy of the field of sociology of art: of the authors represented, only onefourth were actually sociologists, while the rest were in anthropology, comparative literature, history, art history, or were practicing artists, painters, dancers, writers. The happy result of this omnium gatherum was that Albrecht and his coauthors contributed to the creation of an American field that integrated European approaches and was strongly cross-disciplinary, ranging over the fine arts, classical and contemporary, as well as folk art, music, dance, and literature, and their corresponding institutional grounding.
A Sociological Space for Art: Current Trends
In light of changes within sociology itself, as well as developments exogenous to the discipline, the sociology of art in the third millennium may be characterized by four trends. First, continuing from already tested frameworks, sociologists examine the roles of the institutions and processes that give rise to or constrain the emergence of artworks. Second, they analyze the artistic practice of creators and patterns of appreciation and acquisition of patrons and collectors. Third, they investigate degrees of access for diverse publics to the arts and the role of the arts in status reproduction. Fourth, in a radical shift, some scholars call into question the very nature of the category “Art,” arguing that “art” needs to be understood not as selfevident but as a social construction. The rapid succession of art styles that has characterized nineteenth- and twentieth-century Europe and the United States is taken by some to be emblematic of the innovativeness of modernity but by others as an indication of over-ripeness, cultural decadence, and anomie. For some observers, the entry of commercial art forms into galleries and museums (Cherbo 1997), the newly found respectability of previously denigrated musical forms such as jazz (Adorno 1976), the growing presence of non-Western music, simultaneously in commercial and serious musical domains, are a sign of the West’s decline. Many question whether these genres— new entrants to “Art”—deserve to be so designated (Zolberg 1990).
For sociologists of culture, generally more dispassionate than cultural critics, developments of this kind provide opportunities for research and theorizing that many analysts hope will help to understand the nature of societal transformations more generally. The use and misuse of aesthetic creation in the interest of particular groups or political ends is one of their recurring concerns (Gans 1974, 1999; Goldfarb 1982; Halle 1993). At the same time, the idea of a domain of art free from material purposes outside of itself remains a seemingly unrealizable ideal, both for artists and for publics more generally.
Methodological approaches range from an empiricism that relies on quantitative tools to analyze masses of available data, such as the degree of access to cultural resources (Blau 1988), survey data of art world practices, and audience studies (Gans 1974). Equally empirical, but based on microscopic observation and qualitative analysis of cultural practices, is the ethnography of Howard S. Becker’s (1982) Artworlds. Historical and semiotic perspectives have been imported from literary analysis into the social studies. Even more striking is that the range of works and art forms investigated has burgeoned and includes the commercial domain—culture industry—as well as the more traditional fine arts (Peterson 1997). Increasingly, sociologists, following Gans (1974), recognize that the arts may exclude as well as include. The absence of certain classes of aspiring artists such as women and racial minorities from what were defined as the most distinguishing and distinguished art forms is no longer taken for granted (Bourdieu [1979] 1984).
In its most distinctive manifestation, American sociology of culture has synthesized approaches to the social study of science, religion, and work, under the rubric of the “production of culture” (Peterson 1976). Defining culture in a broadly pragmatic sense that allies it to anthropology, it comprises art, popular culture, science, religion, symbols or, more generally, meanings, Richard Peterson and his associates urged that the questions broached by scholars themselves determine the use of synchronic or diachronic modes according to their appropriateness. Proponents of the production of culture approach consider how cultural products were constituted, accentuating the effects of institutional and structural arrangements, both as facilitators of or impediments to creation. Characteristically, they prefer doing middle-range and microscopic analysis that, they believe, more effectively reveals the impact of laws, culture industry practices, and gatekeepers of the form and content of artworks.
Institutions and Processes
Critics and artists have decried, virtually since their establishment, the role of certain institutions, such as official academies and government agencies or ministries that are supposed to provide support for artistic creation. Following the pioneering sociological study by Harrison White and Cynthia White (1965), among the first to analyze systematically the changing structure of opportunity that the French Academy provided for artists of the French painting world in the nineteenth century, more recently, a study of how academies selected for exclusion was carried out by Gladys Engel Lang and Kurt Lang (1990). Focusing on the revival of etching as an art form in the nineteenth century, they show how keeping out or severely limiting women as students and members by most European academies impeded their entry into the highly regarded world of oil painting. Diverted to other, lesser media, such as etching and watercolor, whose professional organizations were newer and less restrictive, aspiring women artists were able to launch careers and gain a measure of status and recognition.
Research on French art institutions has continued to thrive with the work of Raymonde Moulin on the interplay among art museums, the art market, and government policy in providing official recognition for innovative art (1992). In the United States, a system in which the national government’s support for the arts is far more limited, and even declining, the study of how institutions affect the arts has advanced under the leadership of Paul DiMaggio (1986a, 1986b) and Judith Balfe (1993).
Artistic Practices and Worlds of Art
The most significant contribution to understanding how the arts are constituted was Howard S. Becker’s (1982) Artworlds. By adapting a “sociology of work” approach to study what is customarily viewed as unique creations of individual geniuses, Becker’s premise is that making art is not qualitatively different from engagement in other social activities. Becker argues that far from being an individual act, the making of art needs to be understood as a collective process, in which interactions among participants, of whom the named artist is only one, result in the production of “artworks.” The other participants—support personnel— may range from assistants to servants, to managers or agents, critics, buyers, and organizations. Taking into account the size and complexity of modern societies, Becker does not reduce the arts to a single art world. Instead, he argues that art making is constituted in four principal art worlds, each characterized by a particular style of working, based on its own conventions. Thus, the integrated professional artist is trained according to the conventions of an art form such as music, painting, and dance, within the domain either of high culture or commercial. The Maverick is also trained according to those conventions but refuses to abide by them, preferring to risk isolation and failure to innovate on his own terms. The folk artist works within conventions traditional in his community’s lore. Finally, outside of actual constituted art worlds, the least integrated is the naive artist, untrained in art who follows an internal urging to create works that represent idiosyncratic experiences or ideas about religion, representations of personal remembrances, or even aberrations and madness. Whereas the other art worlds have ties to regular art world institutions or practitioners or make it their business to develop ties to them, naive artists must be “discovered” by others or else remain unknown (Becker 1982).
Art and Its Publics: Status Reproduction and Taste
One of the most misleading adages of all time must be there’s no arguing about taste. In reality, taste is always being argued about. Thorstein Veblen (1934) had been one of the first social scientists to interpret the symbolic meanings of taste in his analysis of leisure class behavior during the Gilded Age. Approximately a half century later, Russell Lynes ([1949] 1980) published his classification of high-, middle-, and low-brow taste preferences, in which artworks and fashion are taken as status markers. On the basis of writings by these and other astute analysts, a number of sociologists have noted that taste, in art, design, and fashion may be a person’s social standing. Far from viewing taste as trivial, purely personal, and difficult to fathom because it is nonrational, sociologists such as Bourdieu contend that taste is social in its formation, symbolic in its expression, and has real social consequences for individuals and social institutions. In his more complex level of analysis, Bourdieu goes beyond the idea of taste as a “right” of consumerism. Instead, his observations of social differences in artistic taste enable him to show linkages among taste, symbolic status, and the mechanisms by which they tend to reproduce existing status hierarchies in society at large from generation to generation. Treating taste as an aspect of the individual’s cultural baggage, a durably structured behavioral orientation whose origin stems from early childhood experience in the family, and schooling, Bourdieu employs a variety of methods, quantitative and ethnographic, to show how taste functions as a form of capital to crystallize inequalities based on economic and social advantages or disadvantages. In this way, taste becomes a badge of social honor or, conversely, of scorn, signaling to influential groups that some are more acceptable than others (Bourdieu [1979] 1984, [1992] 1995).
English sociologists of culture have been pursuing cultural reproduction from a parallel perspective. Although they do not, as a rule, use large surveys of taste, many have analyzed the content and uses of aesthetic culture, both high and popular. Raymond Williams (1981), beginning from a Marxian perspective, and moving between literary or film criticism and academic life, was a major influence on what became the field of Culture Studies. Beyond the simple base-superstructure correspondence of Marxism, in which culture is conceived as merely epiphenomenal to existing production relationships, Williams, Stuart Hall (1980), and Janet Wolff (1984), among many others, conceived of culture as a constitutive practice in the construction of social meanings. They have tried to overcome the prevailing, decontextualized, literary-critical mode of analysis by elucidating the relations between, on the one hand, cultural images, objects, and practices, and on the other, social institutions and processes. Scholars associated with the Birmingham Centre for Contemporary Cultural Studies analyzed many aspects of British youth subcultures, and their relationship to new artistic styles.
It would be disingenuous to suggest that there is complete agreement among sociologists about how taste and status are related, and with what consequences. Whereas Bourdieu attributes expertise in manipulating symbolic capital through complex codes available in the lore of dominant class fractions, many others prefer to emphasize observable changes in social stratification patterns, and the conditions of their expression. One of those who question Bourdieu’s analysis is David Halle (1993), who has studied the collection and display of art inside of people’s homes. His interviews with elite collectors of abstract art reveal that, contrary to Bourdieu’s assumption, collectors have little facility or understanding of the works they own. Indeed, such art is nearly as esoteric for them as for nonelites. Halle finds widespread sharing of taste across status lines, especially noting a nearly universal and, it appears, similar mode of appreciation of the landscape genre. Moreover, although educational level is an important enabler of high culture taste, ethnicity and race play important roles in how people select works for the home, in contrast to their responses to questionnaires administered in public spaces (Halle 1993).
Equally unexpected, in their studies of how musical tastes are related to occupational status, Peterson and Simkus suggest that although classical music continues to be a marker for high status occupational groups, more striking is the great breadth of their preference for a variety of music. Thus, whereas less than a third of respondents occupying prestigious occupations say they like classical music best, a somewhat larger proportion say they prefer country and Western music to grand opera. More “distinguishing” is that high-status individuals participate in more cultural activities and enjoy a wider range of music than do those of lesser status. As Peterson and Simkus put it, they are “omnivores” as opposed to less elite groups, whose range of taste in music is much more limited, and whom they characterize as “univores” (Peterson and Simkus 1993:152–86).
For scholars of Renaissance behavior, the omnivore is strongly reminiscent of the character type emergent with the “civilizing process” to which Norbert Elias (1978) devoted his early figurational analysis. In that period of expanded possibilities for travel in Europe as feudalism declined centralized states and monarchical structures began to form, promising young men (and rare women) from more or less isolated localities were being drawn to centers offering new opportunities. They had to learn to behave differently before a new audience and circles of courtly societies than they had in the familiar traditional worlds they inhabited, where their status (for better or for worse), was secure. Cosmopolitanism and the idea of the Renaissance Man came to mark the ideal of behavior, giving rise to a virtual industry of etiquette books, epic poetry, and other literature by authorities such as Erasmus, Castiglione, Chaucer, Shakespeare (Elias 1978). To be considered a country bumpkin was disastrous for seekers after the Renaissance notion of fame. As Bourdieu points out, these qualities became institutionalized in the development of secondary and higher education from the sixteenth through the twentieth centuries, and remnants of this cultural structure persist despite, as Bourdieu noted, the twentieth century’s valorization of science and technology (Bourdieu [1979] 1984).
But What Is Art?
Finally, whereas in the past scholars investigating the place of the arts in society have taken for granted the categories of art conventionally agreed to by art world participants, in recent times certain sociologists have turned their attention to tracing how art classifications are constructed. Like the sociologist of science, Bruno Latour (1987), who questions the processes by which certain frameworks of analysis, categories, and findings come to be incorporated into the scientific canon, some see even more plausible reasons for interrogating how artistic canons are established. Art is a stake in the arena of competition that pervades much of social life, as Bourdieu contends, not only for artists themselves, but for their supporters, patrons, collectors, dealers, and for the writers and scholars who constitute the art worlds in which they exist. In recent times, under pressure from potential publics, market forces, including collectors, and political action, and in light of the openness of the fine arts to new media, existing cultural institutions, such as art museums, are exhibiting works previously excluded from consideration as Art. Previously, for example, African carvings were largely consigned to ethnological collections; now, their entry into art museums has taken the form of an upward spiral in prestige; art of the “insane” has attained high market value (Anne E. Bowler as cited in Zolberg and Cherbo 1997:11–36); and women artists are gaining a level of recognition that had routinely been denied them (Zolberg and Cherbo 1997:1–8). In the worlds of culture industry as well, new musical forms such as “Rock-n-roll” and Rap have emerged from the interplay of business developments, technological innovations, and enacted statutes in such fields as copyright law, which set the parameters for works to come to public attention (Ennis 1992:5–7).
The seemingly impermeable barrier between high art and popular art that took over a century to construct (Levine 1988) has since been breached countless times, not only in America but in Europe as well (Circle 1993:12). In the past three decades, even the massive wall between commercial art forms and the “disinterested” arts has endured a jolting to the point of crumbling. The entry of Latin American, Asian, and African visual and musical forms and motifs into the Western dominated canon has gained increasing legitimacy and audiences (Zolberg 1997:53–72). Moreover, since any kind of art—fine, popular, commercial—may be disseminated through commercial channels of distribution, adding the interplay of official policy with market forces helps to thicken one’s understanding of processes of democratization.
21st Century Prospects for the Arts in American Sociology
By the beginning of the third millennium, the sociological study of culture and the arts is no longer a stepchild of the serious business of sociologists. If not central, then the arts are at least legitimately scholarly, as opposed to a frivolous subject. This flowering came about despite the traditional anti-aesthetic orientation in American social science and the more general unease between social science and the arts. Still, the position of the arts in the social science disciplines continues to remain tenuous and requires repeatedly renewed justification as an intellectual enterprise. In part, this is due to the fact that the crux of the arts since the Renaissance has been the artist as an individual, a tradition of several centuries that emphasizes the uniqueness of the actor and the work he (rarely, she) created. While the notion of such individual agency is relatively compatible with the discipline of psychology, it is less easily reconciled with the collectivist understanding of behavior by sociology. As noted above, this perception underlies the view of art as a collective process (Becker 1982) and sociologists’ emphasis on the production rather than creation of culture. Retaining or reinserting the individual artist as a creative agent has both ethical importance, since it implies respect for the autonomy of the individual, and intellectual validity in a discipline that could easily reduce art to no more than an outcome of general structures and processes. Thus, whereas culture has become a deeply embedded component of sociology dealing with science, theory, macrohistorical questions, education, religion, ethnicity, to name a few, the place of the traditional fine arts has not grown proportionately.
Two edited books published under the aegis of the ASA Culture Section seem to confirm this observation. Whereas the first, Diana Crane’s (1994) edited collection includes an essay on the arts, the second volume, edited by Elizabeth Long, includes not even one chapter on the fine arts and only one that even approaches this domain (Long 1997). On the other hand, the third and most recent collection of Culture Section sponsored essays suggests that the arts have conquered a new place in the sociological sun (Mark D. Jacobs and Nancy Weiss Hanrahan 2005). The coeditors rehearse the several decades in American social science characterized by “the cultural turn,” the reconceptualization of culture away from the functionalist emphasis on the need for culture to bring about a homogeneous consensus in society. Instead, proponents of the cultural turn sought variations and heterogeneity in the arrival on the public scene of pluralism and tolerance of difference. Rather than require uniformity, the goal is for a more “organic” (as in Durkheim’s formulation) conception to be the basis of social solidarity, not to promote conformity but individual human agency.
The cultural turn had challenged the elite standing of high culture by recognizing the existence of talent and striving among all social groups and the democratization embedded in Pragmatism. For all the attractiveness of openness to different forms, culture was frequently reduced to unending debate on ideology, functionalism, and essentialism versus constructivism. In a break from the past, Jacobs and Hanrahan (2005) put forth a new idea in the field of cultural sociology. They refer to “this newly emerging conception of culture as . . . an aesthetic one, which offers possibilities for intensifying and re-imagining the experience of civic life” (p. 12). From a static or, at the most, slowly changing notion of societal existence, their new approaches emphasize the dynamism of process and human intervention and their impact on existing traditional structures. Beyond these important changes, the new aesthetic conception helps, instead, in the more than two dozen essays by American, Canadian, European, and Asian sociologists, to turn toward normative commitments for the revival of civic discourse in relation to legality and social justice, the politics of recognition, and “the potentialities of ordinary experience” Jacobs and Hanrahan (2005).
Democratization in Diversity
In the context of American idea systems, Peterson’s innovations and the efforts of others associated with the production of culture school are likely to continue to drive research. This approach prepares the way for scholars to enlarge their repertoire of questions and take into account the impact on creation and reception of the arts in light of the enormous changes in the ethnic make up of the American population since the end of World War II. Sources of immigration have been changed decisively by new laws and population movements: Hispanic, Chinese, Indian/Pakistani, Middle Eastern, Russian, peoples of a broad range of educational levels and aspirations. They provide an unprecedented opportunity to investigate the interactions with the varied Anglo-centric cultural choices that have until now been the focus of most studies. Demands for access to elite culture now include not merely “visitors” from modest economic backgrounds, whose entry is far from being attained either in North America or in Europe (Circle 1993:96, 103, 129), but crosscutting socioeconomic distinctions, differences of gender, ethnicity, and race or religion. Each of these may have aesthetic implications that the conflict, as usually expressed— quantity versus quality—does not encompass.
The extraordinary transformation of the international arena in recent years requires that scholarship move more explicitly outside of the American scholarly world and into the wider international realm. This is essential in a world that brings together what had been largely national concerns. As is true of other intellectual fields, the arts are no longer understandable in terms of one society alone since few societies are either homogeneous or sealed off from other geographic, national, or societal units. Thus, whereas it may still be possible to study such issues as arts censorship in the context of a single society, it is more likely that political transformations open the door to new conflicts as global phenomena.
Related to globalization, technological innovations in cyberspace and computer technology militate even more poignantly against retaining the single society as the primary unit of analyses. They not only permit new forms of artistic expression but also enhance attempts to evade control over art content. Providing new avenues for artistic dissemination, they also substitute for direct contact with the storehouses of art, the museum. This suggests that this contextual metamorphosis will set the parameters of the next phase of studies in the sociology of the arts. Cultural sociologists have through theory, example, and practice contributed to the vital and potentially dangerous debates that pervade questions of “identity,” including ethnicity, gender, race, or religion, with strongly political loadings. Pursuing questions of meaning, identity, and value in terms of American society alone is clearly insufficient to understanding social processes and emergent structures. As American sociologists burst the bonds of narrow parochialism and enter the adventurous terrain of global processes, they foster a cosmopolitanism that challenges existing approaches and conceptualizations of the social sciences.
Bibliography:
- Adorno, Theodor. [1962] 1976. Introduction to the Sociology of Music. New York: Seabury Press.
- Albrecht, M. C., J. H. Barnett, and M. Griff. 1970. The Sociology of Art and Literature: A Reader. New York: Praeger.
- Balfe, Judith H., ed. 1993. Paying the Piper: Causes and Consequences of Art Patronage. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
- Becker, Howard S. 1982. Art Worlds. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Blau, Judith R. 1988. The Shape of Culture. Rose Monograph Series. Cambridge, England: Polity Press.
- Bourdieu, Pierre. 1980. Questions de Sociologie. Paris, France: Éditions de Minuit.
- Bourdieu, Pierre. [1979] 1984. Distinction: A Social Critique of the Judgement of Taste. Translated by R. Nice. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Bourdieu, Pierre. [1992] 1995. The Rules of Art: Genesis and Structure of the Literary Field. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Bourdieu, Pierre. 2000. Pascalian Meditations. Translated by R. Nice. Cambridge, England: Polity Press.
- Cherbo, Joni M. 1997. “Pop Art: Ugly Duckling to Swan.” Pp. 85–97 in Outsider Art: Contesting Boundaries in Contemporary Culture, edited by V. L. Zolberg and J. M. Cherbo . New York: Cambridge University Press.
- 1993. Participation à la vie culturelle en Europe: Tendances, Stratégies et défis. Paris, France: Conseil de l’Europe.
- Coser, Lewis, ed. 1965. Georg Simmel [Makers of Modern Social Science]. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Crane, Diana. 1987. The Transformation of the Avant-Garde: The New York Art World 1940–85. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Crane, Diana, ed. 1994. The Sociology of Culture. Oxford, England: Blackwell.
- DiMaggio, Paul J. 1986a. “Cultural Entrepreneurship in Nineteenth-Century Boston: The Creation of an Organizational Base for High Culture in America.” Pp. 96–211 in Media, Culture and Society: A Critical Reader. London, England: Sage.
- DiMaggio, Paul J., ed. 1986b. Nonprofit Enterprise in the Arts: Studies in Mission and Constraint. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Elias, Norbert. 1978. The History of Manners. New York: Pantheon Books.
- Ennis, Philip H. 1992. The Seventh Stream: The Emergence of Rock-n-roll in American Popular Music. Hanover, NH: New England Press.
- Gans, Herbert. 1974. Popular Culture and High Culture: An Analysis and Evaluation of Taste. New York: Basic Books.
- Gans, Herbert. 1999. Popular Culture and High Culture: An Analysis and Evaluation of Taste. ed. New York: Basic Books.
- Geertz, Clifford. 1973. “Thick Description: Toward an Interpretive Theory of Culture.” Pp. 3–32 in The Interpretation of Cultures. New York: Basic Books.
- Goldfarb, Jeffrey C. 1982. On Cultural Freedom: An Exploration of Public Life in Poland and America. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Griswold, Wendy. 2000. Bearing Witness: Readers, Writers, and the Novel in Nigeria. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Guilbaut, Serge. 1983. How New York Stole the Idea of Modern Art: Abstract Expressionism, Freedom, and the Cold War. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Hall, Stuart. 1980. “Cultural Studies and the Centre: Some Problematics and Problems.” Pp.15–47 in Culture, Media, Language: Working Papers in Cultural Studies, 1972–79, edited by S. Hall. London, England: Hutchinson.
- Halle, David. 1993. Inside Culture: Art and Class in the Modern American Home. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Hauser, Arnold. 1951. The Social History of Art. 4 vols. New York: Knopf.
- Hauser, Arnold. 1982. The Sociology of Art. Translated by K. J. Northcott. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Jacobs, Mark D. and Nancy Weiss Hanrahan. 2005. The Blackwell Companion to the Sociology of Culture. Oxford, England: Blackwell.
- Lang, Gladys Engel and Kurt Lang. 1990. Etched in Memory: The Building and Survival of Artistic Reputations. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- Latour, Bruno. 1987. Science in Action: How to Follow Scientists and Engineers through Society. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Levine, Lawrence W. 1988. Highbrow/Lowbrow: Emergence of Cultural Hierarchy in America. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Long, Elizabeth. 1997. “Introduction: Engaging Sociology and Cultural Studies: Disciplinarity and Social Change.” Pp. 2–36 in From Sociology to Cultural Studies: New Perspectives, edited by E. Long . Oxford, England: Blackwell.
- Lynes, Russell. [1949] 1980. The Tastemakers: The Shaping of American Popular Taste. New York: Dover.
- Moulin, Raymonde. [1967] 1987. The French Art Market: A Sociological View. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
- Moulin, Raymonde, with Pascaline Costa. 1992. L’Artiste, l’institution, et le marché [Art, Histoire, Société]. Paris, France: Gallimard.
- Peterson, Richard A., ed. 1976. The Production of Culture. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
- Peterson, Richard A., 1994. “Culture Studies through the Production Perspective: Progress and Prospects.” Pp. 161–83 in The Sociology of Culture, edited by D. Crane . Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Peterson, Richard A. 1997. Creating Country Music. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Peterson, Richard A. and Albert Simkus. 1993. “How Musical Tastes Mark Occupational Status Groups.” Pp. 152–68 in Cultivating Differences: Symbolic Boundaries and the Making of Inequality, edited by M. Lamont and M. Fournier. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Saunders, Frances Stonor. 1999. The Cultural cold War: The CIA and the World of Arts and Letters. New York: New Press.
- Simmel, Georg. 1968. The Conflict in Modern Culture and Other Essays. Translated and edited by K. P. Etzkorn. New York: Teachers College Press.
- Sorokin, Pitirim. 1937. Social and Cultural Dynamics, 1, Fluctuations of Forms of Art. New York: American Book.
- Veblen, Thorstein. 1934. The Theory of the Leisure Class (1899). New York: Viking Press.
- Weber, Max. 1958. The Rational and Social Foundations of Music. Carbondale: University of Illinois Press.
- White, Harrison and Cynthia White. 1965. Canvases and Careers. New York: John Wiley.
- Williams, Raymond. 1981. Glasgow, Scotland: William Collins.
- Wilson, Robert N., ed. 1964. The Arts in Society. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Wolff, Janet. 1984. The Social Production of Art. New York: New York University Press.
- Zolberg, Vera. 1990. Constructing a Sociology of the Arts. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Zolberg,Vera. 1997. “African Legacies,American Realities:Art and Artists on the Edge.” Pp. 53–72 in Outsider Art: Contesting Boundaries in Contemporary Culture, edited by V. L. Zolberg and J. M. Cherbo. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Zolberg, Vera L. and Joni M. Cherbo. 1997. Outsider Art: Contesting Boundaries in Contemporary Culture. New York: Cambridge University Press.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Cast & crew
- User reviews
- Episode aired Feb 4, 2022

While the town is rocked by another murder, Reacher heads to New York and learns the truth about the illegal business in Margrave. Roscoe faces danger in the woods. While the town is rocked by another murder, Reacher heads to New York and learns the truth about the illegal business in Margrave. Roscoe faces danger in the woods. While the town is rocked by another murder, Reacher heads to New York and learns the truth about the illegal business in Margrave. Roscoe faces danger in the woods.
- Nick Santora
- Aadrita Mukerji
- Alan Ritchson
- Malcolm Goodwin
- Willa Fitzgerald
- 11 User reviews
- 1 Critic review

- Jack Reacher

- Oscar Finlay

- Roscoe Conklin

- Mayor Grover Teale

- Charlene 'Charlie' Hubble

- Officer Baker

- Paul Hubble

- Professor Castillo
- (as Alex Castillo)

- Professor Bryant's Assistant

- All cast & crew
- Production, box office & more at IMDbPro
Did you know
- Trivia Papier, the title of the episode, is (among others) the French translation of paper.
- Goofs Reacher calls the cop 'Sargent', but he wears no sign of rank, and there's no name plate at the desk bearing a rank title. NYPD badges vary by and are unique to rank of the officer, including naming the rank on the badge. Reacher would have known at a glance that Diaz was a sergeant based on the badge he wore.
Jack Reacher : So, you're living above a smoke shop when you're trying to quit smoking? Wearing a tweed suit in Georgia in the summer? Taking a job in the middle of nowhere? It's all some kind of penance for you not being able to save your wife?
Oscar Finlay : Something like that.
Jack Reacher : Well, that's stupid. And if you really think that, you're stupid.
Oscar Finlay : Fuck you.
Jack Reacher : I like it when you curse. You should do it more often.
Oscar Finlay : Double fuck you twice.
- Soundtracks Carry on Wayward Son (uncredited) Written by Kerry Livgren Performed by Kansas
User reviews 11
- Feb 15, 2024
- February 4, 2022 (United States)
- United States
- Hamilton, Ontario, Canada (Airport)
- Amazon Studios
- Blackjack Films Inc.
- Paramount Television
- See more company credits at IMDbPro
Technical specs
- Runtime 48 minutes
- Dolby Digital
Related news
Contribute to this page.

- See more gaps
- Learn more about contributing
More to explore
Recently viewed.

The Acknowledgements Section
How to write the acknowledgements for your thesis or dissertation
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | January 2024
Writing the acknowledgements section of your thesis might seem straightforward, but it’s more than just a list of names . In this post, we’ll unpack everything you need to know to write up a rock-solid acknowledgements section for your dissertation or thesis.
Overview: The Acknowledgements
- What (exactly) is the acknowledgements section?
Who should you acknowledge?
- How to write the section
- Practical example
- Free acknowledgements template
- Key takeaways
What is the acknowledgements section?
The acknowledgements section of your thesis or dissertation is where you give thanks to the people who contributed to your project’s success. Generally speaking, this is a relatively brief, less formal section.
With the acknowledgements section, you have the opportunity to show appreciation for the guidance, support, and resources provided by others during your research journey. We’ll unpack the exact contents, order and structure of this section in this post.
Need a helping hand?
Although this is a less “academic” section, acknowledging the right people in the correct order is still important. Typically, you’ll start with the most formal (academic) support received, before moving on to other types of support.
Here’s a suggested order that you can follow when writing up your acknowledgements:
Level 1: Supervisors and academic staff
Start with those who have provided you with academic guidance, including your supervisor, advisors, and other faculty members.
Level 2: Funding bodies or sponsors
If your research was funded, acknowledging these organisations is essential. You don’t need to get into the specifics of the funding, but you should recognise the important role that this made in bringing your project to life.
Level 3: Colleagues and peers
Next you’ll want to mention those who contributed intellectually to your work, including your fellow cohort members and researchers.
Level 4: Family, friends and pets
Last but certainly not least, you should acknowledge your personal (non-academic) support system – those who have provided emotional and moral support. If Fido kept you company during those long nights hunched over the keyboard, you can also thank him here 🙂
As you can see, the order of the acknowledgements goes from the most academic to the least . Importantly, your thesis or dissertation supervisor (sometimes also called an advisor) generally comes first . This is because they are typically the person most involved in shaping your project (or at least, they should be). Plus, they’re oftentimes involved in marking your final work and so a kind word never hurts…
All that said, remember that your acknowledgements section is personal . So, feel free to adjust this order, but do pay close attention to any guidelines or rules provided by your university. If they specify a certain order or set of contents, follow their instructions to the letter.

How to write the acknowledgements section
In terms of style, try to strike a balance between conveying a formal tone and a personal touch . In practical terms, this means that you should use plain, straightforward language (this isn’t the time for heavy academic jargon), but avoid using any slang, nicknames, etc.
As a guide, you’ll typically use some of the following phrases in the acknowledgements section:
I would like to express my appreciation to… for their help with… I’m particularly grateful to… as they provided… I could not have completed this project without… as this allowed me to… Special thanks to… who did… I had the pleasure of working with… who helped me… I’d also like to recognise… who assisted me with…
In terms of positioning, the acknowledgements section is typically in the preliminary matter , most commonly after the abstract and before the table of contents. In terms of length, this section usually spans one to three paragraphs , but there’s no strict word limit (unless your university’s brief states otherwise, of course).
If you’re unsure where to place your acknowledgements or what length to make this section, it’s a good idea to have a look at past dissertations and theses from your university and/or department to get a clearer view of what the norms are.

Practical Example
Alright, let’s look at an example to give you a better idea of what this section looks like in practice.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Professor Smith, whose expertise and knowledge were invaluable during this research. My sincere thanks also go to the University Research Fund for their financial support. I am deeply thankful to my colleagues, John and Jane, for their insightful discussions and moral support. Lastly, I must acknowledge my family for their unwavering love and encouragement. Without your support, this project would not have been possible.
As you can see in this example, the section is short and to the point , working from formal support through to personal support. If you’re interested, you can explore a few more examples here .
To simplify the process, we’ve created a free template for the acknowledgements section. If you’re interested, you can download a copy here .

FAQs: Acknowledgements
Can i include some humour in my acknowledgements.
A touch of light humour is okay, but keep it appropriate and professional. Remember that this is still part of an academic document.
Can I acknowledge someone who provided informal or emotional support?
Yes, you can thank anyone who offered emotional support, motivation, or even informal advice that helped you during your studies. This can include friends, family members, or a mentor/coach who provided guidance outside of an academic setting.
Should I mention any challenges or difficulties I faced during my research?
While the acknowledgements section is primarily for expressing gratitude, briefly mentioning significant challenges you overcame can highlight the importance of the support you received. That said, you’ll want to keep the focus on the gratitude aspect and avoid delving too deeply into the challenges themselves.
Can I acknowledge the contribution of participants in my research?
Absolutely. If your research involved participants, especially in fields like social sciences or human studies, acknowledging their contribution is not only courteous but also an ethical practice. It shows respect for their participation and contribution to your research.
How do I acknowledge posthumous gratitude, for someone who passed away during my study period?
Acknowledging a deceased individual who played a significant role in your academic journey can be done respectfully. Mention them in the same way you would a living contributor, perhaps adding a note of remembrance.
For example, “I would like to posthumously acknowledge John McAnders for their invaluable advice and support in the early stages of this research.”.
Is there a limit to the number of people I can acknowledge?
How do i acknowledge a group or organisation.
When thanking a group or organization, mention the entity by name and, if applicable, include specific individuals within the organization who were particularly helpful.
For example, “I extend my thanks to The Speakers Foundation for their support, particularly Mr Joe Wilkins, for their guidance.”
Recap: Key Takeaways
Writing the acknowledgements section of your thesis or dissertation is an opportunity to express gratitude to everyone who helped you along the way.
Remember to:
- Acknowledge those people who significantly contributed to your research journey
- Order your thanks from formal support to personal support
- Maintain a balance between formal and personal tones
- Keep it concise
In a nutshell, use this section to reflect your appreciation in a genuinely and professionally way.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Explore research paper examples in APA, MLA, Chicago & Harvard styles. Get research paper samples for different fields and craft exceptional research papers!
Research paper examples are of great value for students who want to complete their assignments timely and efficiently. If you are a student in the university, your first stop in the quest for research paper examples will be the campus library where you can get to view the research sample papers of lecturers and other professionals in diverse fields plus those of fellow students who preceded ...
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you're following. In addition to citations, APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
As such, this article will discuss how to write a research paper, focusing on the critical things to consider like your aims and motivation, choosing the type of paper you want to publish, and your target venue. The document will also include tips on how to write a research paper outline and the common parts of a research paper.
Are you looking for a sample research paper example to write an amazing one of your own? This blog has everything you need. Have a look to review the examples.
Learn how to format your paper in APA 7th edition with a fillable template and a sample paper. Includes tips on title case and proper nouns.
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
Learn how to write a research paper step by step, including how to cite sources, and get helpful writing and research tips.
Looking for a research paper example to help you draft this most difficult assignment type? This blog has research paper examples for all fields and subjects.
Example of a Research Paper. Martyn Shuttleworth 1.8M reads. What follows is a hypothetical example of a research paper based on an experiment. The experiment: Say you have just conducted the Milgram Study. Now you want to write the research paper for it. (Milgram actually waited two years before writing about his study.)
The introduction of a research paper provides an overview of the study's purpose, scope, and significance. Read this article to understand what is a research paper introduction, its importance and how to write a research paper introduction with examples.
Whether you're in a history, literature, or science class, you'll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you're just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process...
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings. The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research.
Overwhelmed with academic routine? Discover a curated list of 300 compelling research paper topics across various disciplines to inspire your academic projects.
You are going to love this! Save this template somewhere safe or e-mail it to yourself. Then resave it immediately with the name of your new document. This will keep your template safe and ready to reuse again for future assignments.
Looking for stellar, easy research paper topics? Check out our list of good research topics and paper-writing tips to help you get started.
To write a good research paper, your body parts usually contain elements like a literature review, methodology or methods section, analysis, research outcomes (results), sample analysis, and a discussion section.
Art Research Paper. This sample art research paper features: 6600 words (approx. 22 pages) and a bibliography with 52 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help.
From "Papier" to "ATM," we rank the most rewatchable episodes of the hit Prime Video series Reacher.
example research paper. Guys, I am looking for a "model" research paper, which is being used as example for "how to do research in sociology" after selecting a topic. I am vague because I feel vague, struggling how to ask a question. What I want is to try to apply the research methodology to the some problems I have in mind.
Papier: Directed by Omar Madha. With Alan Ritchson, Malcolm Goodwin, Willa Fitzgerald, Chris Webster. While the town is rocked by another murder, Reacher heads to New York and learns the truth about the illegal business in Margrave. Roscoe faces danger in the woods.
Learn how to write the acknowledgements section for your thesis, dissertation or research project. Step-by-step template with examples.